Abstract
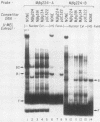
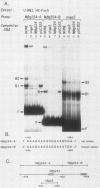
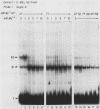
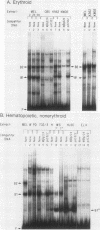
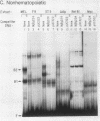
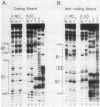
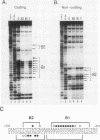
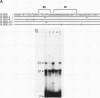
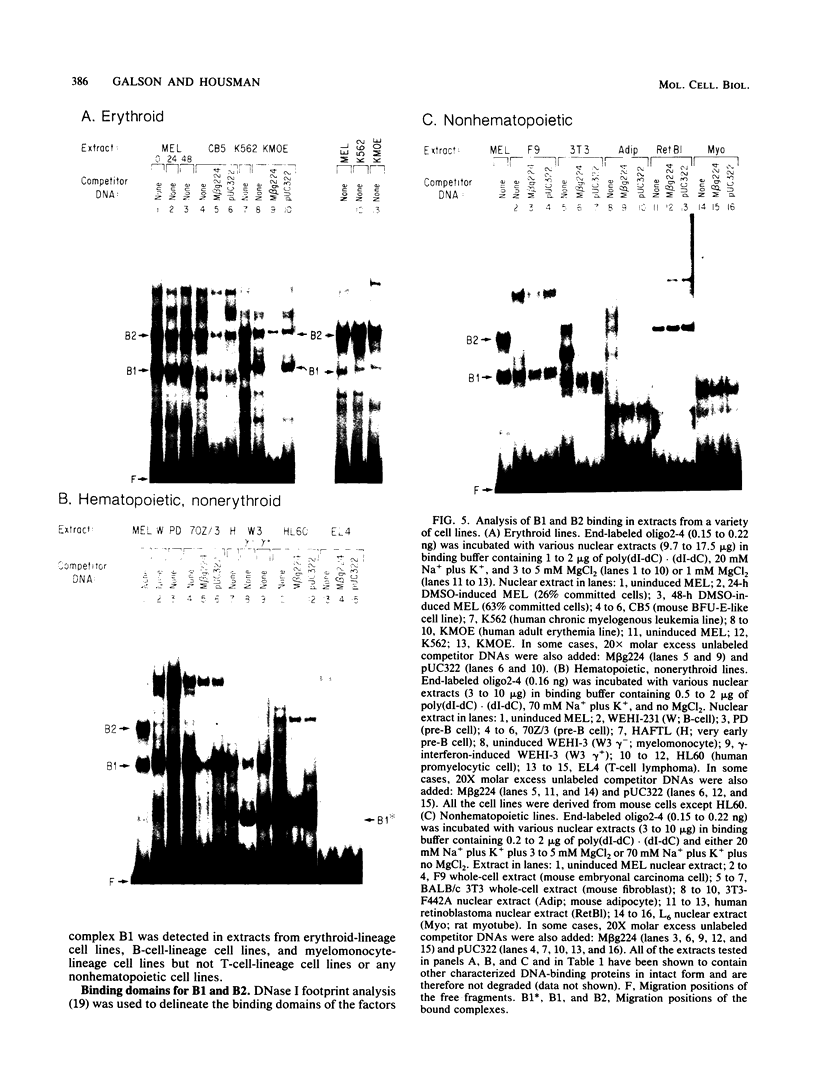
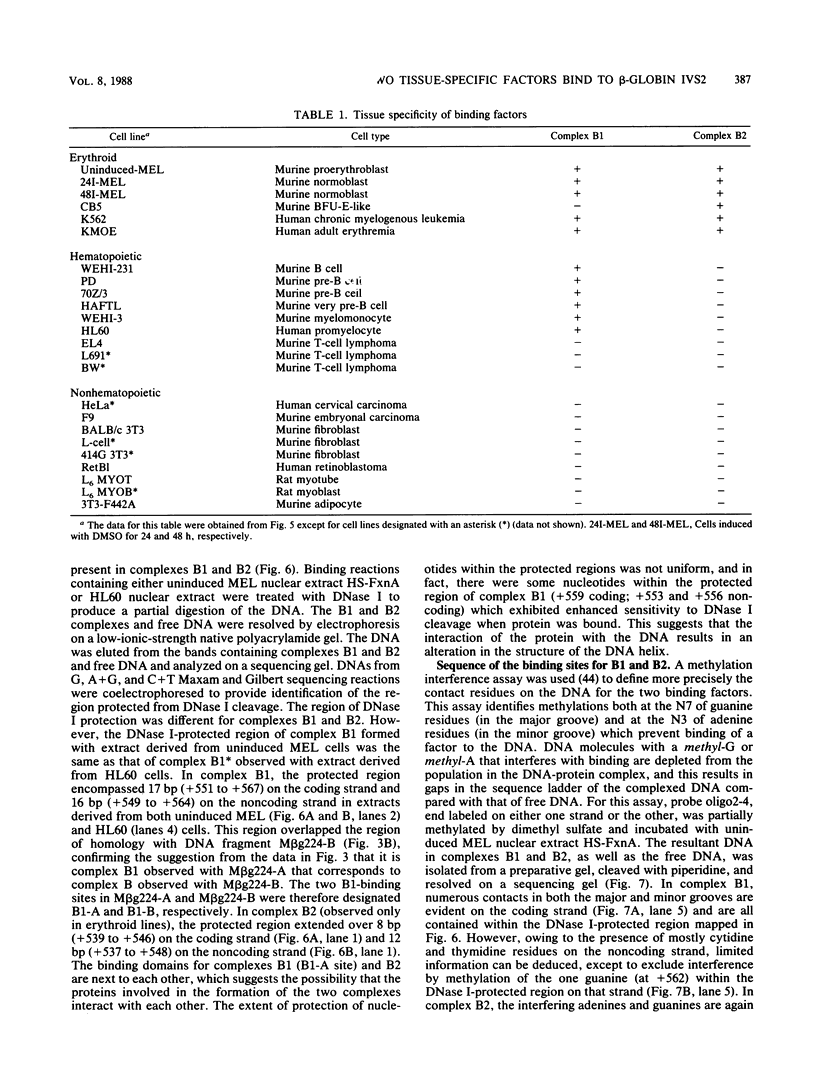
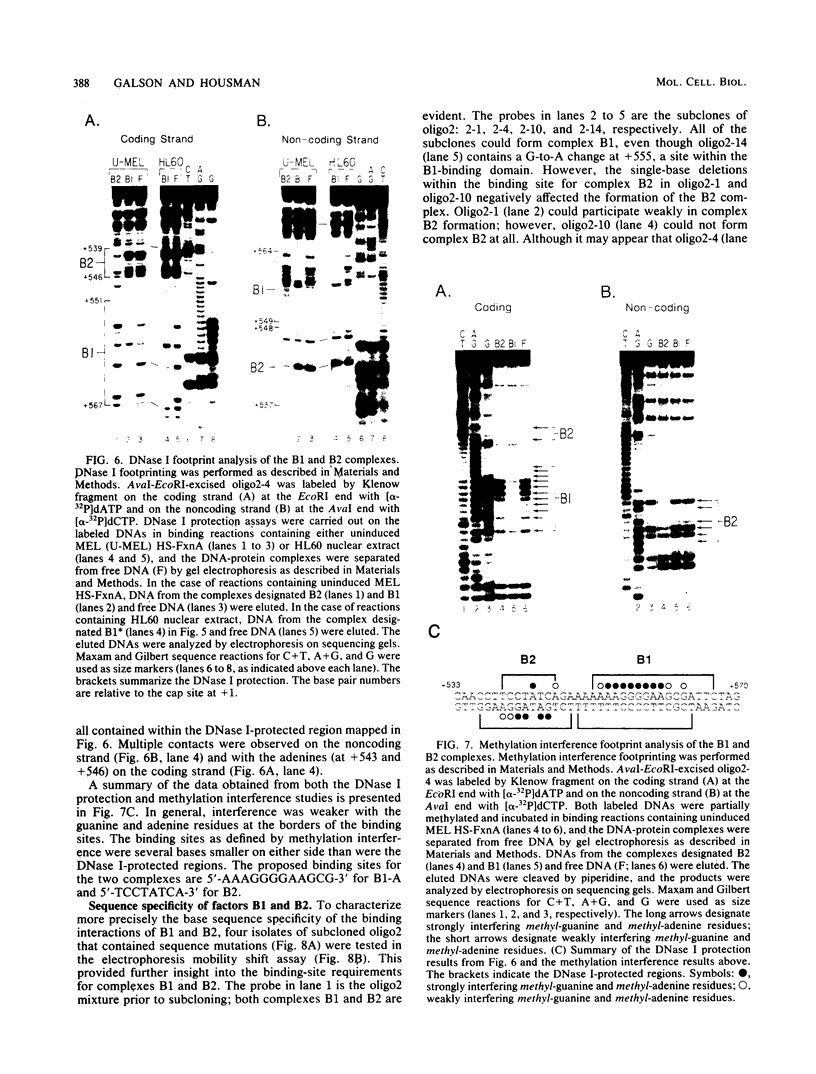
To identify proteins from uninduced murine erythroleukemia nuclear extracts which specifically bind to sequences from the DNase I-hypersensitive region within the mouse beta-globin intervening sequence 2 (IVS2), a gel electrophoretic mobility shift assay was used. Two distinct sequence-specific binding proteins were detected. The specific binding sites for these factors were delineated by both DNase I protection footprinting and methylation interference. Factor B1 bound specifically to two homologous sites, B1-A and B1-B, approximately 100 base pairs apart within the IVS2 and on opposite strands. These two regions could interact with factor B1 independently. Factor B1 was limited to cells of hematopoietic lineages. Factor B2 bound to a site approximately 5 base pairs away from the B1-A site and was limited to cells of the erythroid lineage. The limited tissue distribution of these factors and the locations of their binding sites suggest that one or both of these factors may be involved in the formation of the tissue-specific DNase I-hypersensitive site in the IVS2 of the mouse beta-globin gene.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balcarek J. M., McMorris F. A. DNase I hypersensitive sites of globin genes of uninduced Friend erythroleukemia cells and changes during induction with dimethyl sulfoxide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10622–10628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Cantor C. R., Axel R. Nucleosomes are phased along the mouse beta-major globin gene in erythroid and nonerythroid cells. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90835-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Keller W., Dale T., Schöler H. R., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. A transcription factor which binds to the enhancers of SV40, immunoglobulin heavy chain and U2 snRNA genes. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):268–272. doi: 10.1038/325268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chada K., Magram J., Costantini F. An embryonic pattern of expression of a human fetal globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):685–689. doi: 10.1038/319685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chada K., Magram J., Raphael K., Radice G., Lacy E., Costantini F. Specific expression of a foreign beta-globin gene in erythroid cells of transgenic mice. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):377–380. doi: 10.1038/314377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Mellon P., Maniatis T. Linker scanning mutagenesis of the 5'-flanking region of the mouse beta-major-globin gene: sequence requirements for transcription in erythroid and nonerythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1498–1511. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Treisman R., Mellon P., Chao M., Axel R., Maniatis T. Differences in human alpha- and beta-globin gene expression in mouse erythroleukemia cells: the role of intragenic sequences. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90547-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Fromental C., Augereau P., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Cell-type specific protein binding to the enhancer of simian virus 40 in nuclear extracts. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):544–548. doi: 10.1038/323544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Ro H. S., Rosen B. S., Groves D. L., Spiegelman B. M. Nucleoprotein complexes that regulate gene expression in adipocyte differentiation: direct participation of c-fos. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Interaction of specific nuclear factors with the nuclease-hypersensitive region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene: nature of the binding domain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Gelinas R., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Papayannopoulou T. Human fetal to adult hemoglobin switching: changes in chromatin structure of the beta-globin gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Activation of globin genes during chicken development. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90329-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Propagation of globin DNAase I-hypersensitive sites in absence of factors required for induction: a possible mechanism for determination. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer E., Hofer-Warbinek R., Darnell J. E., Jr Globin RNA transcription: a possible termination site and demonstration of transcriptional control correlated with altered chromatin structure. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):887–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollias G., Wrighton N., Hurst J., Grosveld F. Regulated expression of human A gamma-, beta-, and hybrid gamma beta-globin genes in transgenic mice: manipulation of the developmental expression patterns. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFlamme S., Acuto S., Markowitz D., Vick L., Landschultz W., Bank A. Expression of chimeric human beta- and delta-globin genes during erythroid differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4819–4826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClarin J. A., Frederick C. A., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Grable J., Rosenberg J. M. Structure of the DNA-Eco RI endonuclease recognition complex at 3 A resolution. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1526–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.3024321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. T., Skuzeski J. T., Lund E., Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E. Functional elements of the human U1 RNA promoter. Identification of five separate regions required for efficient transcription and template competition. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1795–1803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F., Arvidson D. N., Tyau E. S., Dunsworth-Browne M., Berk A. J. Transcription control region within the protein-coding portion of adenovirus E1A genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1293–1305. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J. Protein--DNA interaction. Another folding problem? Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):18–19. doi: 10.1038/326018a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt-Georgieff M., Sheffery M., Krauter K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Rifkind R., Marks P. A. Induced transcription of the mouse beta-globin transcription unit in erythroleukemia cells. Time-course of induction and of changes in chromatin structure. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):437–450. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. Gene regulation: why should DNA loop? Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):369–370. doi: 10.1038/327369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffery M., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation: DNase I hypersensitivity and DNA methylation near the globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1180–1184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya T., Mak T. W. Isolation and induction of erythroleukemic cell lines with properties of erythroid progenitor burst-forming cell (BFU-E) and erythroid precursor cell (CFU-E). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3721–3725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuey D. J., Parker C. S. Bending of promoter DNA on binding of heat shock transcription factor. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):459–461. doi: 10.1038/323459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Lingrel J. B., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1715–1723. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A., Klug A. Nucleoprotein complexes. DNA wrapping and writhing. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):280–281. doi: 10.1038/327280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K., Schimmel P. Two nuclear factors compete for the skeletal muscle actin promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9429–9432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., Rosenthal A., Flavell R., Grosveld F. DNA sequences required for regulated expression of beta-globin genes in murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90548-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Kingston R. E., Morimoto R. I. Human HSP70 promoter contains at least two distinct regulatory domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):629–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]