Abstract
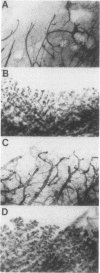
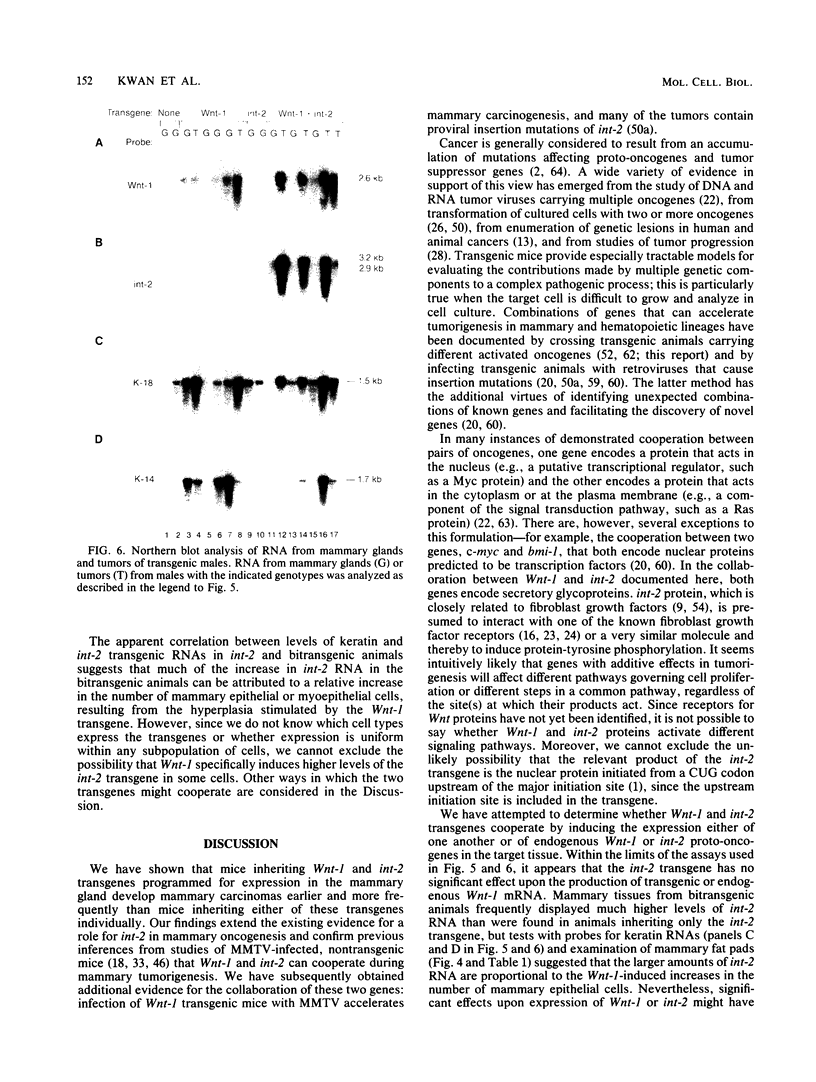
The Wnt-1 and int-2 proto-oncogenes are transcriptionally activated by mouse mammary tumor virus insertion mutations in virus-induced tumors and encode secretory glycoproteins. To determine whether these two genes can cooperate during carcinogenesis, we have crossed two previously characterized lines of transgenic mice to obtain bitransgenic animals carrying both Wnt-1 and int-2 transgenes under the control of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat. Mammary carcinomas appear earlier and with higher frequency in the bitransgenic animals, especially the males, than in either parental line. Nearly all bitransgenic males develop mammary neoplasms within 8 months of birth, whereas only 15% of Wnt-1 transgenic males and none of the int-2 transgenic males have tumors. In virgin bitransgenic females, tumors occur approximately 2 months earlier than in their Wnt-1 transgenic siblings; int-2 transgenic females rarely exhibit tumors. Preneoplastic glands from the bitransgenic animals of either sex demonstrate pronounced epithelial hyperplasia similar to that seen in Wnt-1 transgenic virgin females and males, and both transgenes are expressed in the hyperplastic glands and mammary tumors. RNA from the int-2 transgene is more abundant in mammary glands from bitransgenic animals than from int-2 transgenic animals; the increase is associated with high levels of RNA specific for keratin genes 14 and 18, suggesting that Wnt-1-induced epithelial hyperplasia is responsible for the observed increase in expression of the int-2 transgene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acland P., Dixon M., Peters G., Dickson C. Subcellular fate of the int-2 oncoprotein is determined by choice of initiation codon. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):662–665. doi: 10.1038/343662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard L., Lamarre L., Tremblay P. J., Jolicoeur P. Stochastic appearance of mammary tumors in transgenic mice carrying the MMTV/c-neu oncogene. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):931–936. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90331-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley R. S., Brown A. M. The proto-oncogene int-1 encodes a secreted protein associated with the extracellular matrix. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1569–1575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Wildin R. S., Prendergast T. J., Varmus H. E. A retrovirus vector expressing the putative mammary oncogene int-1 causes partial transformation of a mammary epithelial cell line. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90699-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M. Transgenic mice and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:25–48. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Peters G. Potential oncogene product related to growth factors. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):833–833. doi: 10.1038/326833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Smith R., Brookes S., Peters G. Proviral insertions within the int-2 gene can generate multiple anomalous transcripts but leave the protein-coding domain intact. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):784–793. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.784-793.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Smith R., Brookes S., Peters G. Tumorigenesis by mouse mammary tumor virus: proviral activation of a cellular gene in the common integration region int-2. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M., Deed R., Acland P., Moore R., Whyte A., Peters G., Dickson C. Detection and characterization of the fibroblast growth factor-related oncoprotein INT-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4896–4902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Shackleford G. M., Brown A. M., Sanders G. S., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence and expression in vitro of cDNA derived from mRNA of int-1, a provirally activated mouse mammary oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3337–3344. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallahan D., Callahan R. Mammary tumorigenesis in feral mice: identification of a new int locus in mouse mammary tumor virus (Czech II)-induced mammary tumors. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):66–74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.66-74.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb M., Deed R., MacAllan D., Walther W., Dickson C., Peters G. Cell transformation by Int-2--a member of the fibroblast growth factor family. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb M. The fibroblast growth factor family. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Sep;1(9):439–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. A., Jackson D. P., Percy D. H., Morris V. L. Activation of int-1 and int-2 loci in GRf mammary tumors. Virology. 1986 Oct 30;154(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90453-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Dissecting multistep tumorigenesis in transgenic mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:479–519. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt Y., Alexander W. S., Barri G., Klinken S. P., Adams J. M. Novel zinc finger gene implicated as myc collaborator by retrovirally accelerated lymphomagenesis in E mu-myc transgenic mice. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90383-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Cooperation between oncogenes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):249–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90637-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lee P. L., Lu J., Williams L. T. Diverse forms of a receptor for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4728–4736. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan K., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T., Hayman M. J. Isolation of an additional member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, FGFR-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Pattengale P. K., Kuo A., Stewart T. A., Leder P. Consequences of widespread deregulation of the c-myc gene in transgenic mice: multiple neoplasms and normal development. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):485–495. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90642-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangues R., Seidman I., Pellicer A., Gordon J. W. Tumorigenesis and male sterility in transgenic mice expressing a MMTV/N-ras oncogene. Oncogene. 1990 Oct;5(10):1491–1497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Halter S. A., Holt J. T., Hogan B. L., Coffey R. J. Development of mammary hyperplasia and neoplasia in MMTV-TGF alpha transgenic mice. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1147–1155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90077-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mester J., Wagenaar E., Sluyser M., Nusse R. Activation of int-1 and int-2 mammary oncogenes in hormone-dependent and -independent mammary tumors of GR mice. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1073–1078. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1073-1078.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Sinn E., Pattengale P. K., Wallace R., Leder P. Single-step induction of mammary adenocarcinoma in transgenic mice bearing the activated c-neu oncogene. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Brown A., Papkoff J., Scambler P., Shackleford G., McMahon A., Moon R., Varmus H. A new nomenclature for int-1 and related genes: the Wnt gene family. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):231–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90633-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Theunissen H., Wagenaar E., Rijsewijk F., Gennissen A., Otte A., Schuuring E., van Ooyen A. The Wnt-1 (int-1) oncogene promoter and its mechanism of activation by insertion of proviral DNA of the mouse mammary tumor virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4170–4179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., van Ooyen A., Cox D., Fung Y. K., Varmus H. Mode of proviral activation of a putative mammary oncogene (int-1) on mouse chromosome 15. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):131–136. doi: 10.1038/307131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Moreadith R. W., Leder P. Binary system for regulating transgene expression in mice: targeting int-2 gene expression with yeast GAL4/UAS control elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):698–702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Brown A. M., Varmus H. E. The int-1 proto-oncogene products are glycoproteins that appear to enter the secretory pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3978–3984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Schryver B. Secreted int-1 protein is associated with the cell surface. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2723–2730. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Brookes S., Smith R., Dickson C. Tumorigenesis by mouse mammary tumor virus: evidence for a common region for provirus integration in mammary tumors. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Brookes S., Smith R., Placzek M., Dickson C. The mouse homolog of the hst/k-FGF gene is adjacent to int-2 and is activated by proviral insertion in some virally induced mammary tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5678–5682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Lee A. E., Dickson C. Concerted activation of two potential proto-oncogenes in carcinomas induced by mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):628–631. doi: 10.1038/320628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijsewijk F., van Deemter L., Wagenaar E., Sonnenberg A., Nusse R. Transfection of the int-1 mammary oncogene in cuboidal RAC mammary cell line results in morphological transformation and tumorigenicity. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):127–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04729.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelink H., Wagenaar E., Lopes da Silva S., Nusse R. Wnt-3, a gene activated by proviral insertion in mouse mammary tumors, is homologous to int-1/Wnt-1 and is normally expressed in mouse embryos and adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Krieg T. M., Mehrel T., Cheng C. K., Yuspa S. H. Transcriptional control of high molecular weight keratin gene expression in multistage mouse skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 1;48(11):3245–3252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P. A., Trevor K., Oshima R. G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the Endo B cytokeratin expressed in preimplantation mouse embryos. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):538–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinn E., Muller W., Pattengale P., Tepler I., Wallace R., Leder P. Coexpression of MMTV/v-Ha-ras and MMTV/c-myc genes in transgenic mice: synergistic action of oncogenes in vivo. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. H., Mehrel T., Roop D. R. Differential keratin gene expression in developing, differentiating, preneoplastic, and neoplastic mouse mammary epithelium. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Apr;1(4):161–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Peters G., Dickson C. Multiple RNAs expressed from the int-2 gene in mouse embryonal carcinoma cell lines encode a protein with homology to fibroblast growth factors. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1013–1022. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Pattengale P. K., Leder P. Spontaneous mammary adenocarcinomas in transgenic mice that carry and express MTV/myc fusion genes. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay P. J., Pothier F., Hoang T., Tremblay G., Brownstein S., Liszauer A., Jolicoeur P. Transgenic mice carrying the mouse mammary tumor virus ras fusion gene: distinct effects in various tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):854–859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto A. S., Grosschedl R., Guzman R. C., Parslow T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the int-1 gene in transgenic mice is associated with mammary gland hyperplasia and adenocarcinomas in male and female mice. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek S., van Lohuizen M., van der Valk M., Domen J., Kraal G., Berns A. Mice bearing the E mu-myc and E mu-pim-1 transgenes develop pre-B-cell leukemia prenatally. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1176–1179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The action of oncogenes in the cytoplasm and nucleus. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):770–776. doi: 10.1126/science.2997917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lohuizen M., Verbeek S., Krimpenfort P., Domen J., Saris C., Radaszkiewicz T., Berns A. Predisposition to lymphomagenesis in pim-1 transgenic mice: cooperation with c-myc and N-myc in murine leukemia virus-induced tumors. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90589-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lohuizen M., Verbeek S., Scheijen B., Wientjens E., van der Gulden H., Berns A. Identification of cooperating oncogenes in E mu-myc transgenic mice by provirus tagging. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):737–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90382-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ooyen A., Nusse R. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the putative mammary oncogene int-1; proviral insertions leave the protein-encoding domain intact. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]