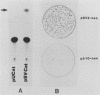
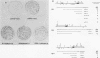
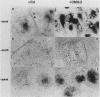
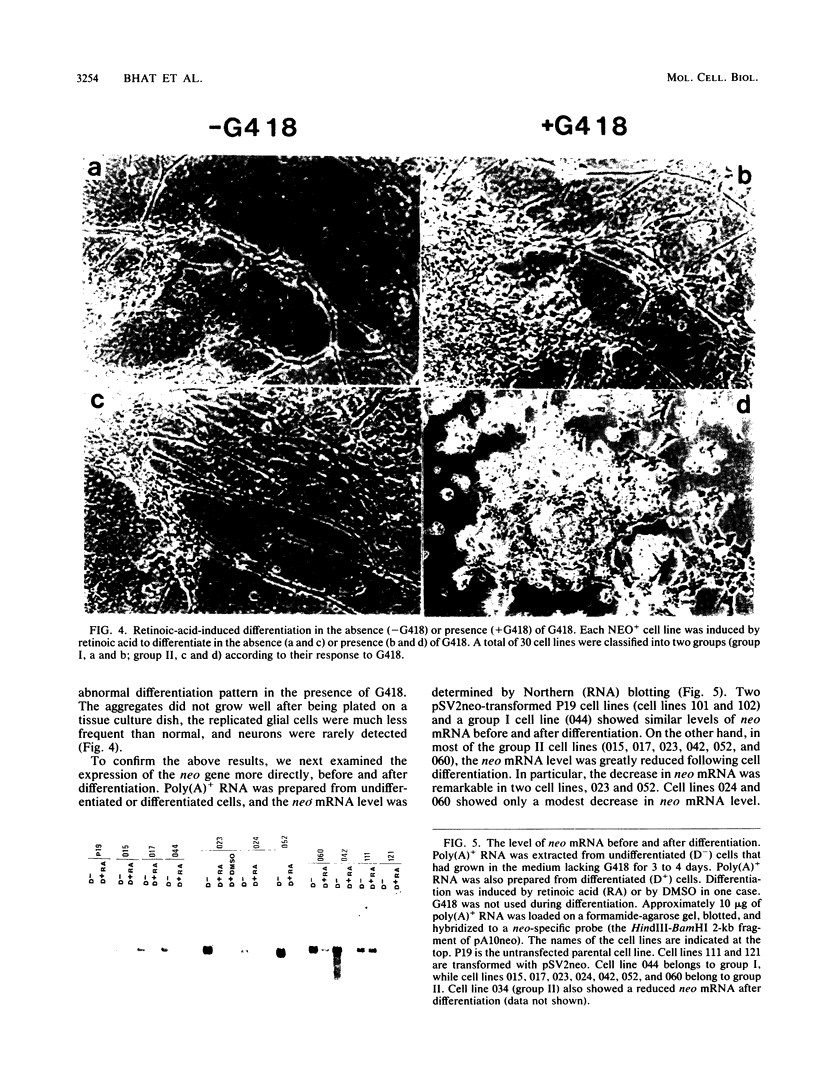
Abstract
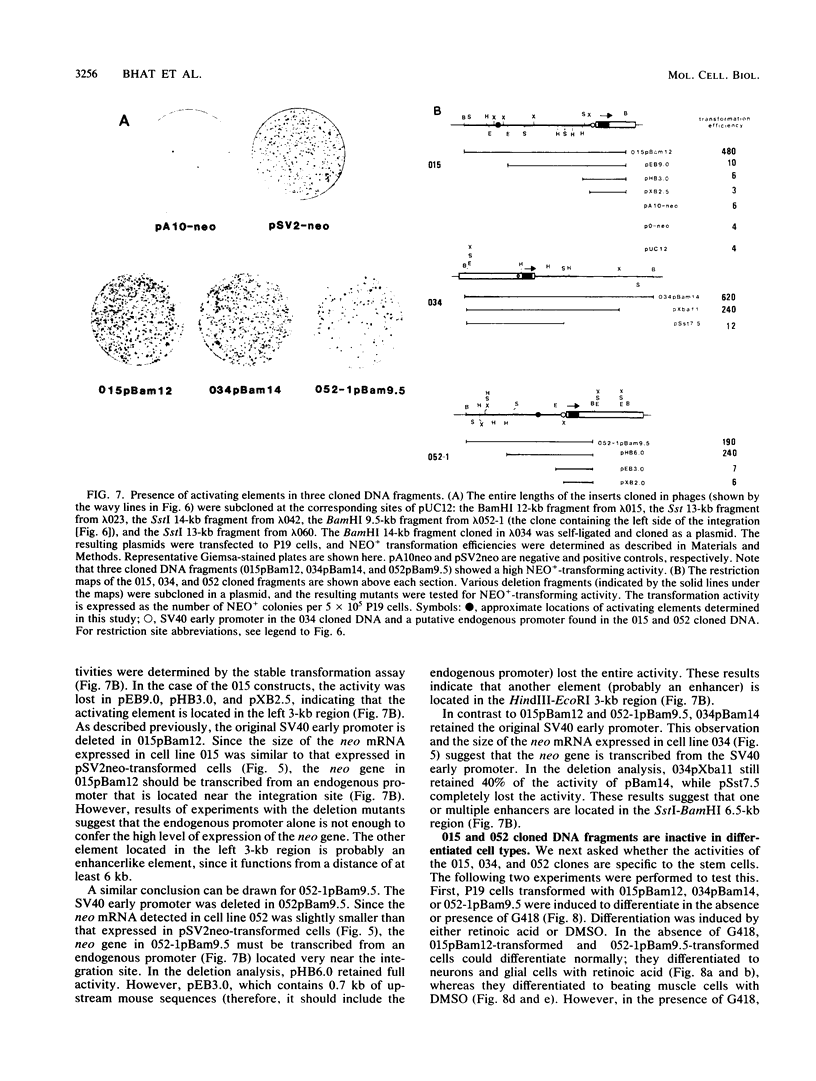
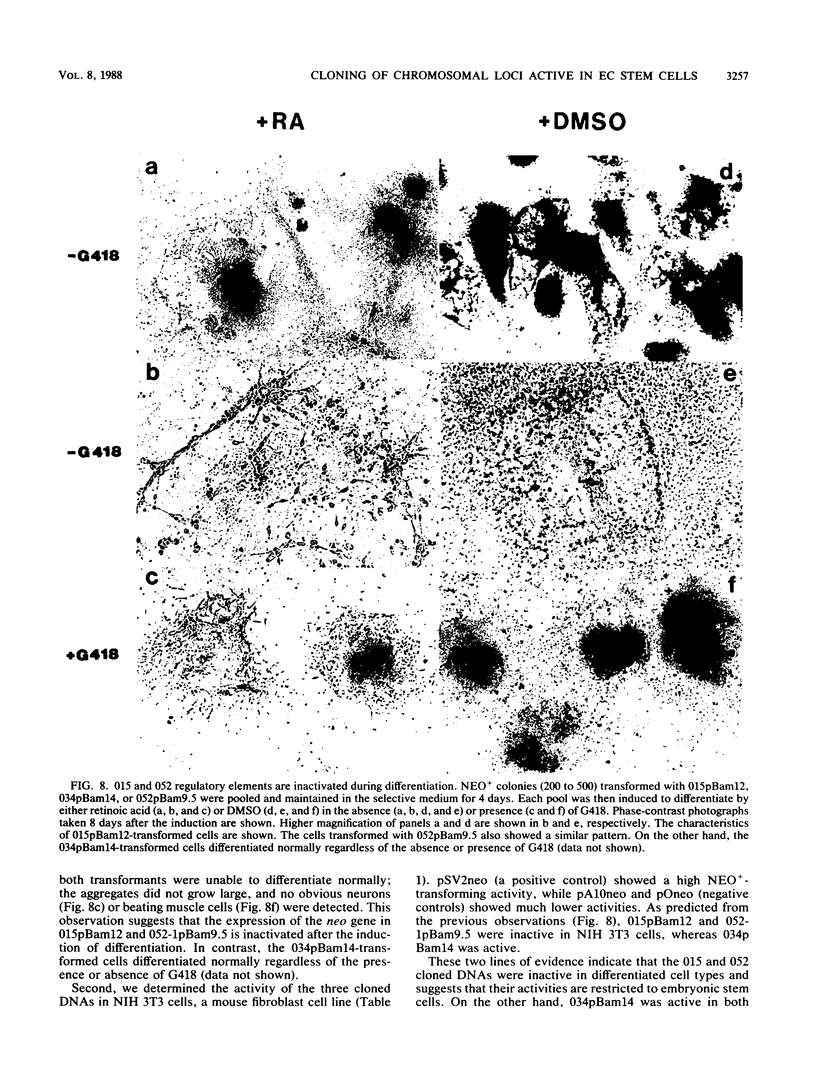
Chromosomal loci that are specifically active in embryonal carcinoma stem cells were cloned from the mouse genome by functional selection. P19 cells, a pluripotent embryonal carcinoma cell line, were transfected with an enhancer trap (a plasmid containing an enhancerless inactive neo gene), and NEO+ transformants were isolated. All of the NEO+ cell lines retained pluripotency and expressed the neo gene. When the cells were induced to differentiate, most of the cell lines continued to express the neo gene, while the neo gene in some cell lines became repressed. From the latter group of cell lines, we have cloned the integrated neo gene plus the flanking cellular DNA sequences. Three of the six cloned DNAs possessed a high NEO+-transforming activity in undifferentiated P19 cells. Among these three, two (015 and 052) were inactive in differentiated P19 cells and NIH 3T3 cells, while the remaining one was active in these differentiated cells. Deletion analysis suggested that both 015 and 052 contain two regulatory elements (promoter and enhancer) of cellular DNA origin. The putative enhancer and promoter are separated by at least 6 kilobases in 015 and 1 kilobase in 052. Therefore, 015 and 052 cloned fragments contain regulatory DNA elements that are specifically active in the embryonal carcinoma stem cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barklis E., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Chromosomal position or virus mutation permits retrovirus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90596-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. R., Taylor A., Hogan B. L. Changes in the rate of laminin and entactin synthesis in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells treated with retinoic acid and cyclic amp. Dev Biol. 1983 Oct;99(2):510–516. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziadek M., Adamson E. Localization and synthesis of alphafoetoprotein in post-implantation mouse embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1978 Feb;43:289–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. K., Harris J. F., McBurney M. W. Induced muscle differentiation in an embryonal carcinoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2280–2286. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. L., Rossant J. Investigation of the fate of 4-5 day post-coitum mouse inner cell mass cells by blastocyst injection. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1979 Aug;52:141–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H. Activation of an enhancerless gene by chromosomal integration. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4179–4184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H. Random isolation of gene activator elements from the human genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4185–4194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Fromental C., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A mutated polyoma virus enhancer which is active in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells is not repressed by adenovirus-2 E1A products. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):249–251. doi: 10.1038/321249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Kao H. T., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Strickland S. Common control of the heat shock gene and early adenovirus genes: evidence for a cellular E1A-like activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):867–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., Rudnicki M. A., Harris J. F., McBurney M. W. Retinoic acid-induced neural differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2271–2279. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S., Gerster T., Picard D., Radbruch A., Schaffner W. Evidence for transient requirement of the IgH enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8901–8912. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. A., LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. Isolation of cDNA clones for genes exhibiting reduced expression after differentiation of murine teratocarcinoma stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2142–2150. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlefield J. W., Felix J. S. Rescue of terminally differentiating teratocarcinoma cells by fusion to undifferentiated parental cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Nov;8(6):743–757. doi: 10.1007/BF01543016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Rogers B. J. Isolation of male embryonal carcinoma cells and their chromosome replication patterns. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natt E., Scherer G. EMBL 12, a new lambda replacement vector with sites for SalI, XbaI, BamHI, SstI and EcoRI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7128–7128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift F. V., Bhat K., Younghusband H. B., Hamada H. Characterization of a cell type-specific enhancer found in the human papilloma virus type 18 genome. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1339–1344. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo M., Tanaka M. A cellular enhancer of retrovirus gene expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3748–3752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. K., Jaeckle H. K. Protein synthesis by rat hepatoma x mouse teratocarcinoma somatic cell hybrids. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 Jan;9(1):111–119. doi: 10.1007/BF01544052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaller D. M., Eckhardt L. A. Deletion of a B-cell-specific enhancer affects transfected, but not endogenous, immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5088–5092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]