Abstract
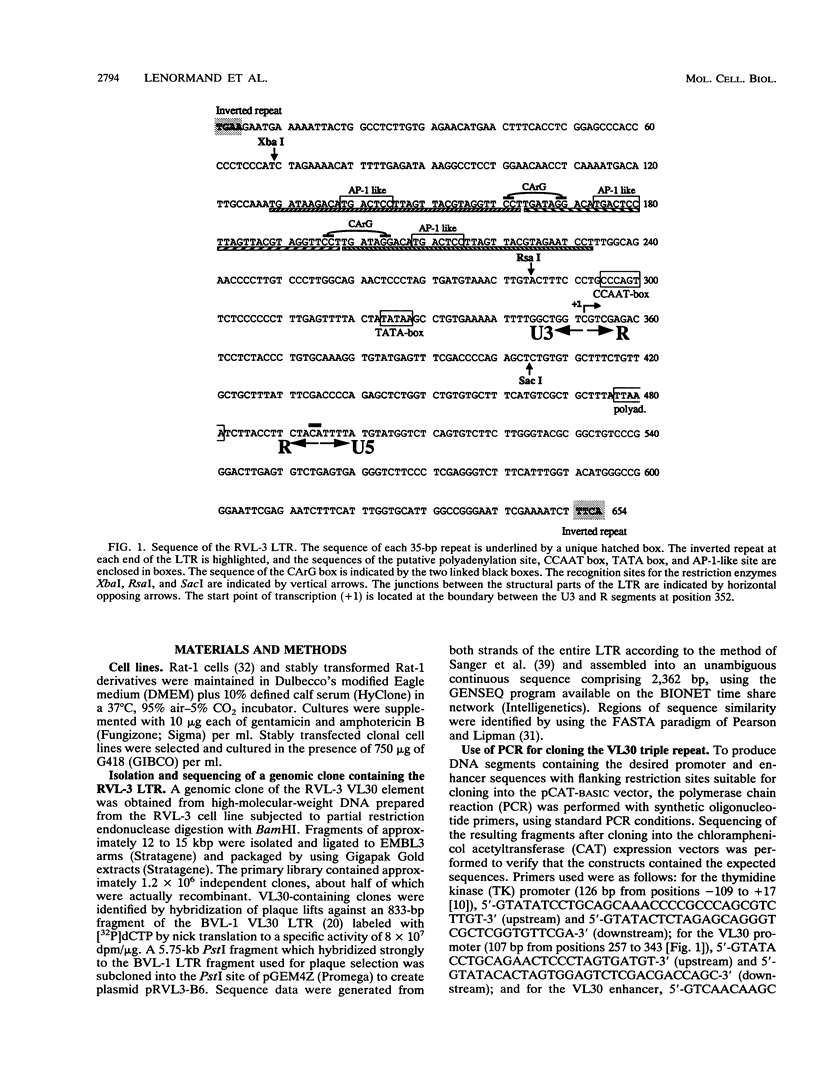
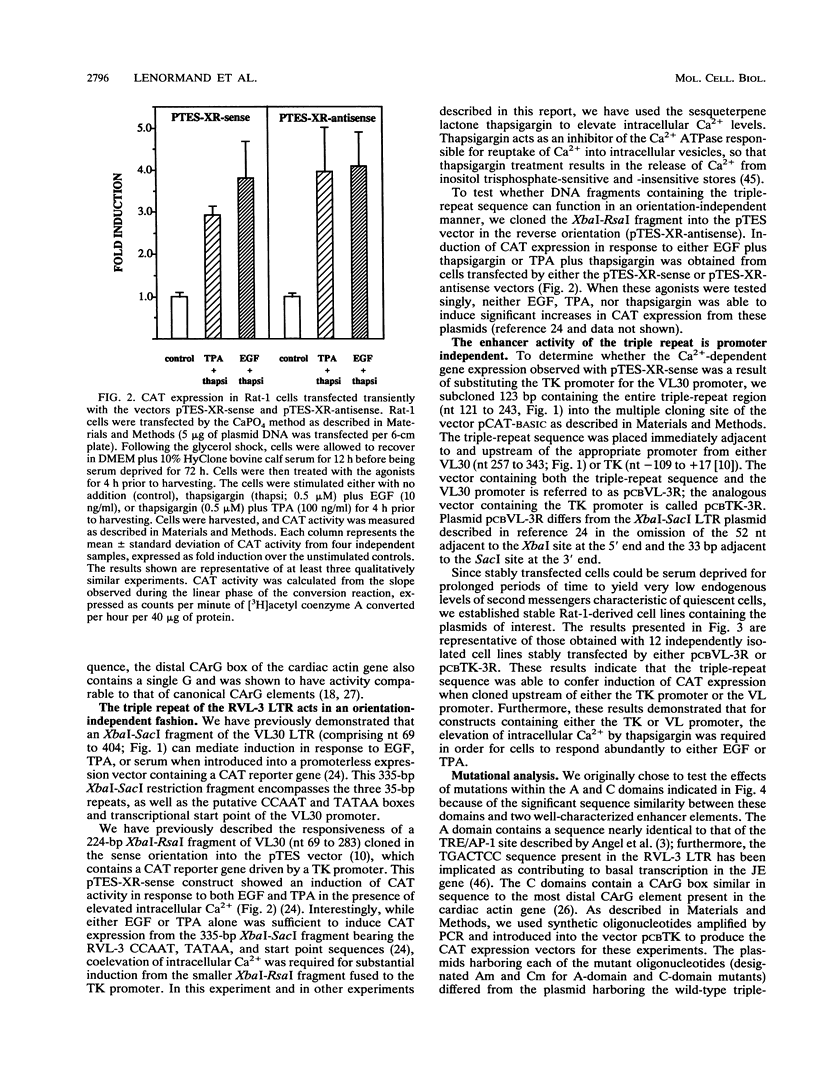
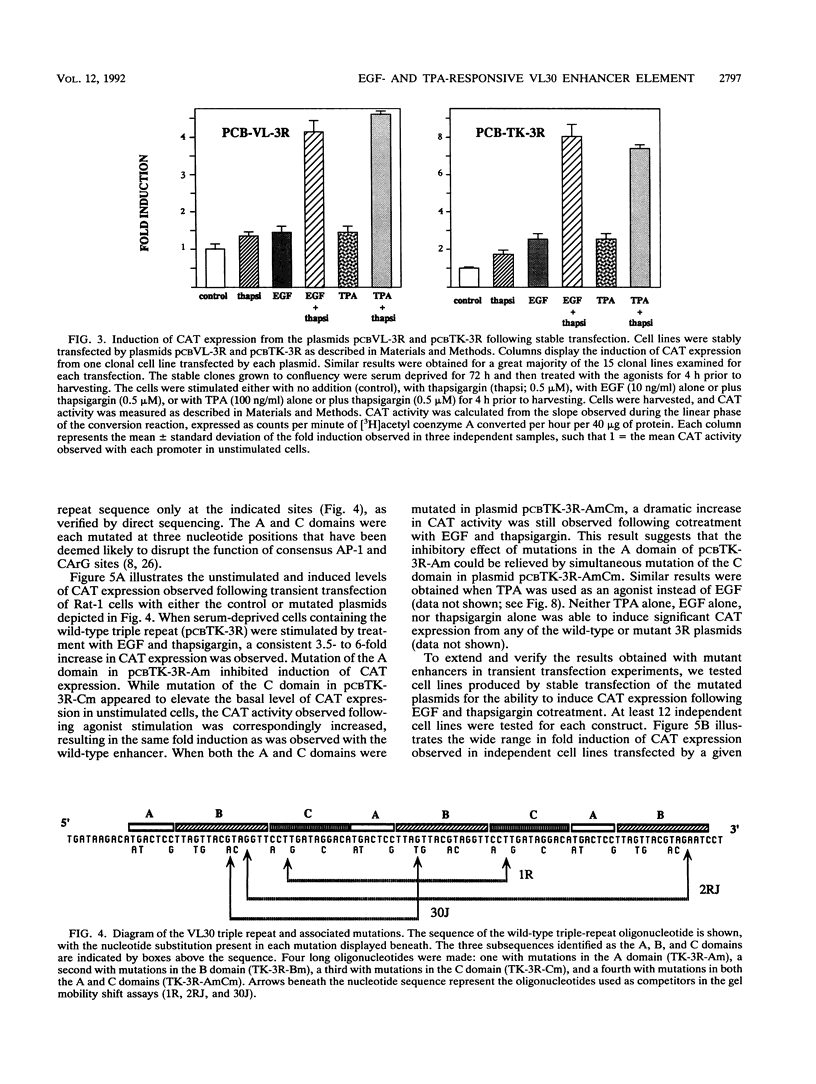
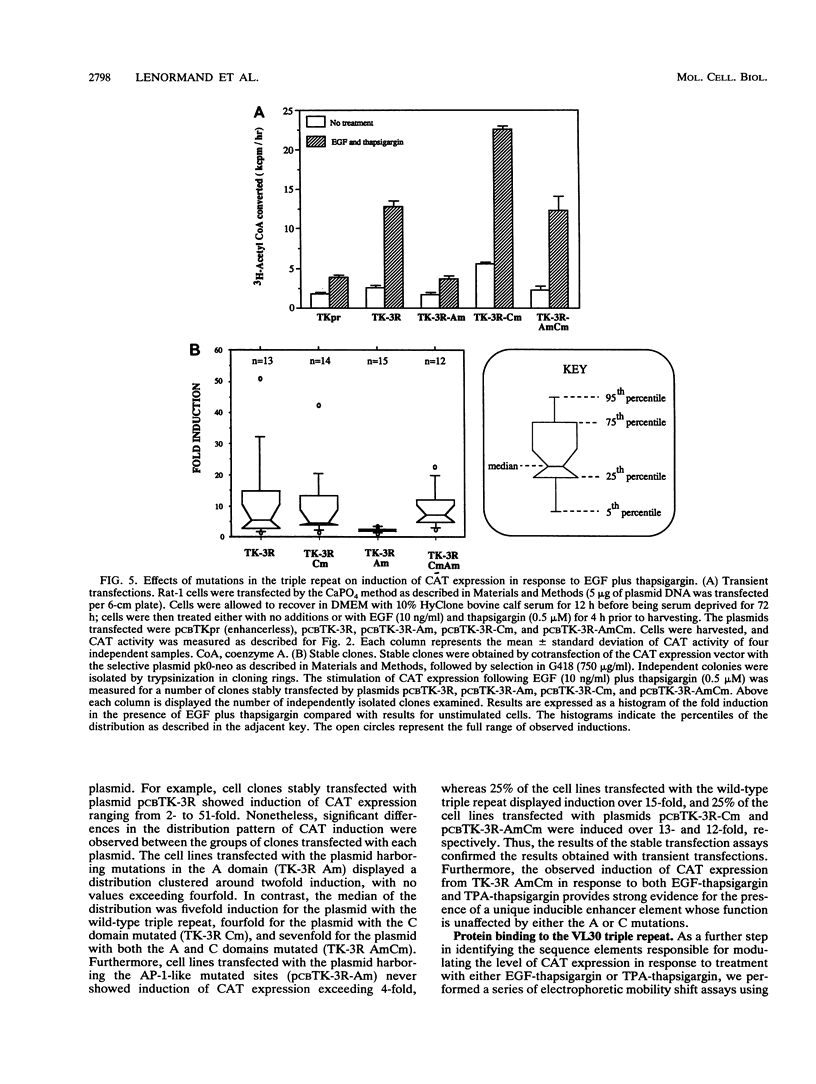
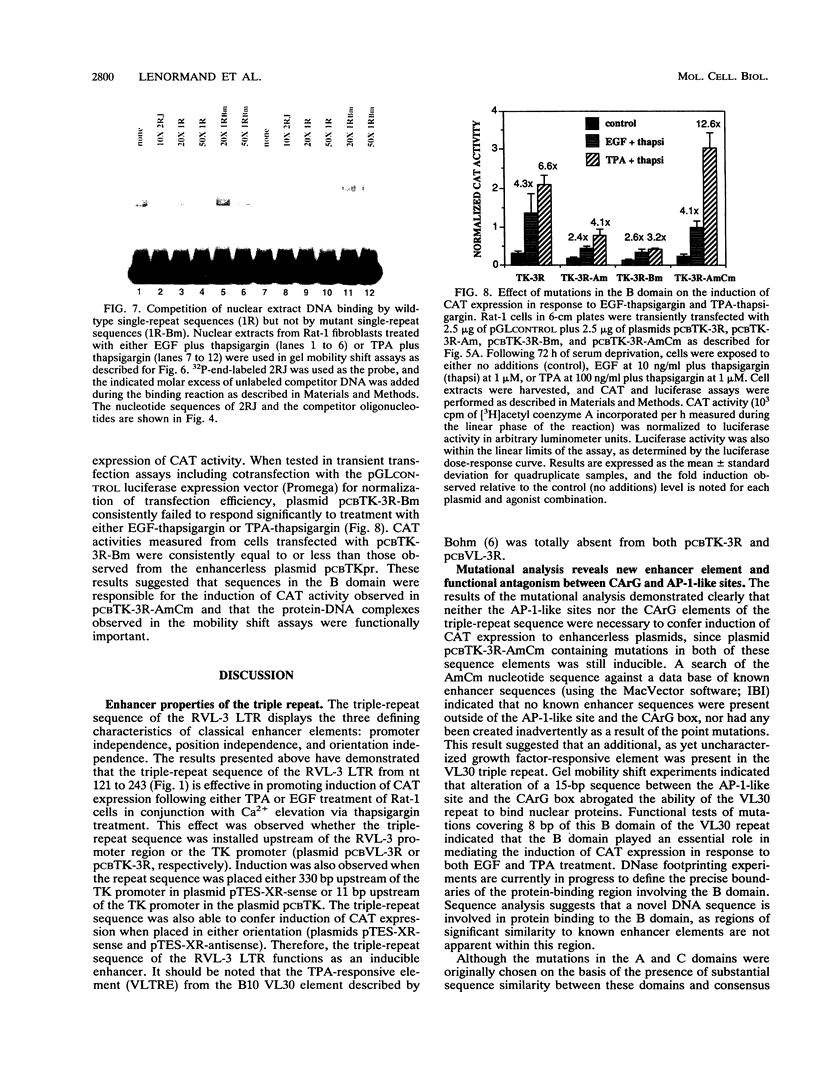
The VL30 family of defective murine retroviruses consists of 100 to 200 members, of which fewer than 5% appear to be transcriptionally active. A genomic clone of the transcriptionally active VL30 element RVL-3 was identified and sequenced. Genetic analysis indicated that a triple-repeat sequence within the RVL-3 long terminal repeat is capable of functioning as an inducible enhancer element responding to a variety of agonists. In Rat-1 fibroblasts, the ability of the RVL-3 enhancer to mediate induction of gene expression from a heterologous promoter in response to either epidermal growth factor (EGF) or phorbol ester treatment required coelevation of intracellular calcium. Two CArG boxes present in the triple-repeat sequence appeared to exert a negative effect on gene expression, as mutation of these sequences elevated the basal level of expression observed without altering the fold induction in response to either EGF or protein kinase C activation. In the presence of these CArG elements, mutation of AP-1-like sites adjacent to the CArG elements significantly inhibited the ability of either EGF or phorbol esters to induce gene expression. The effect of mutating these AP-1-like sites was relieved by simultaneous mutation of the CArG sites, indicating that interactions among these sites modulate RVL-3 expression. Mutational analysis and gel mobility shift experiments have identified a third sequence within the VL30 triple-repeat element that is required for the induction of gene expression and serves as a binding site for nuclear proteins. Sequence comparisons indicate that this enhancer element has not been described previously.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam J., Cook J. L. Reporter genes: application to the study of mammalian gene transcription. Anal Biochem. 1990 Aug 1;188(2):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90601-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson G. R., Stoler D. L., Scarcello L. A. Retrotransposon-like VL30 elements are efficiently induced in anoxic rat fibroblasts. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 20;205(4):765–769. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Retroviruses and retrotransposons: the role of reverse transcription in shaping the eukaryotic genome. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):481–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohm S., Berghard A., Pereswetoff-Morath C., Toftgård R. Isolation and characterization of complementary DNA clones corresponding to genes induced in mouse epidermis in vivo by tumor promoters. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1626–1633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohm S. Identification of protein-binding sequences mediating constitutive and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced VL30 transcription in cultured mouse and human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24834–24841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Mermod N., Hyman S. E., Pearlberg J., Ross M. E., Goodman H. M. Proteins bound at adjacent DNA elements act synergistically to regulate human proenkephalin cAMP inducible transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3793–3805. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney M. G., Schmidt L. J., Getz M. J. Organization and expression of endogenous virus-like (VL30) DNA sequences in nontransformed and chemically transformed mouse embryo cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1982 Feb;42(2):569–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delegeane A. M., Ferland L. H., Mellon P. L. Tissue-specific enhancer of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene: dependence on cyclic AMP-inducible elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3994–4002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragani T. A., Manenti G., Della Porta G., Weinstein I. B. Factors influencing the expression of endogenous retrovirus-related sequences in the liver of B6C3 mice. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):795–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton L., Norton J. D. Independent regulation of mouse VL30 retrotransposon expression in response to serum and oncogenic cell transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2069–2077. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. N., Schmidt L. J., Hodgson C. P., Moses H. L., Getz M. J. Polyadenylylated RNA complementary to a mouse retrovirus-like multigene family is rapidly and specifically induced by epidermal growth factor stimulation of quiescent cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7317–7321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. Identification of multiple proteins that interact with functional regions of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3269–3283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrigan M. T., Baughman G., Campbell N. F., Bourgeois S. Isolation and characterization of glucocorticoid- and cyclic AMP-induced genes in T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3438–3446. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson C. P., Elder P. K., Ono T., Foster D. N., Getz M. J. Structure and expression of mouse VL30 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2221–2231. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itin A., Keshet E. Diverse long terminal repeats are associated with murine retroviruslike (VL30) elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1276–1282. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., Itin A. Patterns of genomic distribution and sequence heterogeneity of a murine "retrovirus-like" multigene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.50-58.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenormand P., Muldoon L. L., Enslen H., Rodland K. D., Magun B. E. Two tumor promoters, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and thapsigargin, act synergistically via distinct signaling pathways to stimulate gene expression. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):627–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Bowden G. T., Magun B. E. Mechanism of synergistic induction of DNA synthesis by epidermal growth factor and tumor promoters. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Sep;108(3):417–425. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Taylor M. V., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. The CArG promoter sequence is necessary for muscle-specific transcription of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus embryos. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1153–1161. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon L. L., Rodland K. D., Forsythe M. L., Magun B. E. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis, diacylglycerol release, and gene expression in response to endothelin, a potent new agonist for fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8529–8536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton J. D., Connor J., Avery R. J. Unusual long terminal repeat sequence of a retrovirus transmissible mouse (VL 30) genetic element: identification of functional domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3445–3460. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad I., Zouzias D., Basilico C. State of the viral DNA in rat cells transformed by polyoma virus. I. Virus rescue and the presence of nonintergrated viral DNA molecules. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):436–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.436-444.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. Regulation of gene expression by tumor promoters. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;48(2):157–188. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90079-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera V. M., Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The inner core of the serum response element mediates both the rapid induction and subsequent repression of c-fos transcription following serum stimulation. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):255–268. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodland K. D., Brown A. M., Magun B. E. Individual mouse VL30 elements transferred to rat cells by viral pseudotypes retain their responsiveness to activators of protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2296–2298. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodland K. D., Jue S. F., Magun B. E. Regulation of VL30 gene expression by activators of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5029–5033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodland K. D., Muldoon L. L., Dinh T. H., Magun B. E. Independent transcriptional regulation of a single VL30 element by epidermal growth factor and activators of protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2247–2250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodland K. D., Muldoon L. L., Lenormand P., Magun B. E. Modulation of RNA expression by intracellular calcium. Existence of a threshold calcium concentration for induction of VL30 RNA by epidermal growth factor, endothelin, and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11000–11007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Frasch S., Nordheim A. Repression of c-fos transcription is mediated through p67SRF bound to the SRE. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2567–2574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Saragosti S., Botchan M. Isolation of cellular genes differentially expressed in mouse NIH 3T3 cells and a simian virus 40-transformed derivative: growth-specific expression of VL30 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2590–2598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Reverse transcription in the eukaryotic genome: retroviruses, pararetroviruses, retrotransposons, and retrotranscripts. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Nov;2(6):455–468. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Hanley M. R., Dawson A. P. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers H. T., Pronk G. J., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. Analysis of the rat JE gene promoter identifies an AP-1 binding site essential for basal expression but not for TPA induction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):23–34. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doren K., Hanahan D., Gluzman Y. Infection of eucaryotic cells by helper-independent recombinant adenoviruses: early region 1 is not obligatory for integration of viral DNA. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):606–614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.606-614.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein I. B. The origins of human cancer: molecular mechanisms of carcinogenesis and their implications for cancer prevention and treatment--twenty-seventh G.H.A. Clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 1;48(15):4135–4143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]