Abstract
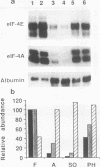
Mammalian liver development is accompanied by a transition from rapid growth in the fetus to a quiescent state in the adult. However, extensive proliferation can be induced in the adult liver by partial hepatectomy. In this study, we examined the regulation of ribosomal protein (rp) gene expression in the developing and regenerating rat liver. Our results indicate that the translation of rp mRNAs is selectively repressed by about 70% upon development from fetal to adult life, as illustrated by the decrease in ribosomal loading. In addition, the relative abundance of these mRNAs, like that of several other, but not all, housekeeping mRNAs, declines during development through a posttranscriptional mechanism. When liver cells commence growth following partial hepatectomy, translation of rp mRNAs is resumed to near-maximal capacity, as judged by their very efficient recruitment into polysomes. The concomitant increase in the abundance rp mRNAs under these circumstances is achieved by a posttranscriptional mechanism. The apparent fluctuations in the translation efficiency of rp mRNAs are accompanied by parallel changes in the expression of the genes encoding the initiation factors eIF-4E and eIF-4A. Our results indicate that selective translational control of rp mRNAs in mammals is not confined to manipulated cells in culture but constitutes an important regulatory mechanism operating in vivo in the course of liver development and regeneration.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal M. G., Bowman L. H. Transcriptional and translational regulation of ribosomal protein formation during mouse myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4868–4875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- All-Robyn J. A., Brown N., Otaka E., Liebman S. W. Sequence and functional similarity between a yeast ribosomal protein and the Escherichia coli S5 ram protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6544–6553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amaldi F., Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Pierandrei-Amaldi P. Expression of ribosomal protein genes and regulation of ribosome biosynthesis in Xenopus development. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 May;14(5):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama Y., Chan Y. L., Meyuhas O., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein L18a. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):242–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81344-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz N., Munro H. N. Both subunits of rat liver ferritin are regulated at a translational level by iron induction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):915–927. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker H., Stanners C. P., Kudlow J. E. Control of macromolecular synthesis in proliferating and resting Syrian hamster cells in monolayer culture. II. Ribosome complement in resting and early G1 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Feb;77(1):43–50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benvenisty N., Reshef L. Developmental acquisition of DNase I sensitivity of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1132–1136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman L. H., Rabin B., Schlessinger D. Multiple ribosomal RNA cleavage pathways in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4951–4966. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Fragapane P., Annesi F., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F., Beccari E. Expression of two Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes in injected frog oocytes. A specific splicing block interferes with the L1 RNA maturation. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):987–1005. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Lin A., McNally J., Peleg D., Meyuhas O., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein L19. A determination from the sequence of nucleotides in a cDNA and from the sequence of amino acids in the protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1111–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Lin A., McNally J., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein L5. A comparison of the sequence of amino acids in the proteins that interact with 5 S rRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12879–12886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri S., Lieberman I. Control of ribosome syntesis in normal and regenerating liver. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):29–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabeva M. D., Dudov K. P. Transcriptional control of ribosome production in regenerating rat liver. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 15;208(1):101–108. doi: 10.1042/bj2080101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Dabeva M. D. Post-transcriptional regulation of ribosome formation in the nucleus of regenerating rat liver. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 15;210(1):183–192. doi: 10.1042/bj2100183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. The gene family encoding the mouse ribosomal protein L32 contains a uniquely expressed intron-containing gene and an unmutated processed gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W. Regulated phosphorylation and low abundance of HeLa cell initiation factor eIF-4F suggest a role in translational control. Heat shock effects on eIF-4F. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):380–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson C. P. Regulation of the synthesis and the stability of ribosomal RNA during contact inhibition of growth. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):101–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio232101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faliks D., Meyuhas O. Coordinate regulation of ribosomal protein mRNA level in regenerating rat liver. Study with the corresponding mouse cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):789–801. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flusser G., Ginzburg V., Meyuhas O. Glucocorticoids induce transcription of ribosomal protein genes in rat liver. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;64(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Chung E. Y., Darnell J. E., Jr Gene expression during liver regeneration. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):37–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90305-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg I., Teichman A., Dodemont H. J., Behar L., Littauer U. Z. Regulation of three beta-tubulin mRNAs during rat brain development. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3667–3673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O., Federman M., Knox W. E. Cytomorphometry of developing rat liver and its application to enzymic differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Feb;52(2):261–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt F., Paul D., Grummt I. Regulation of ATP pools, rRNA and DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells in response to serum or hypoxanthine. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):7–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond M. L., Merrick W., Bowman L. H. Sequences mediating the translation of mouse S16 ribosomal protein mRNA during myoblast differentiation and in vitro and possible control points for the in vitro translation. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1723–1736. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller D. L., Gianola K. M., Leinwand L. A. A highly conserved mouse gene with a propensity to form pseudogenes in mammals. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2797–2803. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs F. A., Bird R. C., Sells B. H. Differentiation of rat myoblasts. Regulation of turnover of ribosomal proteins and their mRNAs. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jul 15;150(2):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo M., Pelletier J., Edery I., Nielsen P. J., Sonenberg N. Multiple mRNAs encode the murine translation initiation factor eIF-4E. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10446–10451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Levis R., Abelson H. T., Green H., Penman S. Changes in RNA in relation to growth of the fibroblast. IV. Alterations in theproduction and processing of mRNA and rRNA in resting and growing cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Dec;71(3):933–938. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.3.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar R. L., Rychlik W., White M. W., Rhoads R. E., Morris D. R. Simultaneous cytoplasmic redistribution of ribosomal protein L32 mRNA and phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E after mitogenic stimulation of Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3619–3622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Hamilton R., Hanson R. W., Tilghman S. M., Taylor J. M. Construction and cloning of rat albumin structural gene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4370–4374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. cis-trans models for post-transcriptional gene regulation. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):870–872. doi: 10.1126/science.2683086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauter K. S., Soeiro R., Nadal-Ginard B. Unco-ordinate regulation of ribosomal RNA and ribosomal protein synthesis during L6E9 myoblast differentiation. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 15;142(2):145–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarca M. J., Wassarman P. M. Relationship between rates of synthesis and intracellular distribution of ribosomal proteins during oogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1984 Apr;102(2):525–530. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazaris-Karatzas A., Montine K. S., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a eukaryotic initiation factor subunit that binds to mRNA 5' cap. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):544–547. doi: 10.1038/345544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S., Avni D., Hariharan N., Perry R. P., Meyuhas O. Oligopyrimidine tract at the 5' end of mammalian ribosomal protein mRNAs is required for their translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Chan Y. L., McNally J., Peleg D., Meyuhas O., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein L7. The presence near the amino terminus of L7 of five tandem repeats of a sequence of 12 amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12665–12671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager W. H. Control of ribosomal protein gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 25;949(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariottini P., Amaldi F. The 5' untranslated region of mRNA for ribosomal protein S19 is involved in its translational regulation during Xenopus development. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):816–822. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J. C., Green H. Regulation of RNA synthesis in fibroblasts during transition from resting to growing state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2819–2822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKELLAR M. The postnatal growth and mitotic activity of the liver of the albino rat. Am J Anat. 1949 Sep;85(2):263-307, incl 6 pl. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000850205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisner H., Loose D. S., Hanson R. W. Effect of hormones on transcription of the gene for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) in rat kidney. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):421–425. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melvin W. T., Keir H. M. Onset of ribosome degradation during cessation of growth in BHK-21/C13 cells. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):933–941. doi: 10.1042/bj1760933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Baldin V., Bouche G., Amalric F. Glucocorticoids repress ribosome biosynthesis in lymphosarcoma cells by affecting gene expression at the level of transcription, posttranscription and translation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 24;1049(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90082-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Construction and identification of cDNA clones for mouse ribosomal proteins: application for the study of r-protein gene expression. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):113–129. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Thompson E. A., Jr, Perry R. P. Glucocorticoids selectively inhibit translation of ribosomal protein mRNAs in P1798 lymphosarcoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2691–2699. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Caravatti M., Robert B., Cohen A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Gros F., Buckingham M. E. Mouse actin messenger RNAs. Construction and characterization of a recombinant plasmid molecule containing a complementary DNA transcript of mouse alpha-actin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohn K. L., Laz T. M., Hsu J. C., Melby A. E., Bravo R., Taub R. The immediate-early growth response in regenerating liver and insulin-stimulated H-35 cells: comparison with serum-stimulated 3T3 cells and identification of 41 novel immediate-early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y. I., Ogata K. Stimulation of the synthesis of ribosomal proteins in regenerating rat liver with special reference to the increase in the amounts of effective mRNAs for ribosomal proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):323–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., McMaster G. K., Trachsel H. Cloning of eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor genes: isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding factor eIF-4A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6867–6880. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolov E. H., Nankova B. B., Dabeva M. D. Activated ribosomal RNA synthesis in regenerated rat liver upon inhibition of protein synthesis. Mol Biol Rep. 1991 Feb;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00369900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER I. T., BLUMER W. F., WITHAM I. J. FREE RIBOSOMES DURING MATURATION OF RAT LIVER. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1963 Sep;10:33–38. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(63)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Yen T. S., Wang Y. F., Kam W. K., Rutter W. J. Cloning and characterization of a human ribosomal protein gene with enhanced expression in fetal and neoplastic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8919–8934. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panduro A., Shalaby F., Shafritz D. A. Changing patterns of transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of liver-specific gene expression during rat development. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1172–1182. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Amaldi F. Ribosomal protein production in normal and anucleolate Xenopus embryos: regulation at the posttranscriptional and translational levels. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):317–323. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80127-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. J., Friedman J. M., Oulette A. J., Krauter K. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of specific messenger RNAs in adult and embryonic liver. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):21–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich B. E., Steitz J. A. Human acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins P0, P1, and P2: analysis of cDNA clones, in vitro synthesis, and assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4065–4074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Pittet A. C. Two promoters of different strengths control the transcription of the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-1a in the parotid gland and the liver. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Tosi M., Pittet A. C., Fabiani L., Wellauer P. K. Tissue-specific expression of mouse alpha-amylase genes. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 5;142(1):93–116. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. H., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Rapid size determination of mRNAs complementary to cloned DNA sequences: plaque and colony hybrid-selection of cDNAs. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Dafni N., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Groner Y. Nucleotide sequence and expression of human chromosome 21-encoded superoxide dismutase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5465–5469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Cap-binding proteins of eukaryotic messenger RNA: functions in initiation and control of translation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:173–207. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanners C. P., Becker H. Control of macromolecular synthesis in proliferating and resting Syrian hamster cells in monolayer culture. I. Ribosome function. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Feb;77(1):31–42. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Belayew A. Transcriptional control of the murine albumin/alpha-fetoprotein locus during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5254–5257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurugi K., Morita T., Ogata K. Studies on the metabolism of ribosomal structural proteins of regenerating rat liver. Sites of biosynthesis of structural proteins of large subunit and of their assembly with RNA moiety. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):117–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tushinski R. J., Warner J. R. Ribosomal proteins are synthesized preferentially in cells commencing growth. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jul;112(1):128–135. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Vitto L., Rubnitz J. Co-amplification of rRNA genes with CAD genes in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant Syrian hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2066–2075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden W. E., Godefroy-Colburn T., Thach R. E. The role of mRNA competition in regulating translation. I. Demonstration of competition in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11739–11746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. J. Ribosomal RNA turnover in contact inhibited cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 12;235(54):58–61. doi: 10.1038/newbio235058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann L. M., Perry R. P. Characterization of the expressed gene and several processed pseudogenes for the mouse ribosomal protein L30 gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2518–2528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S., Sameshima M., Liebhaber S. A., Schlessinger D. Regulation of ribosomal ribonucleic acid levels in growing, 3H-arrested, and crisis-phase WI-38 human diploid fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3484–3490. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo-Warren H., Monahan J. E., Short J., Short H., Bruzel A., Wynshaw-Boris A., Meisner H. M., Samols D., Hanson R. W. Isolation and characterization of the gene coding for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) from the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3656–3660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]