Abstract
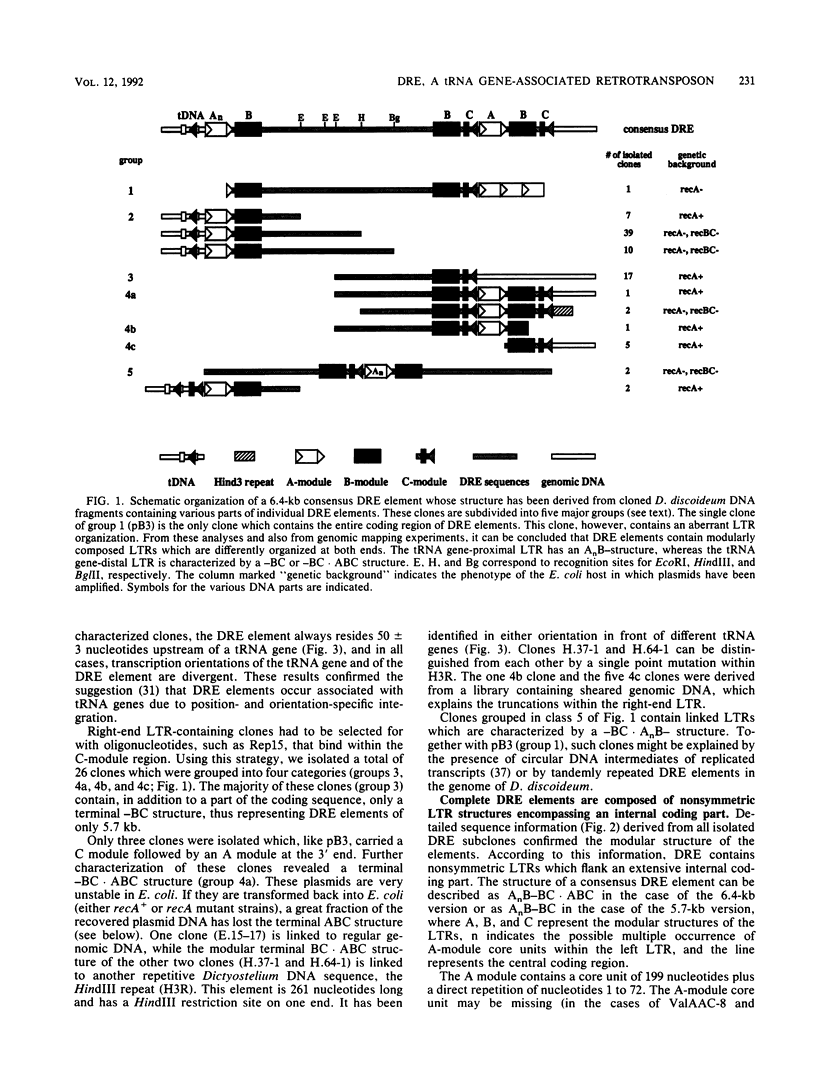
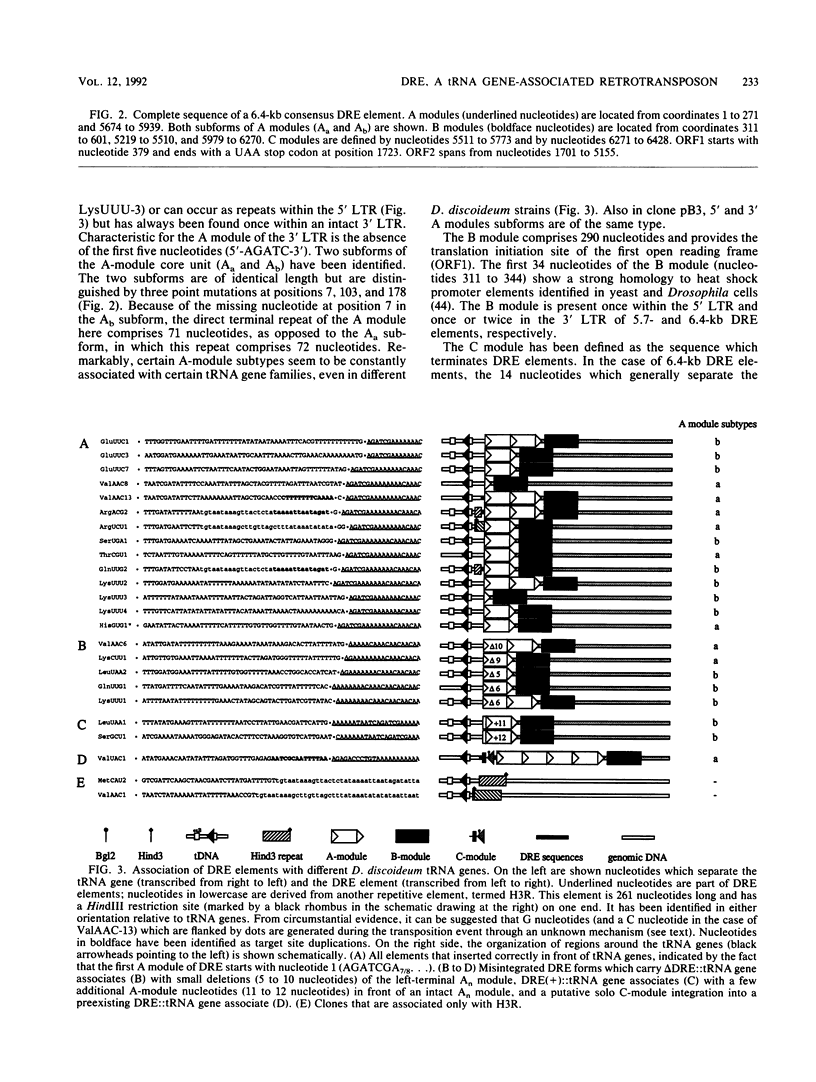
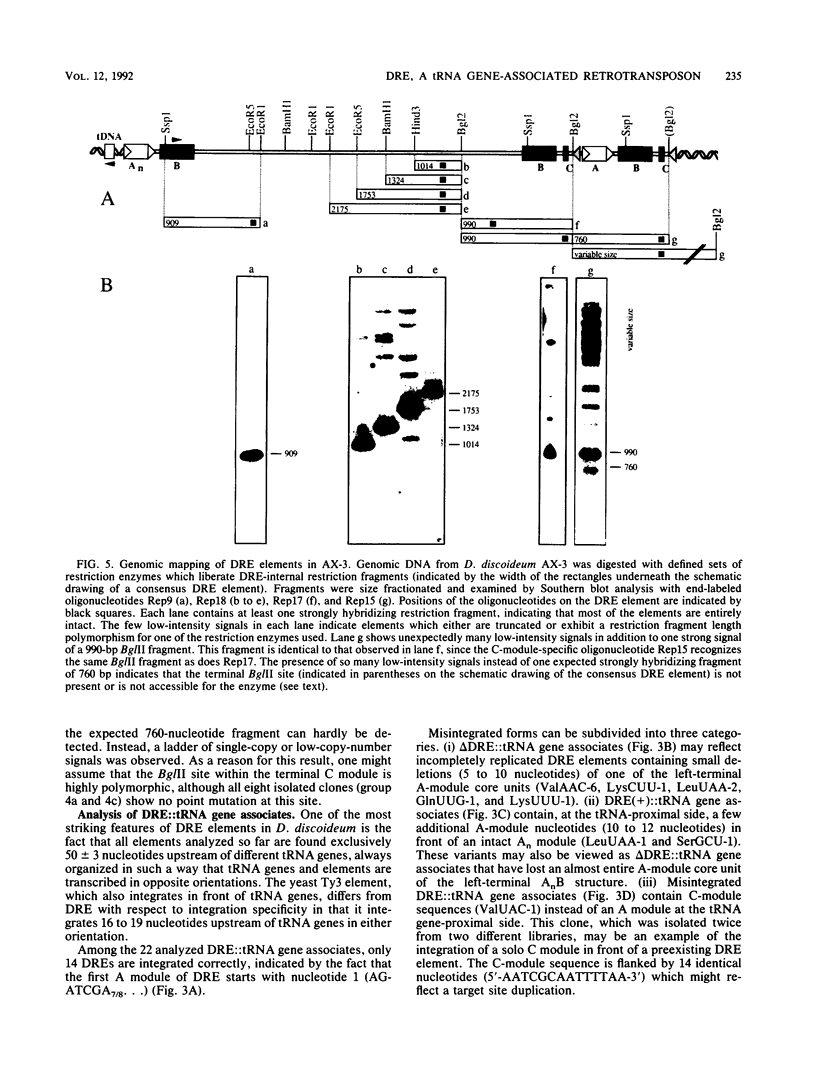
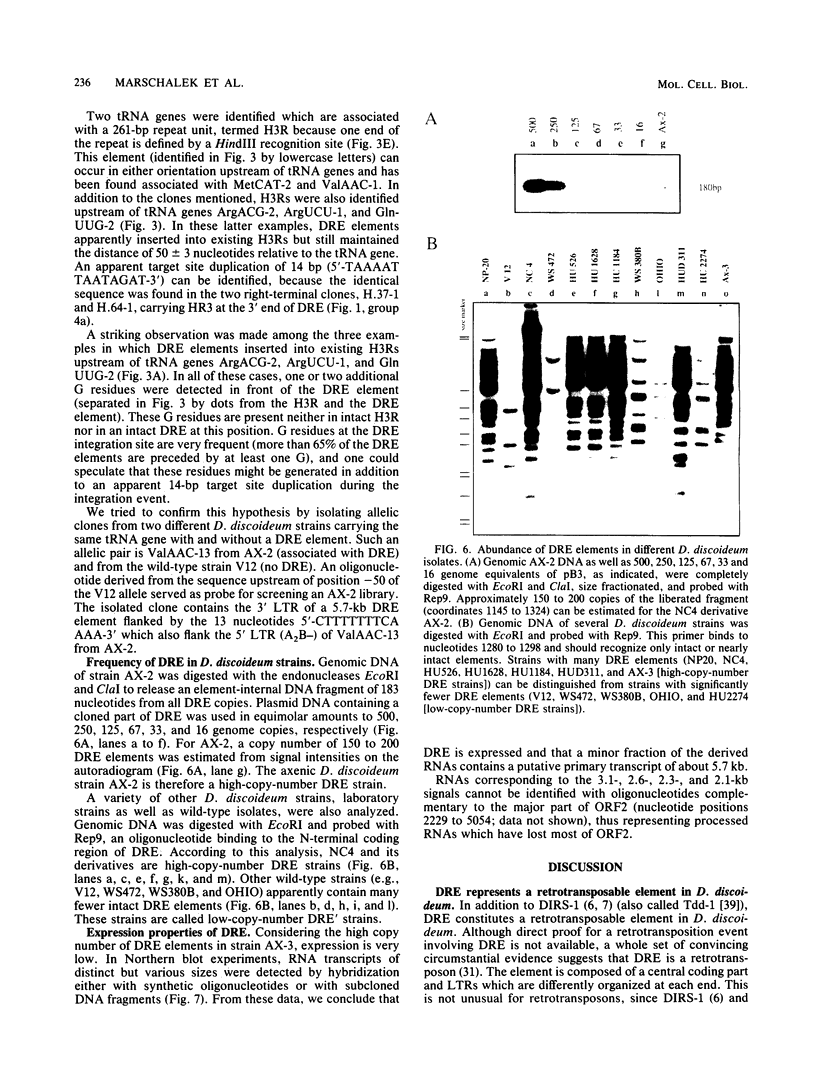
Different Dictyostelium discoideum strains contain between 2 and 200 copies of a retrotransposable element termed DRE (Dictyostelium repetitive element). From the analysis of more than 50 elements, it can be concluded that DRE elements always occur 50 +/- 3 nucleotides upstream of tRNA genes. All analyzed clones contain DRE in a constant orientation relative to the tRNA gene, implying orientation specificity as well as position specificity. DRE contains two open reading frames which are flanked by nonidentical terminal repeats. Long terminal repeats (LTRs) are composed of three distinct modules, called A, B, and C. The tRNA gene-proximal LTR is characterized by one or multiple A modules followed by a single B module (AnB). With respect to the distal LTR, two different subforms of DRE have been isolated. The majority of isolated clones contains a distal LTR composed of a B module followed by a C module (BC), whereas the distal LTR of the other subform contains a consecutive array of a B module, a C module, a slightly altered A module, another B module, and another C module (BC.ABC). Full-length as well as smaller transcripts from DRE elements have been detected, but in comparison with the high copy number in D. discoideum strains derived from the wild-type strain NC4, transcription is rather poor.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksoy S., Williams S., Chang S., Richards F. F. SLACS retrotransposon from Trypanosoma brucei gambiense is similar to mammalian LINEs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):785–792. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belcourt M. F., Farabaugh P. J. Ribosomal frameshifting in the yeast retrotransposon Ty: tRNAs induce slippage on a 7 nucleotide minimal site. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):339–352. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90371-K. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Corces V. G. Transcription and reverse transcription of retrotransposons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:403–434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke W. D., Calalang C. C., Eickbush T. H. The site-specific ribosomal insertion element type II of Bombyx mori (R2Bm) contains the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2221–2230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappello J., Handelsman K., Cohen S. M., Lodish H. F. Structure and regulated transcription of DIRS-1: an apparent retrotransposon of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:759–767. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappello J., Handelsman K., Lodish H. F. Sequence of Dictyostelium DIRS-1: an apparent retrotransposon with inverted terminal repeats and an internal circle junction sequence. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalker D. L., Sandmeyer S. B. Transfer RNA genes are genomic targets for de Novo transposition of the yeast retrotransposon Ty3. Genetics. 1990 Dec;126(4):837–850. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.4.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Bilanchone V. W., Haywood L. J., Dildine S. L., Sandmeyer S. B. A yeast sigma composite element, TY3, has properties of a retrotransposon. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1413–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Amon-Böhm E., Bertling W., Marschalek R., Nerke K. A family of non-allelic tRNA(ValGUU) genes from the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90502-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Brechner T., Marschalek R., Amon-Böhm E., Welker D. L. tRNAGlu(GAA) genes from the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. DNA. 1989 Apr;8(3):193–204. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R., Meselson M. Long terminal repeat nucleotide sequence and specific insertion of the gypsy transposon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4462–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandbastien M. A., Spielmann A., Caboche M. Tnt1, a mobile retroviral-like transposable element of tobacco isolated by plant cell genetics. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):376–380. doi: 10.1038/337376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen L. J., Chalker D. L., Sandmeyer S. B. Ty3, a yeast retrotransposon associated with tRNA genes, has homology to animal retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5245–5256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D., Oroszlan S. The where, what and how of ribosomal frameshifting in retroviral protein synthesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 May;15(5):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90159-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Insertion of a movable genetic element, 297, into the T-A-T-A box for the H3 histone gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4143–4147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Complete nucleotide sequence and genome organization of a Drosophila transposable genetic element, 297. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 15;154(2):417–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Sequence-specific insertion of the Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):332–333. doi: 10.1038/310332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Madhani H. D., Masiarz F. R., Varmus H. E. Signals for ribosomal frameshifting in the Rous sarcoma virus gag-pol region. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90031-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the Rous sarcoma virus pol gene by ribosomal frameshifting. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1237–1242. doi: 10.1126/science.2416054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Riggs D. L., Negri R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription factor IIIB generates extended DNA interactions in RNA polymerase III transcription complexes on tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2551–2566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., ole-MoiYoi O. K., Young J. R. Ingi, a 5.2-kb dispersed sequence element from Trypanosoma brucei that carries half of a smaller mobile element at either end and has homology with mammalian LINEs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino Y., Beier H., Akita N., Nishimura S. Natural UAG suppressor glutamine tRNA is elevated in mouse cells infected with Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2668–2672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marschalek R., Borschet G., Dingermann T. Genomic organization of the transposable element Tdd-3 from Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5751–5757. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marschalek R., Brechner T., Amon-Böhm E., Dingermann T. Transfer RNA genes: landmarks for integration of mobile genetic elements in Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1989 Jun 23;244(4911):1493–1496. doi: 10.1126/science.2567533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Fulton S. M., Dobson M. J., Wilson W., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. A retrovirus-like strategy for expression of a fusion protein encoded by yeast transposon Ty1. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):243–246. doi: 10.1038/313243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Lang B. F. Mitochondrial class II introns encode proteins related to the reverse transcriptases of retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):641–643. doi: 10.1038/316641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Rubin G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. Circles with two tandem LTRs are precursors to integrated retrovirus DNA. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):673–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Firtel R. A. Genomic instability and mobile genetic elements in regions surrounding two discoidin I genes of Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):671–680. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E., Sivertsen A., Firtel R. A. An unusual transposon encoding heat shock inducible and developmentally regulated transcripts in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K., Kugimiya W., Matsuo Y., Inouye S., Yoshioka K., Yuki S. Identification of the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme in a transposable genetic element in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):659–661. doi: 10.1038/312659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeyer S. B., Bilanchone V. W., Clark D. J., Morcos P., Carle G. F., Brodeur G. M. Sigma elements are position-specific for many different yeast tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1499–1515. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeyer S. B., Hansen L. J., Chalker D. L. Integration specificity of retrotransposons and retroviruses. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:491–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuite M. F., Bossier P., Fitch I. T. A highly conserved sequence in yeast heat shock gene promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11845–11845. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voytas D. F., Ausubel F. M. A copia-like transposable element family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):242–244. doi: 10.1038/336242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmington J. R., Waring R. B., Newlon C. S., Indge K. J., Oliver S. G. Nucleotide sequence characterization of Ty 1-17, a class II transposon from yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6679–6693. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts D. J., Ashworth J. M. Growth of myxameobae of the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum in axenic culture. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1190171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker D. L., Williams K. L. A genetic map of Dictyostelium discoideum based on mitotic recombination. Genetics. 1982 Dec;102(4):691–710. doi: 10.1093/genetics/102.4.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. The site-specific ribosomal DNA insertion element R1Bm belongs to a class of non-long-terminal-repeat retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):114–123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki S., Inouye S., Ishimaru S., Saigo K. Nucleotide sequence characterization of a Drosophila retrotransposon, 412. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 15;158(2):403–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]