Abstract
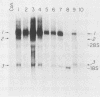
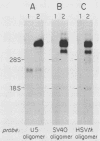
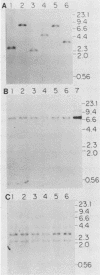
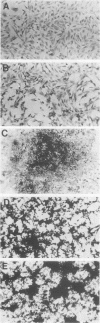
Retroviral vectors were constructed which coexpressed three inserted genes from independent transcriptional promoters in singly infected cells. Several such triple-promoter vectors were constructed with various combinations of oncogenes and selectable drug resistance genes. All expressed three mRNAs of the expected size in infected cells. One vector expressing the v-Ha-ras, v-myc, and neo genes was characterized in detail. This retrovirus did not undergo rearrangement during the process of infection, as judged by Southern analysis, and infection of primary rat embryo fibroblasts demonstrated that ras-myc-cotransformed cells could be selected in G418. This demonstration that retroviral vectors can be used to express three cistrons independently increases their value as gene transfer vehicles, particularly for studies involving oncogene cooperation in primary cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Development of 3T3-like lines from Balb-c mouse embryo cultures: transformation susceptibility to SV40. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2):141–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Ludwig G., Auerswald E. A., Reiss B., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Pearson M. L. Enhancing the efficiency of DNA-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01549662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Lomedico P. T., Ju G. Transcriptional interference in avian retroviruses--implications for the promoter insertion model of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):241–245. doi: 10.1038/307241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Defeo D., Shih T. Y., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Tsuchida N., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. The p21 src genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses originate from divergent members of a family of normal vertebrate genes. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):506–511. doi: 10.1038/292506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. High-frequency deletion in recovered retrovirus vectors containing exogenous DNA with promoters. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):42–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.42-49.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. Quantitative analysis of gene suppression in integrated retrovirus vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):792–800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingeras T. R., Sciaky D., Gelinas R. E., Bing-Dong J., Yen C. E., Kelly M. M., Bullock P. A., Parsons B. L., O'Neill K. E., Roberts R. J. Nucleotide sequences from the adenovirus-2 genome. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13475–13491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gritz L., Davies J. Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Chen A. C., Morgenstern J. P., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Behavior of myc and ras oncogenes in transformation of rat embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1917–1925. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. A., Metcalf D., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., Gonda T. J. Expression of a hemopoietic growth factor cDNA in a factor-dependent cell line results in autonomous growth and tumorigenicity. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langdon W. Y., Harris A. W., Cory S., Adams J. M. The c-myc oncogene perturbs B lymphocyte development in E-mu-myc transgenic mice. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIvor R. S., Johnson M. J., Miller A. D., Pitts S., Williams S. R., Valerio D., Martin D. W., Jr, Verma I. M. Human purine nucleoside phosphorylase and adenosine deaminase: gene transfer into cultured cells and murine hematopoietic stem cells by using recombinant amphotropic retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):838–846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Jolly D. J., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. A transmissible retrovirus expressing human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT): gene transfer into cells obtained from humans deficient in HPRT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4709–4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Law M. F., Verma I. M. Generation of helper-free amphotropic retroviruses that transduce a dominant-acting, methotrexate-resistant dihydrofolate reductase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):431–437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Ong E. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Infectious and selectable retrovirus containing an inducible rat growth hormone minigene. Science. 1984 Sep 7;225(4666):993–998. doi: 10.1126/science.6089340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold R. F., Overell R. W. Fibroblast immortality is a prerequisite for transformation by EJ c-Ha-ras oncogene. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):648–651. doi: 10.1038/304648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overell R. W., Watson J. D., Gallis B., Weisser K. E., Cosman D., Widmer M. B. Nature and specificity of lymphokine independence induced by a selectable retroviral vector expressing v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3394–3401. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Transcriptional interference and termination between duplicated alpha-globin gene constructs suggests a novel mechanism for gene regulation. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):562–565. doi: 10.1038/322562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Goldsborough M. D., Mark G. E., Bonner T. I., Groffen J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4218–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F., Jacob F. Construction of a retrovirus capable of transducing and expressing genes in multipotential embryonic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7137–7140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. S., Joyner A. L., Bernstein A., Whitmore G. F. Molecular identification of a human DNA repair gene following DNA-mediated gene transfer. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):206–208. doi: 10.1038/306206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. C., Stanton L. W., Riley S. C., Marcu K. B., Witte O. N. Synergism of v-myc and v-Ha-ras in the in vitro neoplastic progression of murine lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3221–3231. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Temin H. M. Formation of infectious progeny virus after insertion of herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene into DNA of an avian retrovirus. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Marsh K., Yates J. A vector that replicates as a plasmid and can be efficiently selected in B-lymphoblasts transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):410–413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Hoffmann J. W., Goff S. P., Weinberg R. A. Adaptation of a retrovirus as a eucaryotic vector transmitting the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;2(4):426–436. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.4.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Moscovici C., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning of the avian myelocytomatosis virus genome and recovery of infectious virus by transfection of chicken cells. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):625–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.625-631.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. F., Vanek M., Vennström B. Transfer of genes into embryonal carcinoma cells by retrovirus infection: efficient expression from an internal promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):663–666. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03680.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Lemischka I. R., Nathan D. G., Mulligan R. C. Introduction of new genetic material into pluripotent haematopoietic stem cells of the mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):476–480. doi: 10.1038/310476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]