Abstract
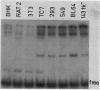
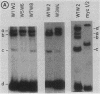
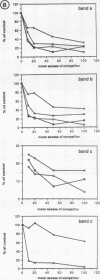
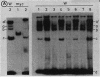
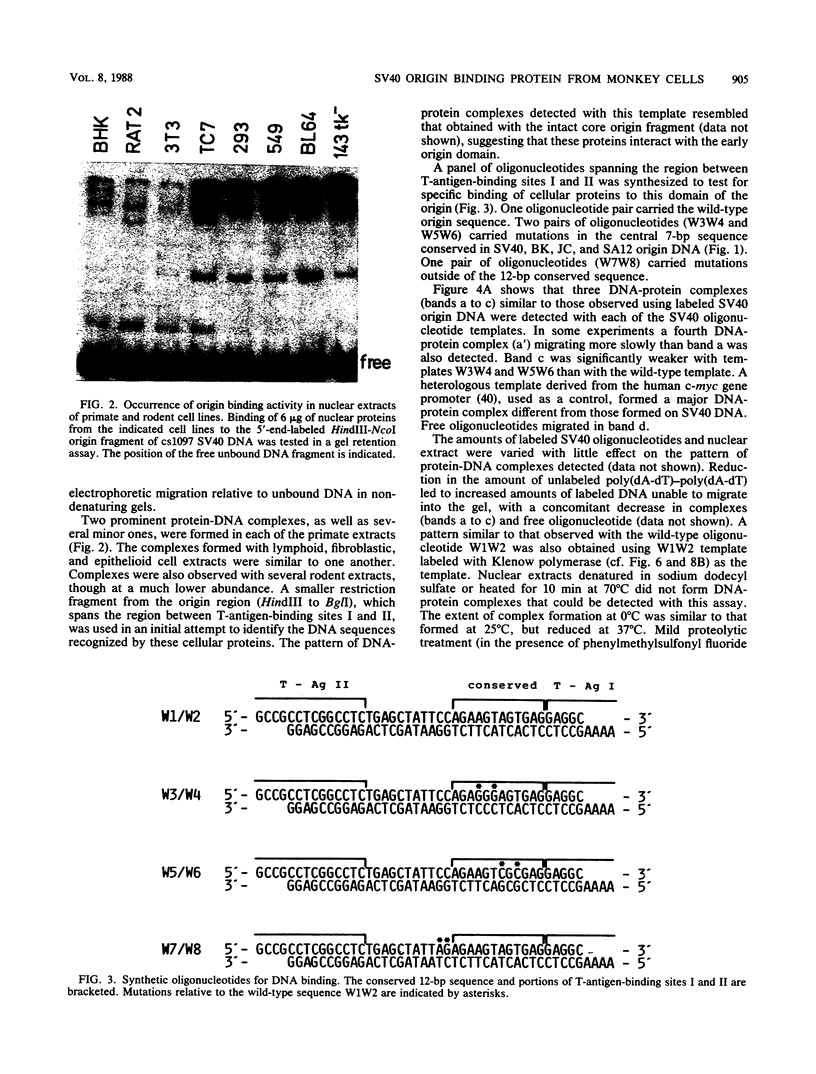
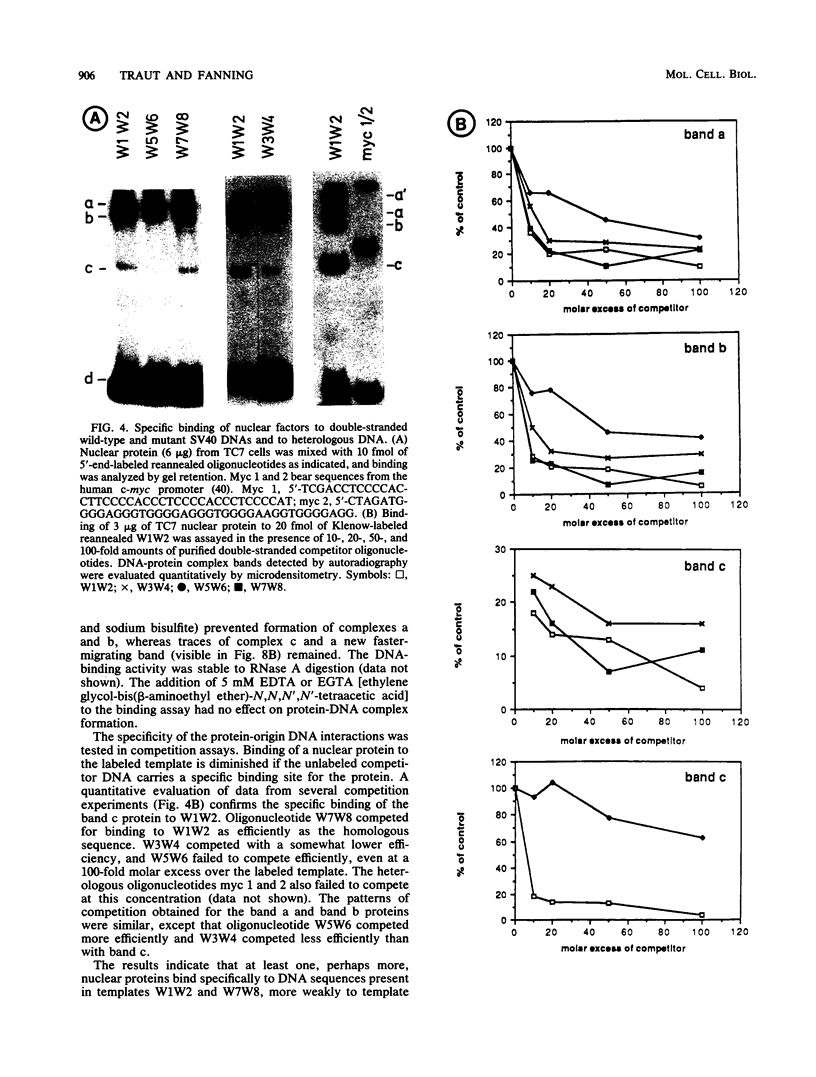
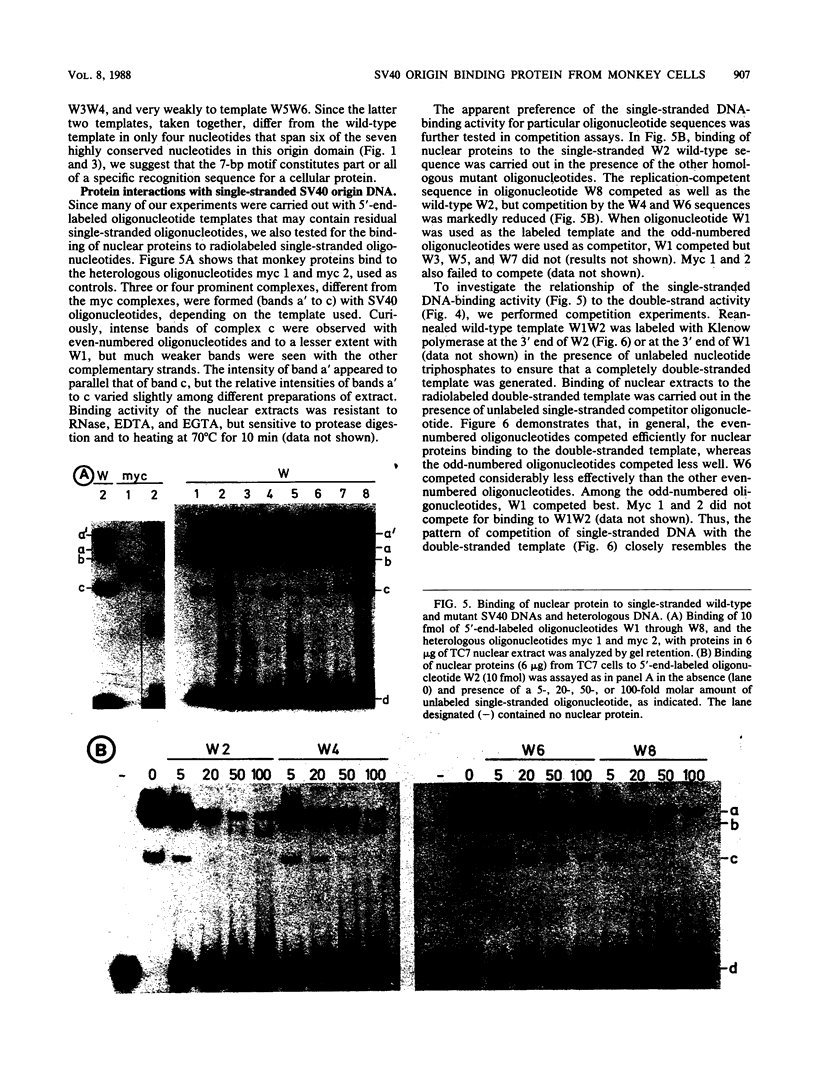
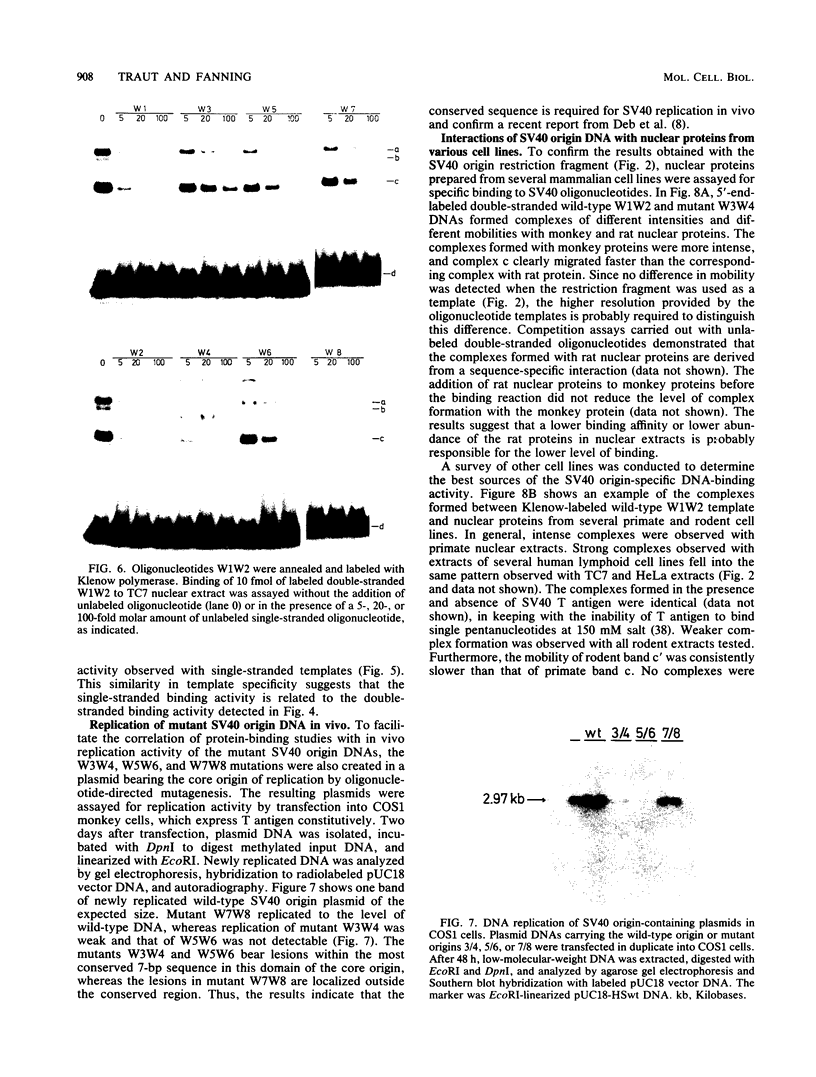
The core origin of simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA replication is composed of a 64-base-pair sequence encompassing T-antigen-binding site II and adjacent sequences on either side. A 7-base-pair sequence to the early side of T-antigen-binding site II which is conserved among the papovavirus genomes SV40, BK, JC, and SA12 was recently shown to be part of a 10-base-pair sequence required for origin activity (S. Deb, A.L. DeLucia, C.-P. Baur, A. Koff, and P. Tegtmeyer, Mol. Cell. Biol. 6:1663-1670, 1986), but its functional role was not defined. In the present report, we have used gel retention assays to identify a monkey cell factor that interacts specifically with double-stranded DNA carrying this sequence and also binds to single-stranded DNA. DNA-protein complexes formed with extracts from primate cells are more abundant and display electrophoretic mobilities distinct from those formed with rodent cell extracts. The binding activity of the factor on mutant templates is correlated with the replication activity of the origin. The results suggest that the monkey cell factor may be involved in SV40 DNA replication.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacchetti S., Graham F. L. Transfer of the gene for thymidine kinase to thymidine kinase-deficient human cells by purified herpes simplex viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1590–1594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Olive D. M., Hartzell S. W., Subramanian K. N. Territorial limits and functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Kamen R. Guanine nucleotide contacts within viral DNA sequences bound by polyomavirus large T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):505–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.505-514.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. P., Pipas J. M. Simian agent 12 is a BK virus-like papovavirus which replicates in monkey cells. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):483–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.483-492.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Deb S., Partin K., Tegtmeyer P. Functional interactions of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication with flanking regulatory sequences. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.138-144.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Bullock P., Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA replication: SV40 large T antigen unwinds DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Baur C. P., Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Domain structure of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1663–1670. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Koff A., Tsui S., Tegtmeyer P. The adenine-thymine domain of the simian virus 40 core origin directs DNA bending and coordinately regulates DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4578–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker R. S., Yamaguchi M., Possenti R., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: aphidicolin causes accumulation of early-replicating intermediates and allows determination of the initial direction of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3815–3825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. Effect of mutations at a T antigen binding site on DNA replication and expression of viral genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):531–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörper T., Winnacker E. L. Improvements in the phosphoramidite procedure for the synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2575–2584. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the region encompassing the JC virus origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):170–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.170-176.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R. D., Montelone B. A., Walter C. F., Innis J. W., Scott W. A. Role of specific simian virus 40 sequences in the nuclease-sensitive structure in viral chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R., Gluzman Y. Functional analysis of the role of the A + T-rich region and upstream flanking sequences in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4570–4577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl P., Lipp M. Generation of a variant t(2;8) translocation of Burkitt's lymphoma by site-specific recombination via the kappa light-chain joining signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2037–2045. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication in vivo: location and structure of 5' ends of DNA synthesized in the ori region. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A., Silver D., Seed B. Minimal size plasmids containing an M13 origin for production of single-strand transducing particles. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(6):507–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6973–6977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: specificity of initiation and evidence for bidirectional replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1238–1246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Peden K. W., Dixon R. A., Kelly T. Functional organization of the simian virus 40 origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1117–1128. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolskee R. F., Nathans D. Simian virus 40 mutant T antigens with relaxed specificity for the nucleotide sequence at the viral DNA origin of replication. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):386–393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.386-393.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Role of DNA polymerase alpha and DNA primase in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2869–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlita M., Clad A., zur Hausen H. Complete DNA sequence of lymphotropic papovavirus: prototype of a new species of the polyomavirus genus. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):196–211. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A., Huebner K. Effect of cell chromosome number on simian virus 40 replication. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Sep;81(1):120–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Vakalopoulou E., Mertz R., Mastrangelo I., Hough P., Tegtmeyer P., Fanning E. Seventeen base pairs of region I encode a novel tripartite binding signal for SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):539–548. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller A., Prives C. Simian virus 40 and polyomavirus large tumor antigens have different requirements for high-affinity sequence-specific DNA binding. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):532–545. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.532-545.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Gander I., Müller U., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L. A sensitive and rapid gel retention assay for nuclear factor I and other DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1303–1317. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Khoury G., Dhar R. The genome of human papovavirus BKV. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):963–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. T-antigen-DNA polymerase alpha complex implicated in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4077–4087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B., Gerard R. D., Guggenheimer R. A., Gluzman Y. T antigen and template requirements for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2933–2939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Lewton B. A., DeLucia A. L., Wilson V. G., Ryder K. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of protein bound to the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):151–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.151-161.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., DePamphilis M. L. DNA binding site for a factor(s) required to initiate simian virus 40 DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1646–1650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]