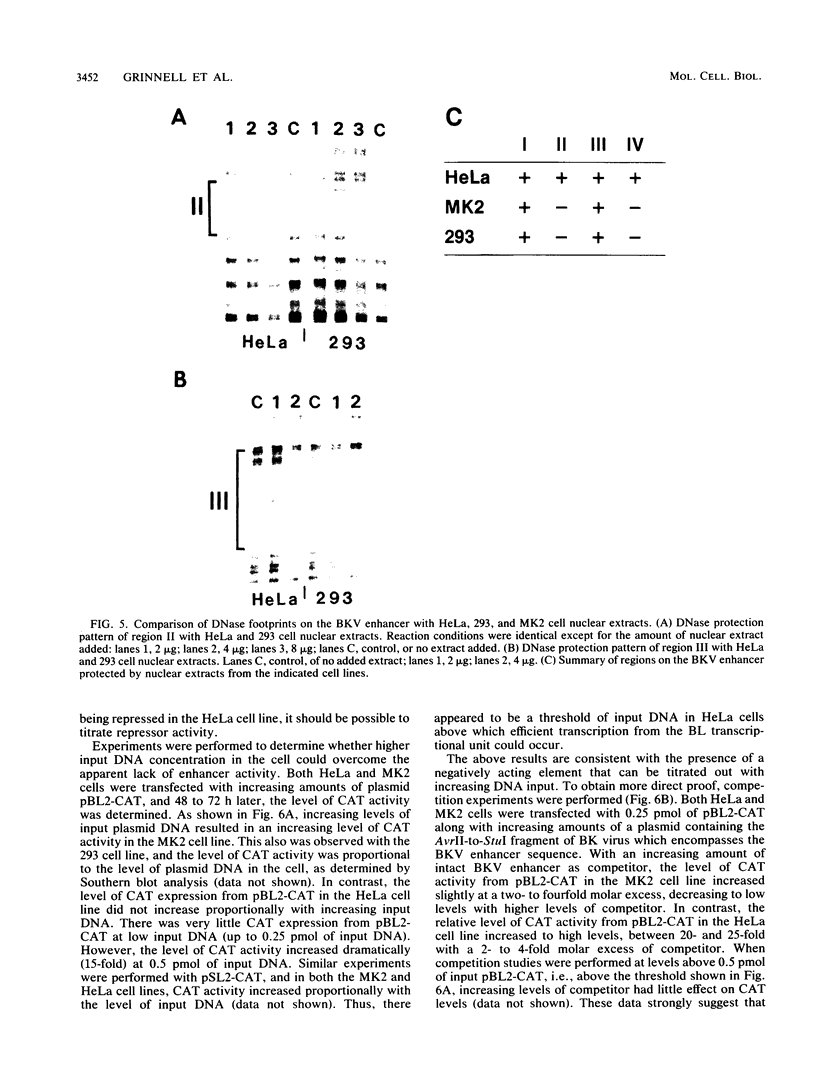
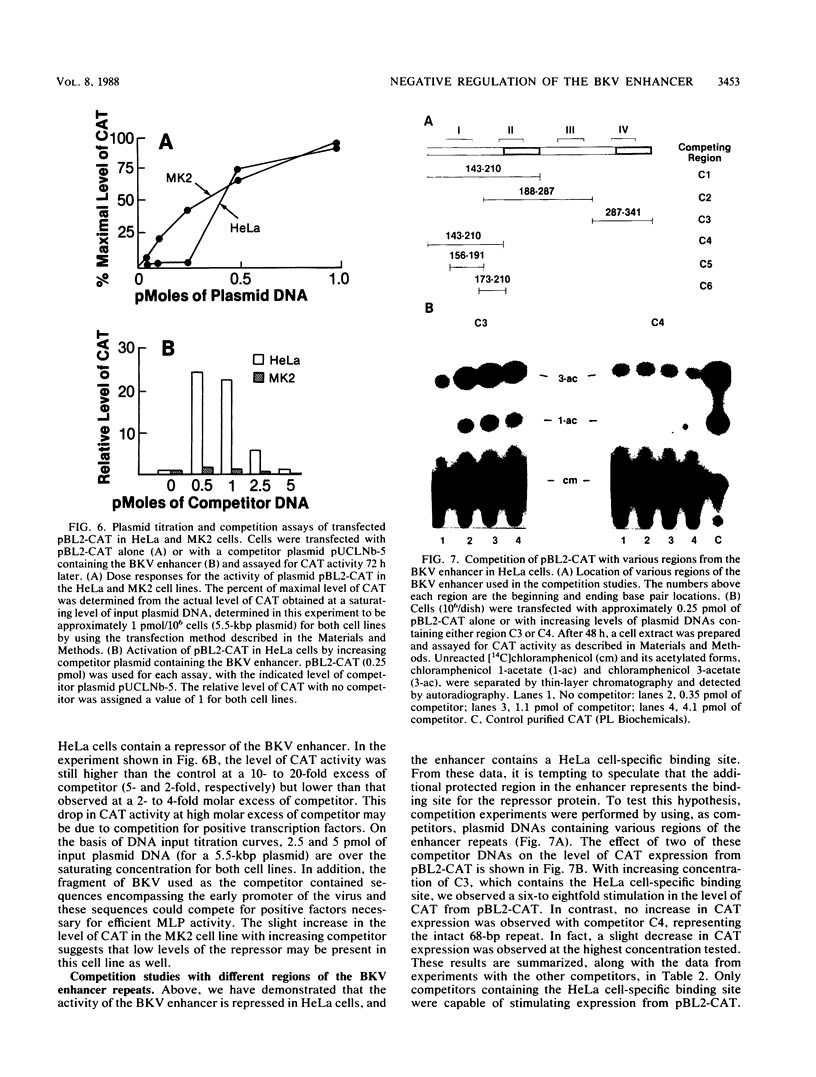
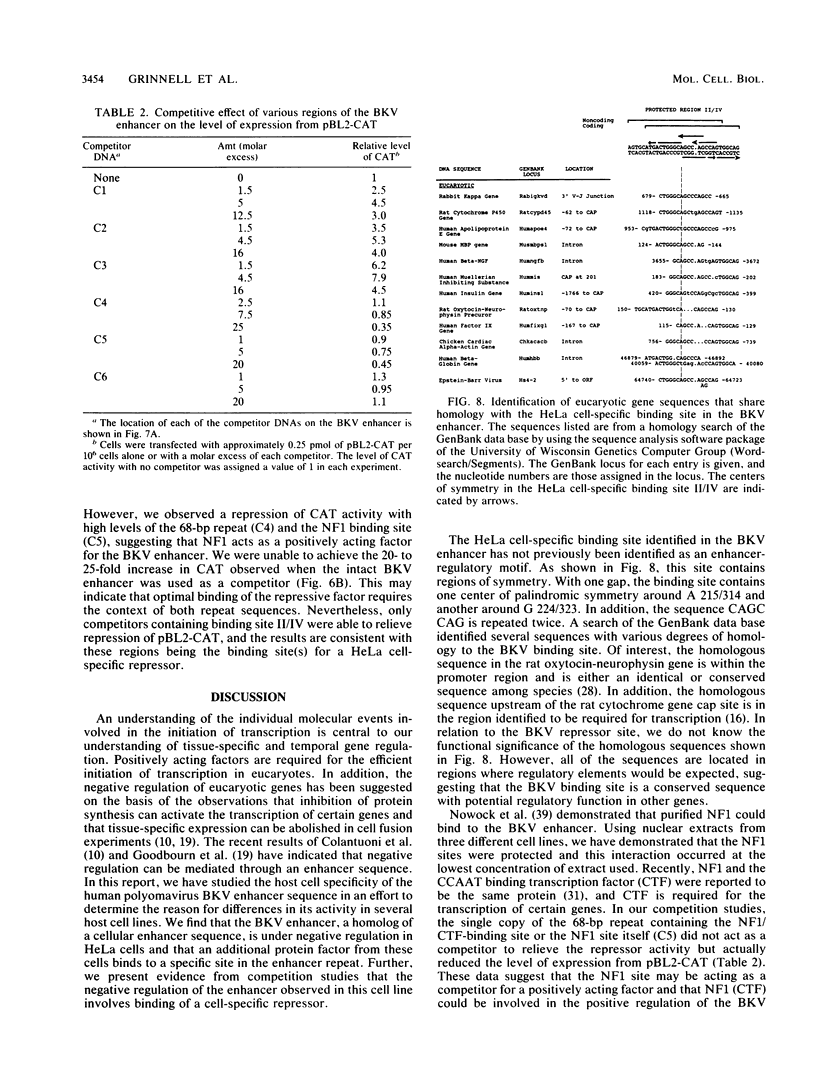
Abstract
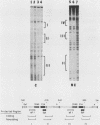
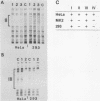
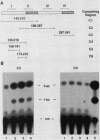
We have examined the cell type-specific regulation of the human BK virus (BKV) enhancer. This enhancer functions efficiently in cis to activate expression from the adenovirus major late promoter in the human kidney cell line, 293, and in a monkey kidney cell line, MK2, but not in the HeLa cell line. In gel retardation migration assays, specific BKV enhancer-protein complexes could be observed by using nuclear extracts prepared from each cell line. Moreover, a unique DNA-protein complex was observed by using the HeLa cell nuclear extracts. By DNase footprint analysis, four binding regions for HeLa cell nuclear proteins were defined within the BKV enhancer repeat region. Two of the protected regions encompassed nuclear factor 1 or CCAAT transcription factor binding sites. These nuclear factor 1 sites also were protected by nuclear proteins from the 293 and MK2 cell lines. The other two protected sites encompassed a region of symmetry which included a sequence similar to the simian virus 40 TC enhancer motif and to a conserved sequence present upstream or within the introns of several cellular genes. These two sites were not protected by either the 293 or MK2 nuclear proteins. Competition studies in transfected cells indicated that the reduced activity of the BKV enhancer in the HeLa cell line was due to negative regulation. Further, we have demonstrated that binding of a nuclear factor(s) to the HeLa cell-specific site is involved in the repression of enhancer activity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The role of the kappa enhancer and its binding factor NF-kappa B in the developmental regulation of kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augereau P., Chambon P. The mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer: effect on transcription in vitro and binding of proteins present in HeLa and lymphoid B cell extracts. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1791–1797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett P., Clark L., Hay R. T. A cellular protein binds to a conserved sequence in the adenovirus type 2 enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2719–2735. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Keller W., Dale T., Schöler H. R., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. A transcription factor which binds to the enhancers of SV40, immunoglobulin heavy chain and U2 snRNA genes. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):268–272. doi: 10.1038/325268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B., Chambon P. The immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer is stimulated by the adenovirus type 2 E1A products in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2846–2849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R. Repression of transcription in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantuoni V., Pirozzi A., Blance C., Cortese R. Negative control of liver-specific gene expression: cloned human retinol-binding protein gene is repressed in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):631–636. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Fromental C., Augereau P., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Cell-type specific protein binding to the enhancer of simian virus 40 in nuclear extracts. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):544–548. doi: 10.1038/323544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K. Nuclear activity from F9 embryonal carcinoma cells binding specifically to the enhancers of wild-type polyoma virus and PyEC mutant DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2845–2861. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Sogawa K., Nishi C., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Regulatory DNA elements localized remotely upstream from the drug-metabolizing cytochrome P-450c gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1465–1477. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Lubon H., Fleckenstein B., Hennighausen L. Binding of transcription factors and creation of a large nucleoprotein complex on the human cytomegalovirus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3658–3662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell B. W., Berg D. T., Walls J. Activation of the adenovirus and BK virus late promoters: effects of the BK virus enhancer and trans-acting viral early proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3596–3605. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell B. W., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Comparison of infectious JC virus DNAs cloned from human brain. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):299–308. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.299-308.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell B. W., Wagner R. R. Nucleotide sequence and secondary structure of VSV leader RNA and homologous DNA involved in inhibition of DNA-dependent transcription. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):533–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Chambon P. Repression of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer by the adenovirus-2 E1A products. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1391–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2999984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Lemaire C., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Negative regulation contributes to tissue specificity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2558–2567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Kimura A., Kieran M., Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. A common positive trans-acting factor binds to enhancer sequences in the promoters of mouse H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivell R., Richter D. Structure and comparison of the oxytocin and vasopressin genes from rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2006–2010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalinot P., Kédinger C. Negative regulatory sequences in the EIa-inducible enhancer of the adenovirus-2 early EIIa promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2651–2669. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Satake M., Furukawa K., Reichel R., Ito Y., Nevins J. R. A factor discriminating between the wild-type and a mutant polyomavirus enhancer. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):87–89. doi: 10.1038/328087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryszke M. H., Piette J., Yaniv M. Induction of a factor that binds to the polyoma virus A enhancer on differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):254–256. doi: 10.1038/328254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L., Holmgren-König M., Khoury G. Transcriptional "silencer" element in rat repetitive sequences associated with the rat insulin 1 gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3151–3155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowock J., Borgmeyer U., Püschel A. W., Rupp R. A., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA protein binds to the MMTV-LTR, the adenovirus origin of replication, and the BK virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2045–2061. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostapchuk P., Diffley J. F., Bruder J. T., Stillman B., Levine A. J., Hearing P. Interaction of a nuclear factor with the polyomavirus enhancer region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8550–8554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers E. F., Yang J. Q., Marcu K. B. A negative transcriptional control element located upstream of the murine c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):899–904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Siegele D. A., Cowing D. W., Gross C. A. The regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:355–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N., Kress M., Gruss P., Khoury G. BK viral enhancer element and a human cellular homolog. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):749–755. doi: 10.1126/science.6314501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Wildeman A., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor is responsible for the simian virus 40 enhancer activity in vitro. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):458–463. doi: 10.1038/313458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Khoury G., Dhar R. The genome of human papovavirus BKV. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):963–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Zenke M., Schatz C., Wintzerith M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Takahashi K., Chambon P. Specific protein binding to the simian virus 40 enhancer in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2098–2105. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]