Abstract
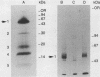
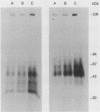
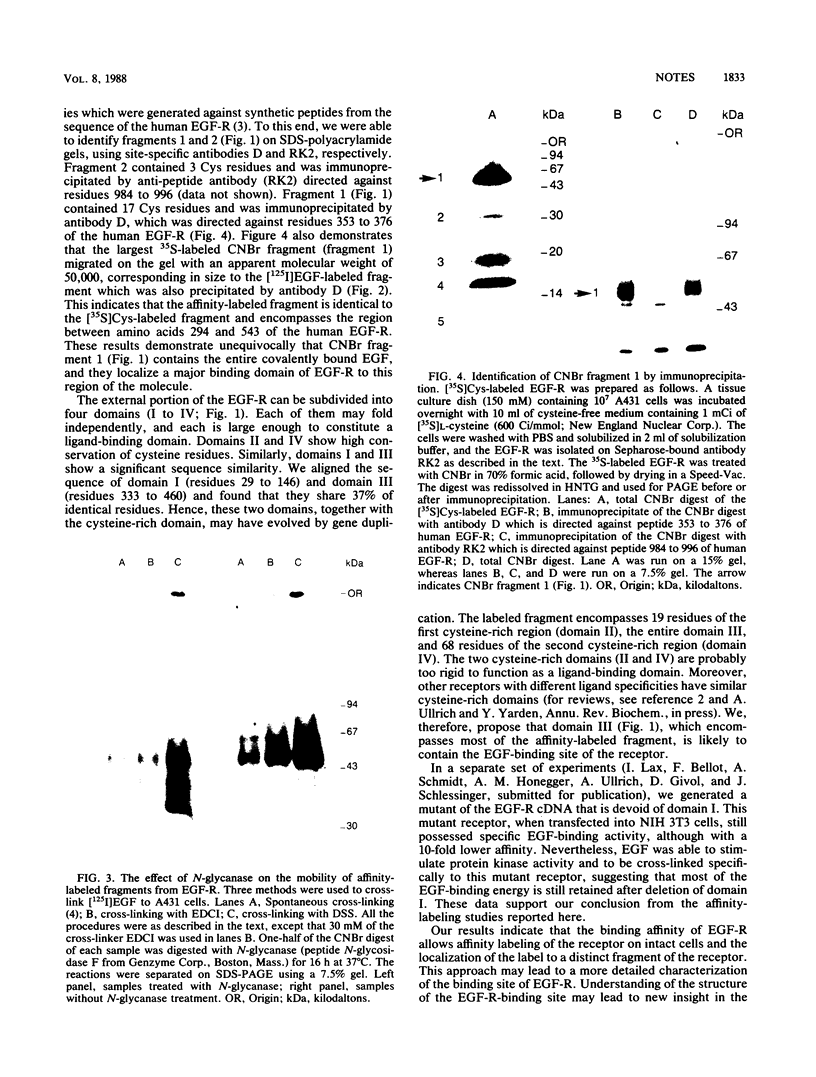
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor was affinity labeled with 125I-labeled EGF, using bifunctional covalent cross-linking agents. The affinity-labeled receptor was isolated and cleaved with CNBr to yield a single-labeled fragment, which was unequivocally identified by site-specific antibodies and other methods to encompass residues 294 to 543 of the EGF receptor. On the basis of amino acid sequence conservation, the extracellular portion of EGF receptor can be divided into four domains. The labeled CNBr fragment contains the entire sequence which is flanked by the two cysteine-rich domains of extracellular portion of the EGF receptor denoted as domain III. On the basis of these and other results, we propose that domain III contributes most of the interactions that define ligand-binding specificity of the EGF receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris R. M., Lax I., Gullick W., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Fridkin M., Schlessinger J. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide as a probe for the kinase activity of the avian EGF receptor and v-erbB protein. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Fox C. F. Direct linkage of EGF to its receptor: characterization and biological relevance. J Supramol Struct. 1980;14(4):441–459. doi: 10.1002/jss.400140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. Allosteric regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2067–2072. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderquist A. M., Carpenter G. Glycosylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in A-431 cells. The contribution of carbohydrate to receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12586–12594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]