Abstract
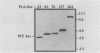
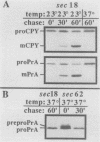
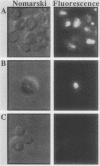
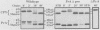
An inactive precursor form of proteinase A (PrA) transits through the early secretory pathway before final vacuolar delivery. We used gene fusions between the gene coding for PrA (PEP4) and the gene coding for the secretory enzyme invertase (SUC2) to identify vacuolar protein-sorting information in the PrA precursor. We found that the 76-amino-acid preprosegment of PrA contains at least two sorting signals: an amino-terminal signal peptide that is cleaved from the protein at the level of the endoplasmic reticulum followed by the prosegment which functions as a vacuolar protein-sorting signal. PrA-invertase hybrid proteins that carried this sequence information were accurately sorted to the yeast vacuole as determined by cell fractionation and immunolocalization studies. Hybrid proteins lacking all or a portion of the PrA prosegment were secreted from the cell. Our gene fusion data together with an analysis of the wild-type PrA protein indicated that N-linked carbohydrate modifications are not required for vacuolar sorting of this protein. Furthermore, results obtained with a set of deletion mutations constructed in the PrA prosegment indicated that this sequence also contributes to proper folding of this polypeptide into a stable transit-competent molecule.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammerer G., Hunter C. P., Rothman J. H., Saari G. C., Valls L. A., Stevens T. H. PEP4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes proteinase A, a vacuolar enzyme required for processing of vacuolar precursors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2490–2499. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGER M., BACON E. E., BACON J. S. Some observations on the form and location of invertase in the yeast cell. Biochem J. 1961 Mar;78:504–511. doi: 10.1042/bj0780504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Johnson L. M., Emr S. D. Isolation of yeast mutants defective in protein targeting to the vacuole. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9075–9079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedwell D. M., Klionsky D. J., Emr S. D. The yeast F1-ATPase beta subunit precursor contains functionally redundant mitochondrial protein import information. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4038–4047. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blachly-Dyson E., Stevens T. H. Yeast carboxypeptidase Y can be translocated and glycosylated without its amino-terminal signal sequence. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1183–1191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. W., Tkacz J. S., Lampen J. O. Asparagine-linked carbohydrate does not determine the cellular location of yeast vacuolar nonspecific alkaline phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):865–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.865-873.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. W., Abelson J. The subnuclear localization of tRNA ligase in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1515–1526. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. A yeast mutant defective at an early stage in import of secretory protein precursors into the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):633–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Schekman R., Flessel M. C., Thorner J. An MF alpha 1-SUC2 (alpha-factor-invertase) gene fusion for study of protein localization and gene expression in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7080–7084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Lampen J. O. Beta-D-fructofuranoside fructohydrolase from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:504–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSON H., ELLIAS L. The purification and properties of an alpha-glucosidase of Saccharomyces italicus Y1225. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Oct;30(1):28–40. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Johnson A. D. Homeo domain of the yeast repressor alpha 2 is a sequence-specific DNA-binding domain but is not sufficient for repression. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):1007–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2887035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbeck A., Schekman R. Interorganelle transfer and glycosylation of yeast invertase in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2017–2021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Tanner W. Biosynthesis of carboxypeptidase Y in yeast. Evidence for a precursor form of the glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1430–1436. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Tanner W. Biosynthesis of the vacuolar yeast glycoprotein carboxypeptidase Y. Conversion of precursor into the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):599–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Tanner W. Carbohydrate moiety of carboxypeptidase Y and perturbation of its biosynthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 15;91(2):567–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Zubenko G. S., Hasilik A., Jones E. W. Mutant defective in processing of an enzyme located in the lysosome-like vacuole of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):435–439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. N., Sielecki A. R. Molecular structure of an aspartic proteinase zymogen, porcine pepsinogen, at 1.8 A resolution. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):33–38. doi: 10.1038/319033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Botstein D. Secretion-defective mutations in the signal sequence for Saccharomyces cerevisiae invertase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2382–2391. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y., Tamai Y., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of PHO8 expression by PHO regulatory genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):248–252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Pathways of protein secretion in eukaryotes. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):25–32. doi: 10.1126/science.2994224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota S., Yoshida Y., Kumaoka H., Furumichi A. Studies on the microsomal electron-transport system of anaerobically grown yeast. V. Purification and characterization of NADPH-cytochrome c reductase. J Biochem. 1977 Jan;81(1):197–205. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Lampen J. O. Tunicamycin--an inhibitor of yeast glycoprotein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90925-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenney J. F., Matile P., Wiemken A., Schellenberg M., Meyer J. Activities and cellular localization of yeast proteases and their inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1378–1383. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage M. G. Preparation of Fab fragments from IgGs of different animal species. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):142–150. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechler B., Müller H., Wolf D. H. Maturation of vacuolar (lysosomal) enzymes in yeast: proteinase yscA and proteinase yscB are catalysts of the processing and activation event of carboxypeptidase yscY. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2157–2163. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechler B., Müller M., Müller H., Meussdoerffer F., Wolf D. H. In vivo biosynthesis of the vacuolar proteinases A and B in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11203–11206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechler B., Müller M., Müller H., Wolf D. H. In vivo biosynthesis of vacuolar proteinases in proteinase mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):770–778. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehle C. M., Aynardi M. W., Kolodny M. R., Park F. J., Jones E. W. Protease B of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation and regulation of the PRB1 structural gene. Genetics. 1987 Feb;115(2):255–263. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Lin R. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Molecular consequences of specific intron mutations on yeast mRNA splicing in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):335–344. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Schekman R. Secretion and cell-surface growth are blocked in a temperature-sensitive mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H. R., Tkacz J. S., Lampen J. O. Glycoprotein nature of yeast alkaline phosphatase. Formation of active enzyme in the presence of tunicamycin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11943–11952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opheim D. J. alpha-D-Mannosidase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Characterization and modulation of activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 11;524(1):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Raney P., Halvorson H. O. Mutations affecting the signal sequence alter synthesis and secretion of yeast invertase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5033–5037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston R. A., Murphy R. F., Jones E. W. Apparent endocytosis of fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated dextran by Saccharomyces cerevisiae reflects uptake of low molecular weight impurities, not dextran. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):1981–1987. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Roberts B. L., Smith A. E. Nuclear location signals in polyoma virus large-T. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riezman H. Endocytosis in yeast: several of the yeast secretory mutants are defective in endocytosis. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. H., Hunter C. P., Valls L. A., Stevens T. H. Overproduction-induced mislocalization of a yeast vacuolar protein allows isolation of its structural gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3248–3252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. H., Stevens T. H. Protein sorting in yeast: mutants defective in vacuole biogenesis mislocalize vacuolar proteins into the late secretory pathway. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1041–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90819-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaiger H., Hasilik A., von Figura K., Wiemken A., Tanner W. Carbohydrate-free carboxypeptidase Y is transferred into the lysosome-like yeast vacuole. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 11;104(3):950–956. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91341-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly W. S., Fischer H. D. The phosphomannosyl recognition system for intracellular and intercellular transport of lysosomal enzymes. J Cell Biochem. 1982;18(1):67–85. doi: 10.1002/jcb.1982.240180107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T. H., Rothman J. H., Payne G. S., Schekman R. Gene dosage-dependent secretion of yeast vacuolar carboxypeptidase Y. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1551–1557. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T., Esmon B., Schekman R. Early stages in the yeast secretory pathway are required for transport of carboxypeptidase Y to the vacuole. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Maley F., Chu F. K. GlycoProtein biosynthesis in yeast. protein conformation affects processing of high mannose oligosaccharides on carboxypeptidase Y and invertase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2562–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Maley F. The use of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H in characterizing the structure and function of glycoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 10;78(3):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valls L. A., Hunter C. P., Rothman J. H., Stevens T. H. Protein sorting in yeast: the localization determinant of yeast vacuolar carboxypeptidase Y resides in the propeptide. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman L. S., Bacallao R., Wickner W. Multiple methods of visualizing the yeast vacuole permit evaluation of its morphology and inheritance during the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1539–1547. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickerham L. J. A Critical Evaluation of the Nitrogen Assimilation Tests Commonly Used in the Classification of Yeasts. J Bacteriol. 1946 Sep;52(3):293–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland F. T., Gleason M. L., Serafini T. A., Rothman J. E. The rate of bulk flow from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford C. A., Daniels L. B., Park F. J., Jones E. W., Van Arsdell J. N., Innis M. A. The PEP4 gene encodes an aspartyl protease implicated in the posttranslational regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae vacuolar hydrolases. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2500–2510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubenko G. S., Park F. J., Jones E. W. Mutations in PEP4 locus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae block final step in maturation of two vacuolar hydrolases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):510–514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]