Abstract
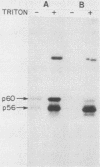
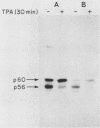
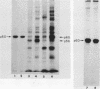
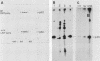
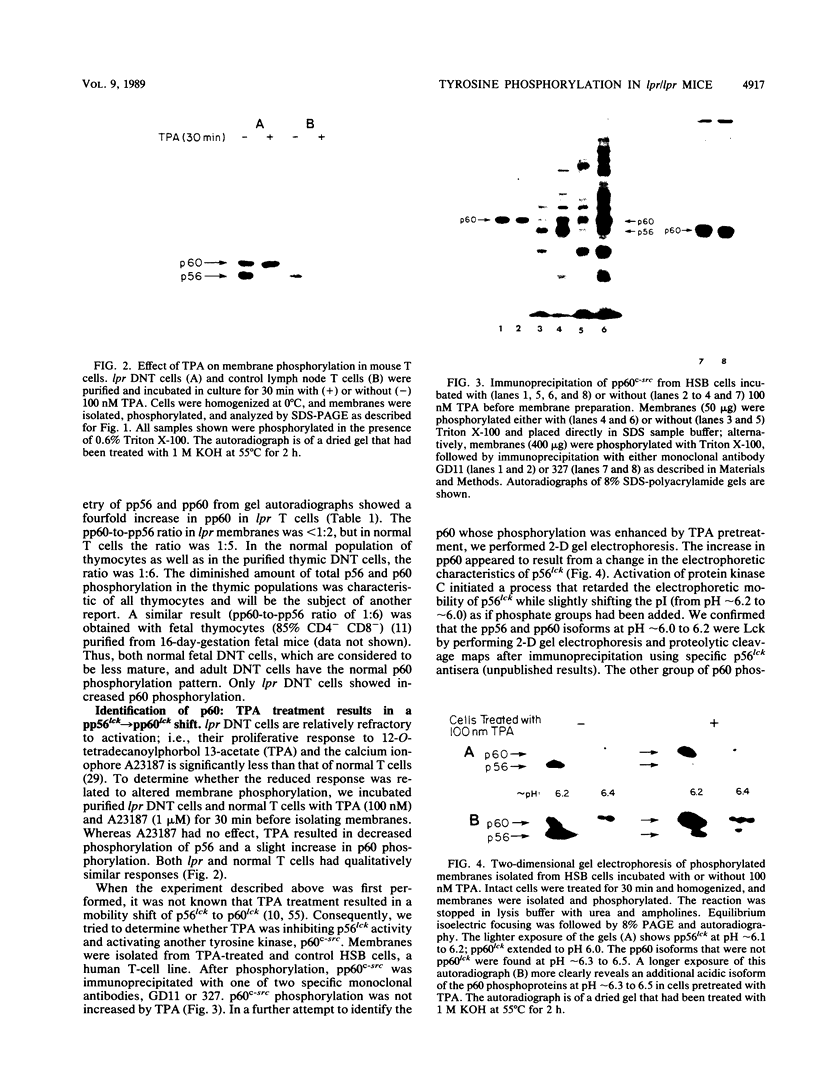
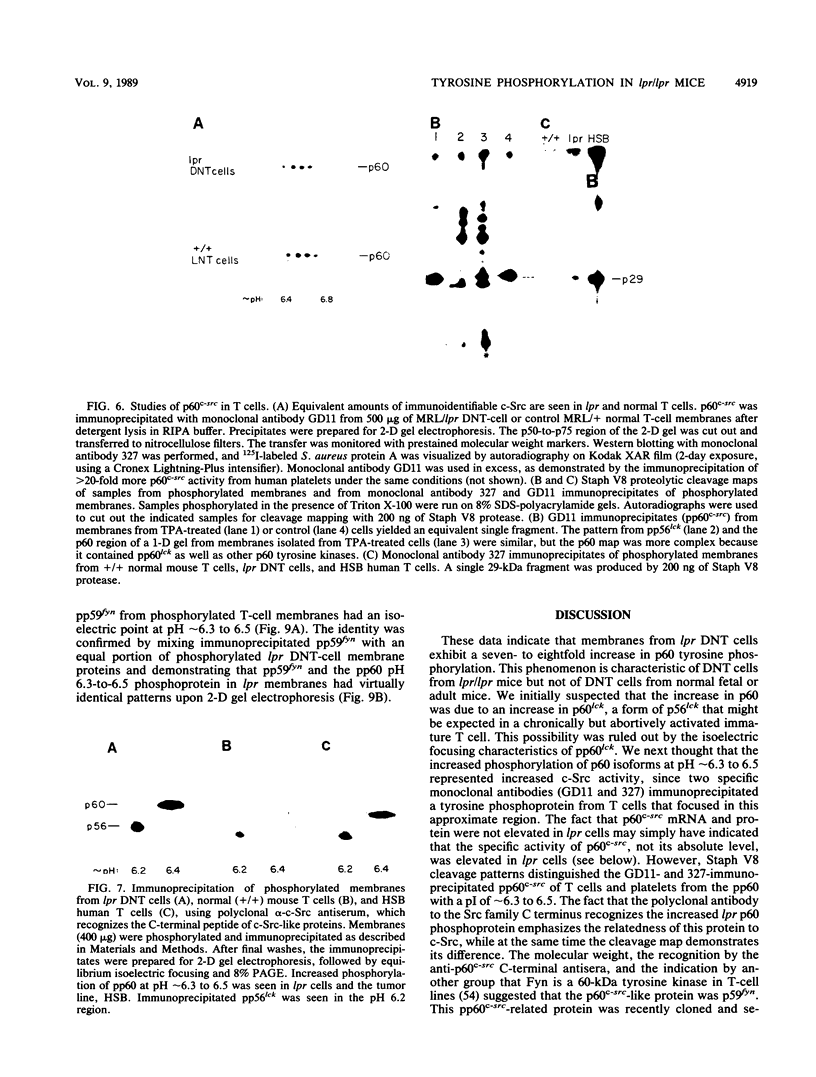
Mice homozygous for the autosomal recessive lpr gene have a disorder that results in autoimmunity and massive accumulation of T lymphocytes lacking CD4 and CD8 surface markers. These abnormal T cells exhibit constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation of a component of the CD3-T-cell receptor complex. We compared membrane tyrosine phosphorylation in lpr/lpr CD4- CD8- T cells and control T cells, lpr membranes exhibited a 7.3-fold increase (n = 16) in tyrosine phosphorylation of a 60-kilodalton protein. The increase was correlated with the Lpr but not the CD4- CD8- phenotype in that p60 phosphorylation was not increased in membranes from normal CD4- CD8- thymocytes. To identify the p60 in lpr cells, we examined the activity of several T-cell tyrosine-specific protein kinases. p56lck phosphorylation was only slightly increased in lpr membranes (2.2-fold; n = 16). Phorbol ester treatment of intact T cells before membrane isolation caused p56lck to migrate as pp60lck; however, pp60lck could be clearly distinguished from the pp60 in lpr cells by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. The pp60 from lpr cells exhibited several isoforms at pH approximately 6.3 to 6.5. Although on two-dimensional gels pp60c-src had a pI (6.4 to 6.8) within a similar region, p60c-src mRNA, protein, and kinase activities were not increased in lpr cells. In addition, staphylococcal V8 proteolytic cleavage of the lpr pp60 isolated on two-dimensional gels yielded two major fragments, a pattern distinct from that of pp60c-src. However, by using an antiserum against the C-terminal sequence of c-Src and other related kinases, including p59fyn, the pp60 could be immunoprecipitated in greater amounts from lpr than from control T cells. When pp59(fyn) was selectively immunoprecipitated from T-cell membranes with specific antisera, its molecular weight, proteolytic cleavage pattern, and behavior on two-dimensional gels were identical to those of the pp60 from lpr cells. We conclude that p59(fyn) phosphorylation is increased in membranes from lpr/lpr CD4(-) CD8(-) T cells and that the increase is correlated with constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation and perhaps with the expansion of this unusual T-cell population.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein K. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of a site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase, p56lck, reveals its oncogenic potential in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4247–4251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. K., Gibbs C. P., Tanaka A., Kung H. J., Fujita D. J. Human cellular src gene: nucleotide sequence and derived amino acid sequence of the region coding for the carboxy-terminal two-thirds of pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1122–1129. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley J. E., Bishop G. A., St John T., Frelinger J. A. A simple, rapid method for the purification of poly A+ RNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):114–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Veillette A., Schwartz A. M., DeSeau V., Rosen N. Activation of pp60c-src protein kinase activity in human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2251–2255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd R. C., Schreyer M., Miescher G. C., MacDonald H. R. T cell lineages in the thymus of lpr/lpr mice. Evidence for parallel pathways of normal and abnormal T cell development. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2200–2210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Harrison M. L., Hellstrom K. E., Krebs E. G. A lymphoma cell line expressing elevated levels of tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10738–10742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Harrison M. L., Hellstrom K. E., Krebs E. G. A lymphoma protein with an in vitro site of tyrosine phosphorylation homologous to that in pp60src. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13877–13879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Lamberts R. J. Tumor promoters cause changes in the state of phosphorylation and apparent molecular weight of a tyrosine protein kinase in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4921–4925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceredig R., Dialynas D. P., Fitch F. W., MacDonald H. R. Precursors of T cell growth factor producing cells in the thymus: ontogeny, frequency, and quantitative recovery in a subpopulation of phenotypically mature thymocytes defined by monoclonal antibody GK-1.5. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1654–1671. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceredig R., Lowenthal J. W., Nabholz M., MacDonald H. R. Expression of interleukin-2 receptors as a differentiation marker on intrathymic stem cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):98–100. doi: 10.1038/314098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chackalaparampil I., Shalloway D. Altered phosphorylation and activation of pp60c-src during fibroblast mitosis. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90422-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J. L., Cohen P. L., Eisenberg R. A. Rapid T cell receptor modulation accompanies lack of in vitro mitogenic responsiveness of double negative T cells to anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody in MRL/Mp-lpr mice. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):1848–1854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earp H. S., Austin K. S., Buessow S. C., Dy R., Gillespie G. Y. Membranes from T and B lymphocytes have different patterns of tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2347–2351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earp H. S., Austin K. S., Gillespie G. Y., Buessow S. C., Davies A. A., Parker P. J. Characterization of distinct tyrosine-specific protein kinases in B and T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4351–4356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. L., Boyle W. J., Ting J. P. Molecular basis of elevated c-myb expression in the abnormal L3T4-, Lyt-2- T lymphocytes of autoimmune mice. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3497–3505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes B. J., Edison L., Mathieson B. J., Chused T. M. Early T lymphocytes. Differentiation in vivo of adult intrathymic precursor cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):802–822. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Woodgett J. R., Cooper J. A., Buss J. E., Shalloway D., Hunter T. Protein kinase C phosphorylates pp60src at a novel site. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groghan T. W., Davignon J. L., Evans J., Allison J. P., Eisenberg R. A., Frelinger J. A., Cohen P. L. Diminished expression of the T cell receptor on the expanded lymphocyte population in MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. Autoimmunity. 1989;2(2):97–111. doi: 10.3109/08916938909019947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. L., Low P. S., Geahlen R. L. T and B lymphocytes express distinct tyrosine protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9348–9350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Kelley V. E., Masuda K., Yoshida H., Roths J. B., Murphy E. D. Induction of various autoantibodies by mutant gene lpr in several strains of mice. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Hanafusa H. Cell transformation by the viral src oncogene. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:31–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri K., Katagiri T., Eisenberg R. A., Ting J., Cohen P. L. Interleukin 2 responses of lpr and normal L3T4-/Lyt-2- T cells induced by TPA plus A23187. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri T., Cohen P. L., Eisenberg R. A. The lpr gene causes an intrinsic T cell abnormality that is required for hyperproliferation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):741–751. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J. Y., Takeya T., Grandori C., Iba H., Levy J. B., Hanafusa H. Amino acid substitutions sufficient to convert the nontransforming p60c-src protein to a transforming protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4155–4160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T., Pennington C. Y., Robbins K. C. Isolation and oncogenic potential of a novel human src-like gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4195–4201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Iba H., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transforming potential of p60c-src by a single amino acid change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Cooper J. A., King C. S., Ziegler S. F., Tinker D. A., Overell R. W., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Neoplastic transformation induced by an activated lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (pp56lck). Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):540–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Peet R., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. A lymphocyte-specific protein-tyrosine kinase gene is rearranged and overexpressed in the murine T cell lymphoma LSTRA. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Mathey-Prevot B., Bernards A., Baltimore D. Neuronal pp60c-src contains a six-amino acid insertion relative to its non-neuronal counterpart. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):411–415. doi: 10.1126/science.2440106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menko A. S., Boettiger D. Inhibition of chicken embryo lens differentiation and lens junction formation in culture by pp60v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1414–1420. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Schreurs J., Miyajima A., Wang J. Y. Hematopoietic growth factors activate the tyrosine phosphorylation of distinct sets of proteins in interleukin-3-dependent murine cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2214–2218. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Davidson W. F., Yetter R. A., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Coffman R. L. Abnormalities induced by the mutant gene Ipr: expansion of a unique lymphocyte subset. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2612–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountz J. D., Steinberg A. D., Klinman D. M., Smith H. R., Mushinski J. F. Autoimmunity and increased c-myb transcription. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1087–1089. doi: 10.1126/science.6494925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemazee D. A., Studer S., Steinmetz M., Dembić Z., Kiefer M. The lymphoproliferating cells of MRL-lpr/lpr mice are a polyclonal population that bear the T lymphocyte receptor for antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Aug;15(8):760–764. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., McCarley D. J., Ely C. M., Benjamin D. C., Parsons J. T. Monoclonal antibodies to Rous sarcoma virus pp60src react with enzymatically active cellular pp60src of avian and mammalian origin. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):272–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.272-282.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raveche E. S., Steinberg A. D., DeFranco A. L., Tjio J. H. Cell cycle analysis of lymphocyte activation in normal and autoimmune strains of mice. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1219–1226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman E. M., Thom R. R., Casnellie J. E. Activation of a tyrosine protein kinase is an early event in the stimulation of T lymphocytes by interleukin-2. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):6956–6959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Davidson W. F., Morse H. C., 3rd, Klausner R. D. Abnormal tyrosine phosphorylation on T-cell receptor in lymphoproliferative disorders. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):674–676. doi: 10.1038/324674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Patel M. D., Weissman A. M., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Antigen activation of murine T cells induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a polypeptide associated with the T cell antigen receptor. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1083–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90708-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. IgG or IgM monoclonal antibodies reactive with different determinants on the molecular complex bearing Lyt 2 antigen block T cell-mediated cytolysis in the absence of complement. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2665–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh S. M., Brugge J. S. Investigation of factors that influence phosphorylation of pp60c-src on tyrosine 527. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2465–2471. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semba K., Nishizawa M., Miyajima N., Yoshida M. C., Sukegawa J., Yamanashi Y., Sasaki M., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. yes-related protooncogene, syn, belongs to the protein-tyrosine kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5459–5463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A. F., Sefton B. M. Expression of a new tyrosine protein kinase is stimulated by retrovirus promoter insertion. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):682–685. doi: 10.1038/319682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willman C. L., Stewart C. C., Griffith J. K., Stewart S. J., Tomasi T. B. Differential expression and regulation of the c-src and c-fgr protooncogenes in myelomonocytic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4480–4484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsy D., Hardy R. R., Seaman W. E. The proliferating cells in autoimmune MRL/lpr mice lack L3T4, an antigen on "helper" T cells that is involved in the response to class II major histocompatibility antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2686–2689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota S., Yuan D., Katagiri T., Eisenberg R. A., Cohen P. L., Ting J. P. The expression and regulation of c-myb transcription in B6/lpr Lyt-2-, L3T4-T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2810–2817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]