Abstract
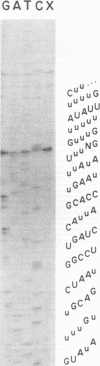
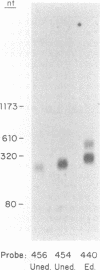
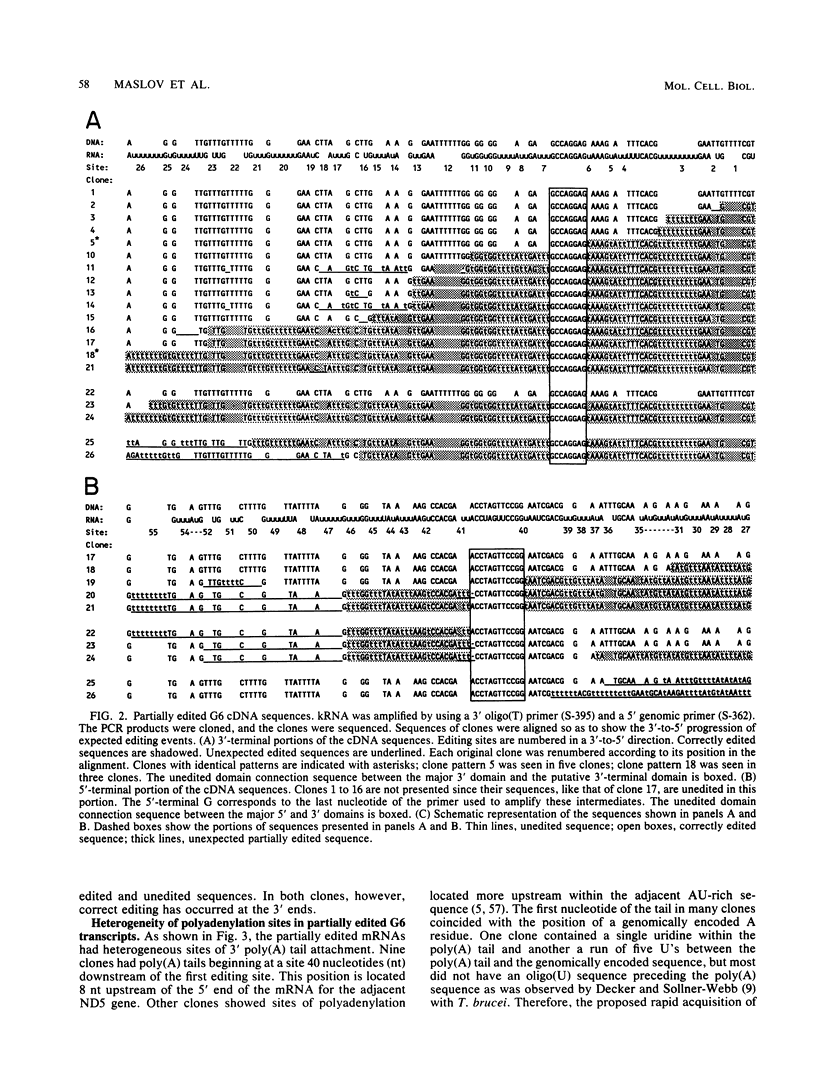
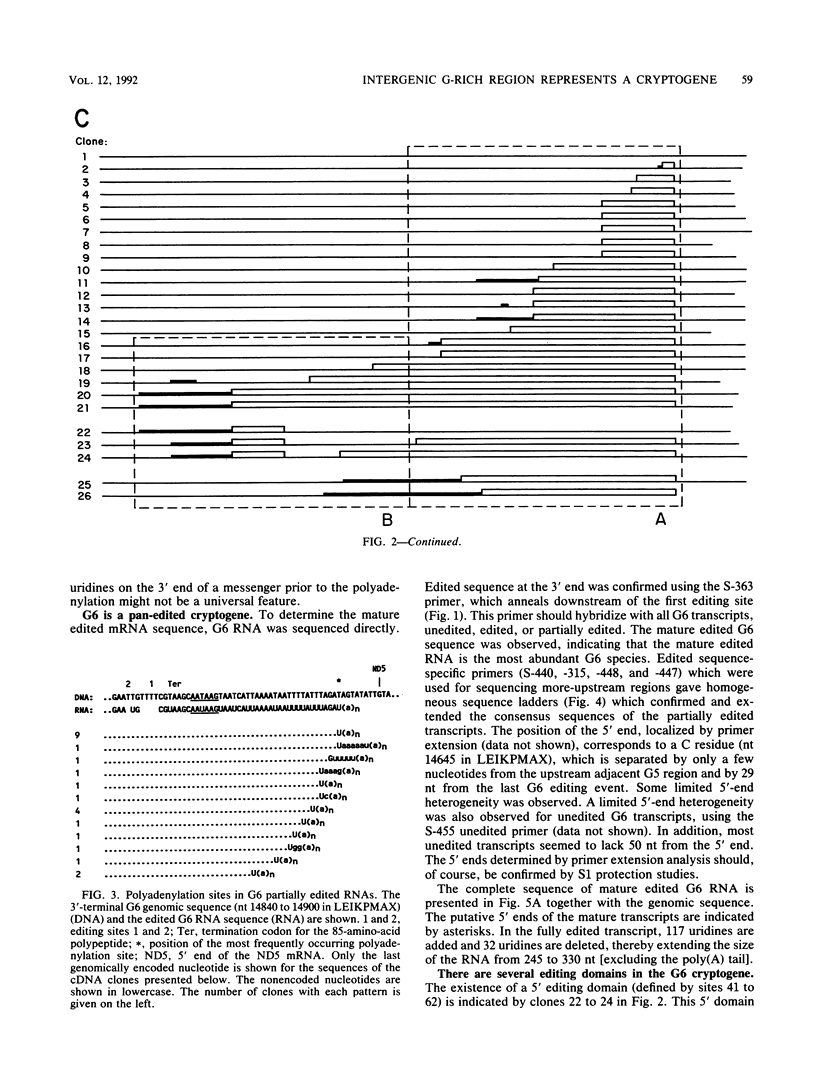
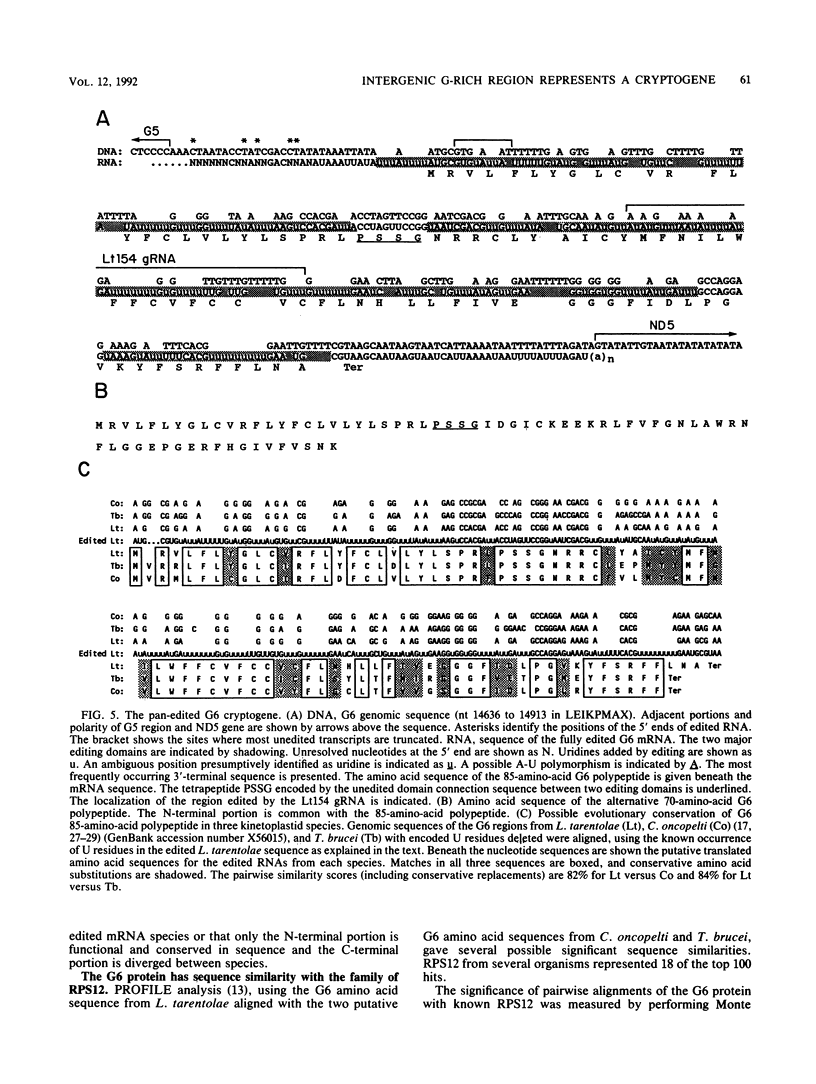
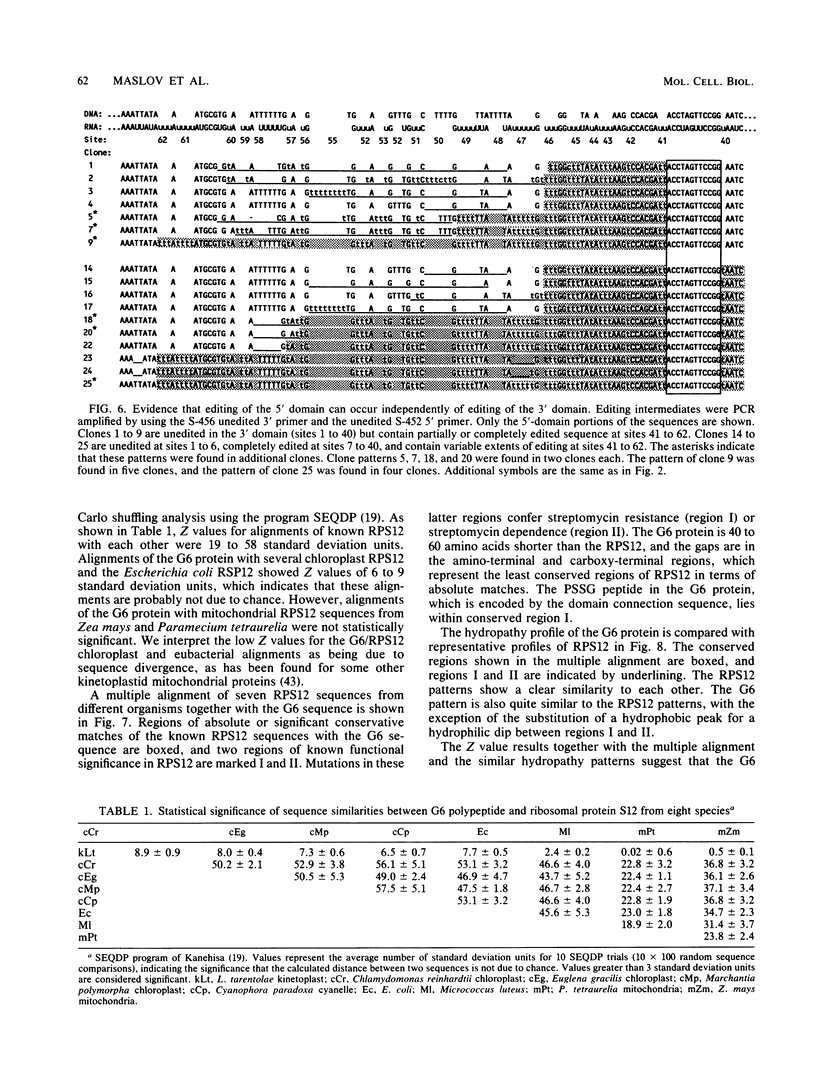
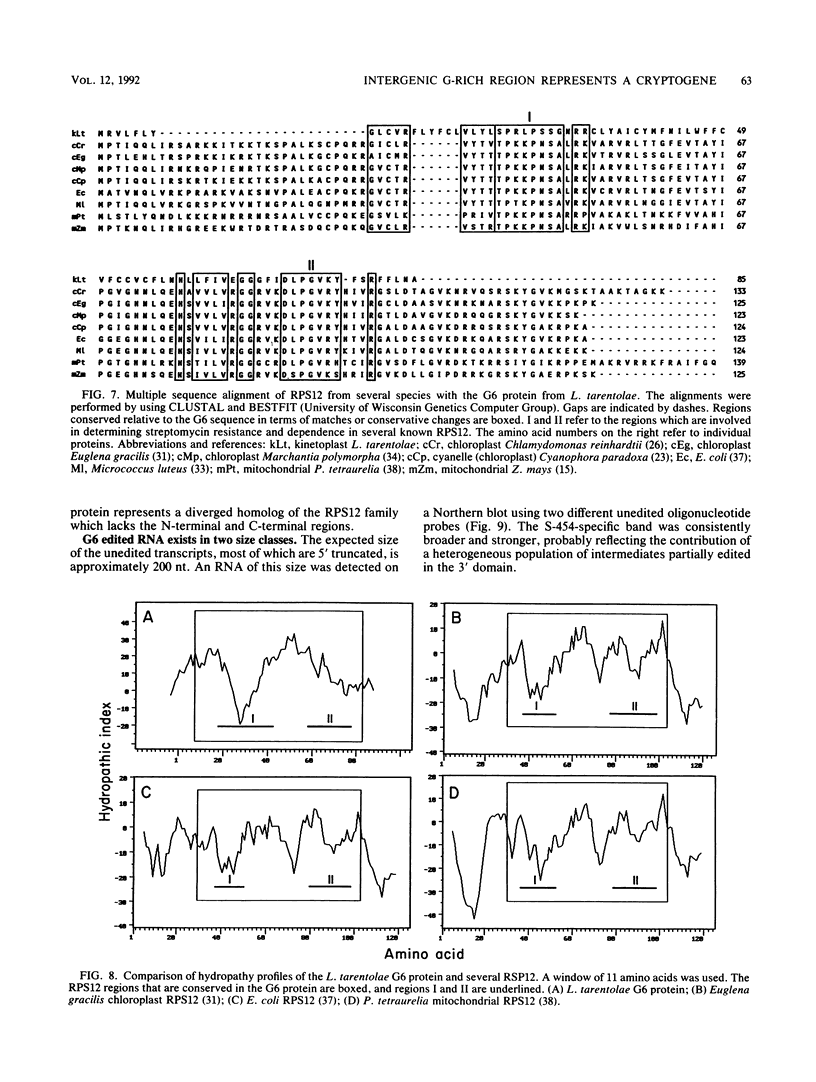
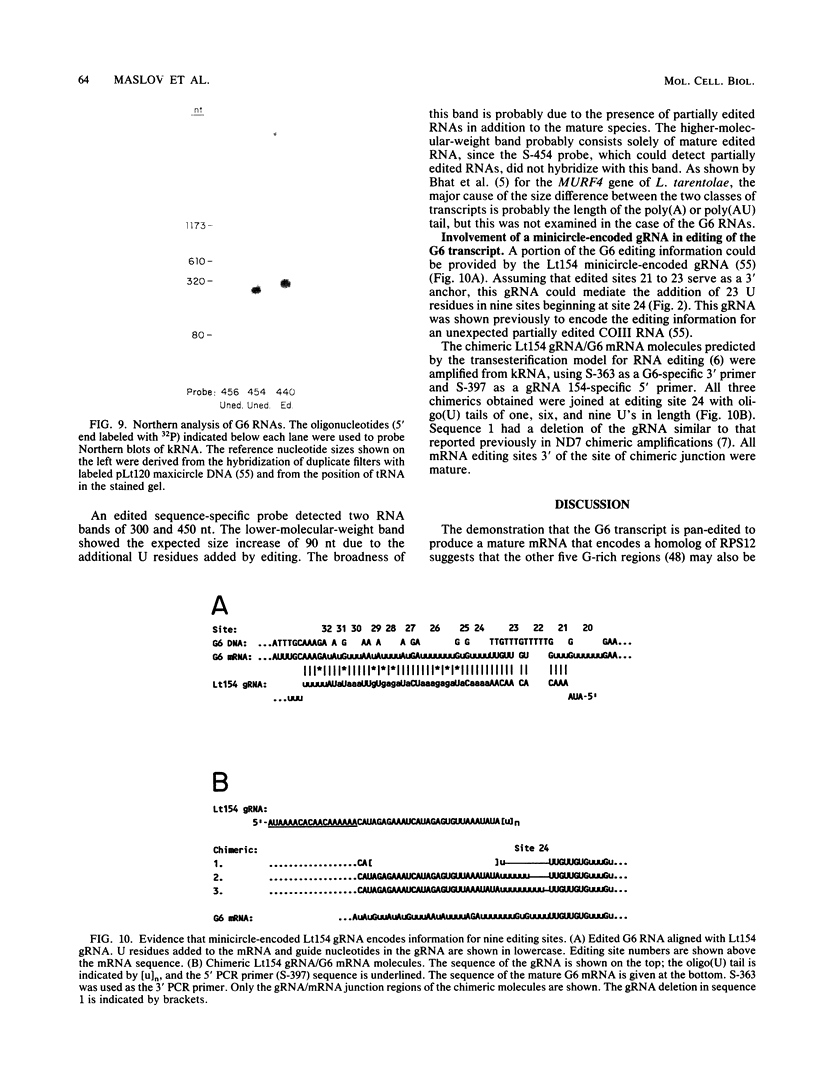
Six short G-rich intergenic regions in the maxicircle of Leishmania tarentolae are conserved in location and polarity in two other kinetoplastid species. We show here that G-rich region 6 (G6) represents a pan-edited cryptogene which contains at least two domains edited independently in a 3'-to-5' manner connected by short unedited regions. In the completely edited RNA, 117 uridines are added at 49 sites and 32 uridines are deleted at 13 sites, creating a translated 85-amino-acid polypeptide. Similar polypeptides are probably encoded by pan-edited G6 transcripts in two other species. The G6 polypeptide has significant sequence similarity to the family of S12 ribosomal proteins. A minicircle-encoded gRNA overlaps 12 editing sites in G6 mRNA, and chimeric gRNA/mRNA molecules were shown to exist, in agreement with the transesterification model for editing.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. M., Feagin J. E., Stuart K. Characterization of cytochrome c oxidase III transcripts that are edited only in the 3' region. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R. RNA-editing in trypanosome mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 1;1007(2):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat G. J., Koslowsky D. J., Feagin J. E., Smiley B. L., Stuart K. An extensively edited mitochondrial transcript in kinetoplastids encodes a protein homologous to ATPase subunit 6. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90199-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat G. J., Myler P. J., Stuart K. The two ATPase 6 mRNAs of Leishmania tarentolae differ at their 3' ends. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Oct;48(2):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90110-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum B., Bakalara N., Simpson L. A model for RNA editing in kinetoplastid mitochondria: "guide" RNA molecules transcribed from maxicircle DNA provide the edited information. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90735-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum B., Sturm N. R., Simpson A. M., Simpson L. Chimeric gRNA-mRNA molecules with oligo(U) tails covalently linked at sites of RNA editing suggest that U addition occurs by transesterification. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):543–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90087-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braly P., Simpson L., Kretzer F. Isolation of kinetoplast-mitochondrial complexes from Leishmania tarentolae. J Protozool. 1974 Nov;21(5):782–790. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker C. J., Sollner-Webb B. RNA editing involves indiscriminate U changes throughout precisely defined editing domains. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1001–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90065-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Abraham J. M., Stuart K. Extensive editing of the cytochrome c oxidase III transcript in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. The evolutionary origins of organelles. Trends Genet. 1989 Sep;5(9):294–299. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Lüthy R., Eisenberg D. Profile analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:146–159. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83011-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualberto J. M., Wintz H., Weil J. H., Grienenberger J. M. The genes coding for subunit 3 of NADH dehydrogenase and for ribosomal protein S12 are present in the wheat and maize mitochondrial genomes and are co-transcribed. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):118–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00331312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock K., Hajduk S. L. The mitochondrial tRNAs of Trypanosoma brucei are nuclear encoded. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19208–19215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horváth A., Maslov D. A., Kolesnikov A. A. The nucleotide sequence of the 12S ribosomal RNA gene from kinetoplast DNA of the protozoan Crithidia oncopelti. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2811–2811. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasmer D. P., Feagin J. E., Payne M., Stuart K. Variation of G-rich mitochondrial transcripts among stocks of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jan 15;22(2-3):259–272. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa M. I. Los Alamos sequence analysis package for nucleic acids and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):183–196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidane G. Z., Hughes D., Simpson L. Sequence heterogeneity and anomalous electrophoretic mobility of kinetoplast minicircle DNA from Leishmania tarentolae. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koslowsky D. J., Bhat G. J., Perrollaz A. L., Feagin J. E., Stuart K. The MURF3 gene of T. brucei contains multiple domains of extensive editing and is homologous to a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90265-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M., Götz M., Löffelhardt W. The cyanelle str operon from Cyanophora paradoxa: sequence analysis and phylogenetic implications. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Oct;15(4):561–573. doi: 10.1007/BF00017831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljas A. Comparative biochemistry and biophysics of ribosomal proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;124:103–136. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. Q., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Chloroplast ribosomal protein gene rps12 of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Wild-type sequence, mutation to streptomycin resistance and dependence, and function in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16100–16108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Stutz E. The genes for the ribosomal proteins S12 and S7 are clustered with the gene for the EF-Tu protein on the chloroplast genome of Euglena gracilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2851–2859. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhich M. L., Simpson L. Specific cleavage of kinetoplast minicircle DNA from Leishmania tarentolae by mung bean nuclease and identification of several additional minicircle sequence classes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5531–5556. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohama T., Yamao F., Muto A., Osawa S. Organization and codon usage of the streptomycin operon in Micrococcus luteus, a bacterium with a high genomic G + C content. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4770–4777. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4770-4777.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard V. W., Hajduk S. L. Trypanosoma equiperdum minicircles encode three distinct primary transcripts which exhibit guide RNA characteristics. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1668–1675. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard V. W., Rohrer S. P., Michelotti E. F., Hancock K., Hajduk S. L. Organization of minicircle genes for guide RNAs in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):783–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Nomura M. DNA sequences from the str operon of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4660–4666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Seilhamer J. J., Mahalingam R., Sable C. L., Venuti S. E., Cummings D. J. Nucleotide sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Paramecium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):173–180. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. M., Feagin J. E., Stuart K., Simpson L. Editing of kinetoplastid mitochondrial mRNAs by uridine addition and deletion generates conserved amino acid sequences and AUG initiation codons. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):401–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson A. M., Suyama Y., Dewes H., Campbell D. A., Simpson L. Kinetoplastid mitochondria contain functional tRNAs which are encoded in nuclear DNA and also contain small minicircle and maxicircle transcripts of unknown function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5427–5445. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L., Braly P. Synchronization of Leishmania tarentolae by hydroxyurea. J Protozool. 1970 Nov;17(4):511–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1970.tb04719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. Isolation of maxicircle component of kinetoplast DNA from hemoflagellate protozoa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. Kinetoplast DNA in trypanosomid flagellates. Int Rev Cytol. 1986;99:119–179. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61426-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L., Neckelmann N., de la Cruz V. F., Simpson A. M., Feagin J. E., Jasmer D. P., Stuart K. Comparison of the maxicircle (mitochondrial) genomes of Leishmania tarentolae and Trypanosoma brucei at the level of nucleotide sequence. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6182–6196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. RNA editing--a novel genetic phenomenon? Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):512–513. doi: 10.1126/science.1700474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L., Shaw J. RNA editing and the mitochondrial cryptogenes of kinetoplastid protozoa. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):355–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90911-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L., Simpson A. G. Kinetoplast RNA of Leishmania tarentolae. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. The mitochondrial genome of kinetoplastid protozoa: genomic organization, transcription, replication, and evolution. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:363–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Alonso R. A., Peattie D. A. Phylogenetic meaning of the kingdom concept: an unusual ribosomal RNA from Giardia lamblia. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2911720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Powers T., Changchien L. M., Noller H. F. Interaction of ribosomal proteins S5, S6, S11, S12, S18 and S21 with 16 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 20;201(4):683–695. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart K., Feagin J. E., Abraham J. M. RNA editing: the creation of nucleotide sequences in mRNA--a minireview. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm N. R., Simpson L. Kinetoplast DNA minicircles encode guide RNAs for editing of cytochrome oxidase subunit III mRNA. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90198-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm N. R., Simpson L. Partially edited mRNAs for cytochrome b and subunit III of cytochrome oxidase from Leishmania tarentolae mitochondria: RNA editing intermediates. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):871–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90197-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessier L. H., Keller M., Chan R. L., Fournier R., Weil J. H., Imbault P. Short leader sequences may be transferred from small RNAs to pre-mature mRNAs by trans-splicing in Euglena. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2621–2625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07804.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Spek H., Speijer D., Arts G. J., Van den Burg J., Van Steeg H., Sloof P., Benne R. RNA editing in transcripts of the mitochondrial genes of the insect trypanosome Crithidia fasciculata. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):257–262. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08103.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley R. D., Simpson L. Studies on kinetoplast DNA. 3. Kinetic complexity of kinetoplast and nuclear DNA from Leishmania tarentolae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 7;319(3):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Cruz V. F., Lake J. A., Simpson A. M., Simpson L. A minimal ribosomal RNA: sequence and secondary structure of the 9S kinetoplast ribosomal RNA from Leishmania tarentolae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1401–1405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]