Abstract
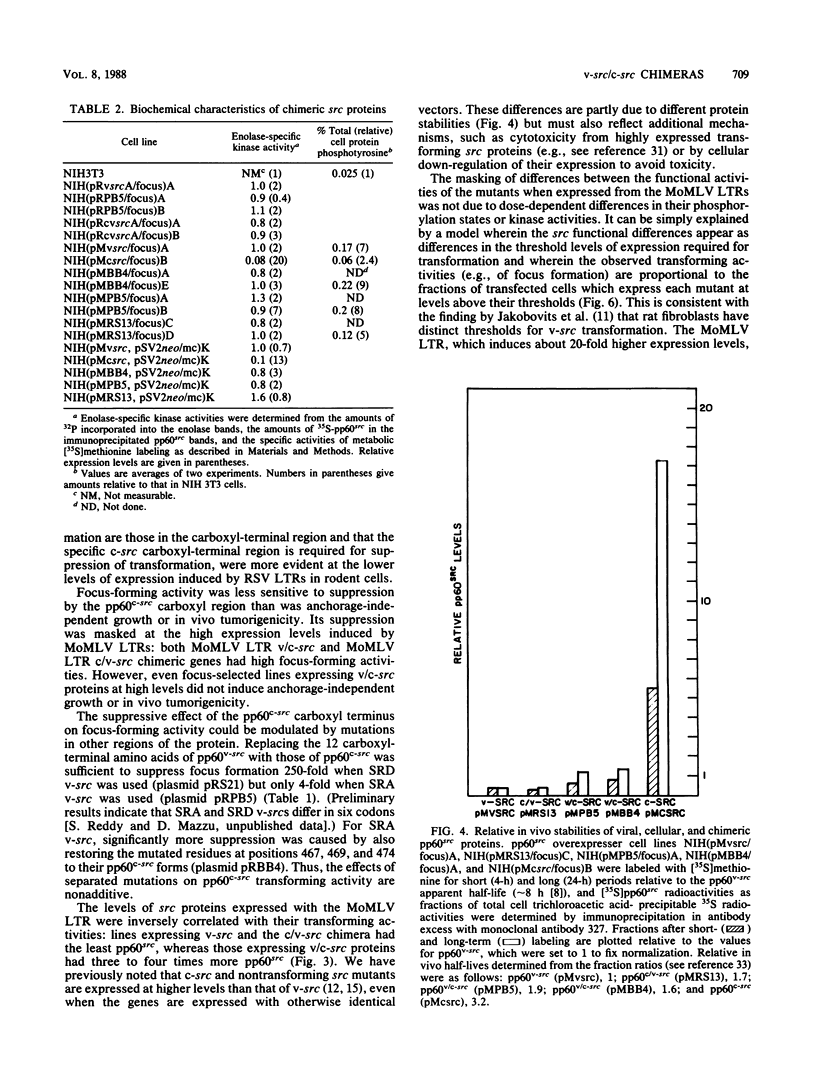
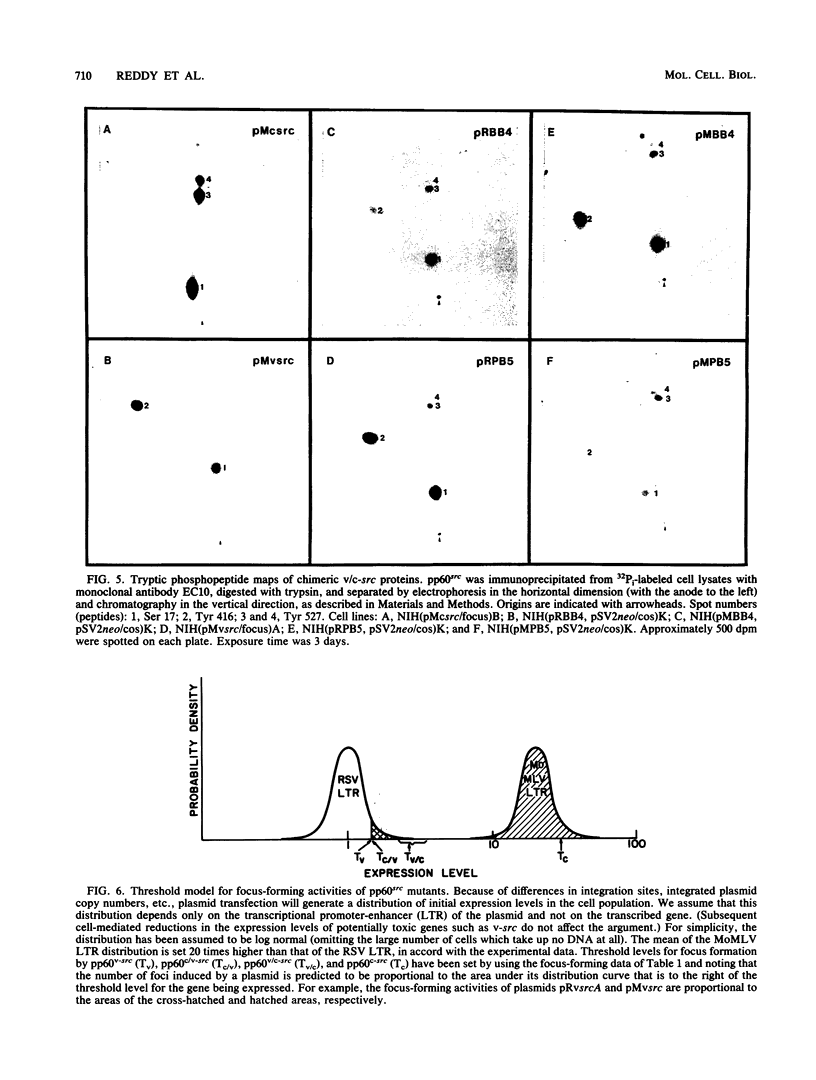
Previous studies have shown that carboxyl-terminal mutation of pp60c-src can activate its transforming ability. Conflicting results have been reported for the transforming ability of pp60c-src mutants having only mutations outside its carboxyl-terminal region. To clarify the effects of such mutations, we tested the activities of chimeric v(amino)- and c(carboxyl)-src (v/c-src) proteins at different dosages in NIH 3T3 cells. The focus-forming activity of Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat (LTR)-src expression plasmids was significantly reduced when the v-src 3' coding region was replaced with the corresponding c-src region. This difference was masked when the Rous sarcoma virus LTR was replaced with the Moloney murine leukemia virus LTR, which induced approximately 20-fold more protein expression, but even focus-selected lines expressing v/c-src proteins were unable to form large colonies in soft agarose or tumors in NFS mice. This suggests that pp60c-src is not equally sensitive to mutations in its different domains and that there are at least two distinguishable levels of regulation, the dominant one being associated with its carboxyl terminus. v/c-src chimeric proteins expressed with either LTR had high in vitro specific kinase activity equal to that of pp60v-src but, in contrast, were phosphorylated at both Tyr-527 and Tyr-416. Total cell protein phosphotyrosine was enhanced in cells incompletely transformed by v/c-src proteins to the same extent as in v-src-transformed cells, suggesting that the carboxyl-terminal region may affect substrate specificity in a manner that is important for transformation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brugge J. S., Darrow D. Analysis of the catalytic domain of phosphotransferase activity of two avian sarcoma virus-transforming proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4550–4557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens P. M., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Shalloway D. Restriction of the in vitro and in vivo tyrosine protein kinase activities of pp60c-src relative to pp60v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2753–2763. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Tischer E., Goodman H. Corrections to the nucleotide sequence of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):736–738. doi: 10.1038/301736b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockhart D. A., Corbin J. D. Regulatory mechanisms in the control of protein kinases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982 Feb;12(2):133–186. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Low level of cellular protein phosphorylation by nontransforming overproduced p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1058–1066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Takeya T., Cross F. R., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Rous sarcoma virus variants that carry the cellular src gene instead of the viral src gene cannot transform chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4424–4428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa S., Hagino-Yamagishi K., Kawai S., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Activation of the cellular src gene by transducing retrovirus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2420–2428. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Hormonal regulation of the Rous sarcoma virus src gene via a heterologous promoter defines a threshold dose for cellular transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. J., Coussens P. M., Danko A. V., Shalloway D. Overexpressed pp60c-src can induce focus formation without complete transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1073–1083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein lacking myristic acid phosphorylates known polypeptide substrates without inducing transformation. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J. Y., Takeya T., Grandori C., Iba H., Levy J. B., Hanafusa H. Amino acid substitutions sufficient to convert the nontransforming p60c-src protein to a transforming protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4155–4160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler M., Perez C. F., Hardy C., Botchan M. Transformation mediated by the SV40 T antigens: separation of the overlapping SV40 early genes with a retroviral vector. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90503-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Iba H., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transforming potential of p60c-src by a single amino acid change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E. The structure and protein kinase activity of proteins encoded by nonconditional mutants and back mutants in the sec gene of avian sarcoma virus. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):47–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90526-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Expression of v-src and chicken c-src in rat cells demonstrates qualitative differences between pp60v-src and pp60c-src. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., McCarley D. J., Ely C. M., Benjamin D. C., Parsons J. T. Monoclonal antibodies to Rous sarcoma virus pp60src react with enzymatically active cellular pp60src of avian and mammalian origin. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):272–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.272-282.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Vila J., Lansing T. J., Potts W. M., Weber M. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of the oncogenic potential of the avian cellular src protein by specific structural alteration of the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2359–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Coussens P. M., Yaciuk P. Overexpression of the c-src protein does not induce transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7071–7075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Zelenetz A. D., Cooper G. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of the chicken gene homologous to the transforming gene of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):531–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Transduction of a cellular oncogene: the genesis of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2519–2523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarpley W. G., Temin H. M. The location of v-src in a retrovirus vector determines whether the virus is toxic or transforming. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2653–2660. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson V. W., Bryant D. L., Parsons J. T. Rous sarcoma virus variants that encode src proteins with an altered carboxy terminus are defective for cellular transformation. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):314–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.314-321.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaciuk P., Shalloway D. Features of the pp60v-src carboxyl terminus that are required for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2807–2819. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]