Abstract
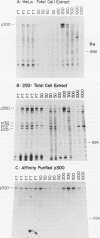
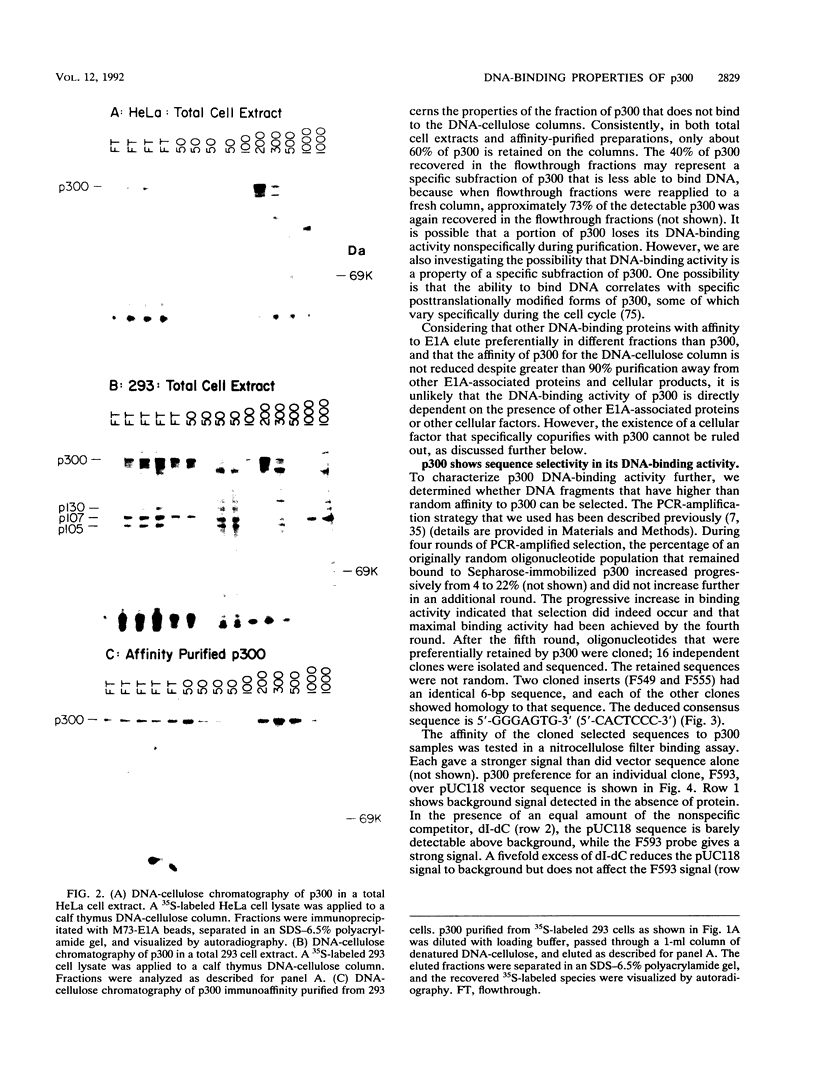
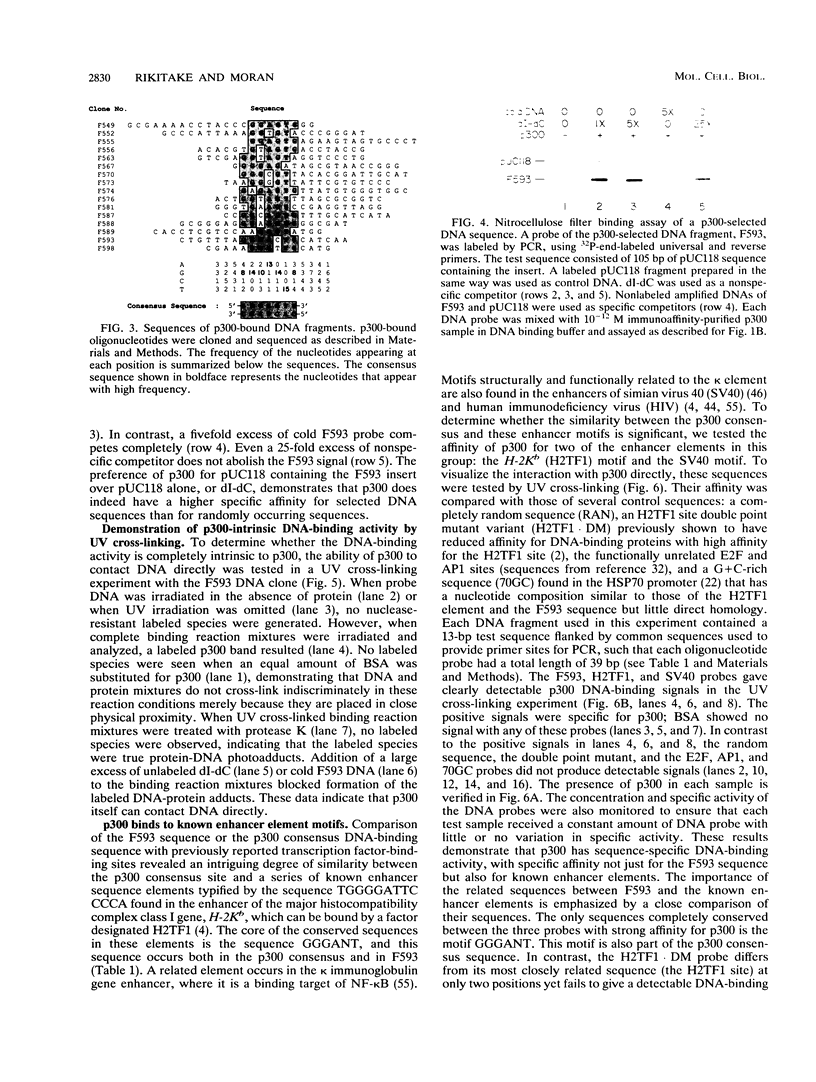
One of the major E1A-associated cellular proteins is a 300-kDa product (p300) that binds to the N-terminal region of the E1A products. The p300 binding site is distinct from sequences involved in binding the retinoblastoma product and other E1A-associated cellular products such as p60-cyclin A and p107. p300 binding to E1A is linked genetically to the enhancer repression function of E1A and the other E1A-mediated gene-regulating functions as well as to the transforming functions of E1A. However, the biochemical properties of p300 have not yet been characterized. We report here that p300 has an intrinsic DNA-binding activity and shows a preferential affinity for specific DNA sequences. The sequences selectively bound by p300 are related to those of a series of enhancer elements that are recognized by NF-kappa B. The direct physical interaction of p300 with enhancer elements provides a biochemical basis for the genetic evidence linking the E1A-mediated enhancer repression function with the p300-binding activity of E1A.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi S., Weinmann R., Raychaudhuri P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90558-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, LeClair K. P., Singh H., Sharp P. A. A large protein containing zinc finger domains binds to related sequence elements in the enhancers of the class I major histocompatibility complex and kappa immunoglobulin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1406–1414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Two transcription factors, NF-kappa B and H2TF1, interact with a single regulatory sequence in the class I major histocompatibility complex promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., La Thangue N. B. Cyclin A and the retinoblastoma gene product complex with a common transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):249–251. doi: 10.1038/352249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., La Thangue N. B. Adenovirus E1a prevents the retinoblastoma gene product from complexing with a cellular transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):494–497. doi: 10.1038/351494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger P. A., Blair G. E. Expression and interactions of human adenovirus oncoproteins. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):281–299. doi: 10.1042/bj2750281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1073–1082. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90559-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L., Pollock R. M., Hay R. T. Identification and purification of EBP1: a HeLa cell protein that binds to a region overlapping the 'core' of the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):991–1002. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dery C. V., Herrmann C. H., Mathews M. B. Response of individual adenovirus promoters to the products of the E1A gene. Oncogene. 1987;2(1):15–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan C., Jelsma T. N., Howe J. A., Bayley S. T., Ferguson B., Branton P. E. Mapping of cellular protein-binding sites on the products of early-region 1A of human adenovirus type 5. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3955–3959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enkemann S. A., Konieczny S. F., Taparowsky E. J. Adenovirus 5 E1A represses muscle-specific enhancers and inhibits expression of the myogenic regulatory factor genes, MyoD1 and myogenin. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Aug;1(8):375–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Xing Y. G., Lawrence J. B., Livingston D. M. Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and expression of the cDNA for p107, a retinoblastoma gene product-related protein. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1155–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90038-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. A DNA-binding protein containing two widely separated zinc finger motifs that recognize the same DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–42. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Krippl B., Andrisani O., Jones N., Westphal H., Rosenberg M. E1A 13S and 12S mRNA products made in Escherichia coli both function as nucleus-localized transcription activators but do not directly bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2653–2661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. J., Ricciardi R. P. Adenovirus type 12 E1A gene represses accumulation of MHC class I mRNAs at the level of transcription. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90689-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., McCall C., Whyte P., Franza B. R., Jr Human cyclin A and the retinoblastoma protein interact with similar but distinguishable sequences in the adenovirus E1A gene product. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J. M., Kingston R. E. TATA-dependent and TATA-independent function of the basal and heat shock elements of a human hsp70 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1319–1328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1A proteins: extensive heterogeneity in early region 1A products. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):533–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.533-546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Chambon P. Repression of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer by the adenovirus-2 E1A products. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1391–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2999984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Fromental C., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A mutated polyoma virus enhancer which is active in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells is not repressed by adenovirus-2 E1A products. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):249–251. doi: 10.1038/321249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. M., Yandell D. W., Park S. H., Canning S., Whyte P., Buchkovich K., Harlow E., Weinberg R. A., Dryja T. P. Point mutational inactivation of the retinoblastoma antioncogene. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):937–940. doi: 10.1126/science.2521957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. A., Mymryk J. S., Egan C., Branton P. E., Bayley S. T. Retinoblastoma growth suppressor and a 300-kDa protein appear to regulate cellular DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5883–5887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Kimura A., Kieran M., Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. A common positive trans-acting factor binds to enhancer sequences in the promoters of mouse H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsma T. N., Howe J. A., Mymryk J. S., Evelegh C. M., Cunniff N. F., Bayley S. T. Sequences in E1A proteins of human adenovirus 5 required for cell transformation, repression of a transcriptional enhancer, and induction of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):120–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90518-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Complex inhibitions. Curr Biol. 1991 Aug;1(4):224–226. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno M., Fromental C., Staub A., Ruffenach F., Davidson I., Chambon P. The SV40 TC-II(kappa B) and the related H-2Kb enhansons exhibit different cell type specific and inducible proto-enhancer activities, but the SV40 core sequence and the AP-2 binding site have no enhanson properties. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4205–4214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh S., Ozawa K., Kondoh S., Soeda E., Israel A., Shiroki K., Fujinaga K., Itakura K., Gachelin G., Yokoyama K. Identification of sequences responsible for positive and negative regulation by E1A in the promoter of H-2Kbm1 class I MHC gene. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):127–135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Whole genome PCR: application to the identification of sequences bound by gene regulatory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3645–3653. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko J. L., Dalie B. L., Goldman E., Harter M. L. Adenovirus-2 early region IA protein synthesized in Escherichia coli extracts indirectly associates with DNA. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1645–1651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy M. N., Chinnadurai G. Relationship between the transforming and transcriptional regulatory functions of adenovirus 2 E1a oncogene. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90344-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Shew J. Y., Hong F. D., Sery T. W., Donoso L. A., Young L. J., Bookstein R., Lee E. Y. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein associated with DNA binding activity. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):642–645. doi: 10.1038/329642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Loewenstein P. M., Green M. R., Green M. Functional domains of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Sudo T., Ishii S. Putative metal finger structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 enhancer binding protein HIV-EP1. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14591–14593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFall R. C., Sery T. W., Makadon M. Characterization of a new continuous cell line derived from a human retinoblastoma. Cancer Res. 1977 Apr;37(4):1003–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchelmore C., Traboni C., Cortese R. Isolation of two cDNAs encoding zinc finger proteins which bind to the alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter and to the major histocompatibility complex class I enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):141–147. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Devoto S. H., Hiebert S. W., Hunter T., Pines J., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle regulation of the E2F transcription factor involves an interaction with cyclin A. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1243–1253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90019-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Donovan D. M., Hamada K., Sax C. M., Norman B., Flanagan J. R., Ozato K., Westphal H., Piatigorsky J. Regulation of the mouse alpha A-crystallin gene: isolation of a cDNA encoding a protein that binds to a cis sequence motif shared with the major histocompatibility complex class I gene and other genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3700–3708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomiyama H., Fromental C., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. Cell-specific activity of the constituent elements of the simian virus 40 enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7881–7885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Morris J. F., Tournay O. E., Cook D. M., Curran T. Binding of the Wilms' tumor locus zinc finger protein to the EGR-1 consensus sequence. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1259–1262. doi: 10.1126/science.2244209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri P., Bagchi S., Devoto S. H., Kraus V. B., Moran E., Nevins J. R. Domains of the adenovirus E1A protein required for oncogenic activity are also required for dissociation of E2F transcription factor complexes. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1200–1211. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly C., Fromental C., Chambon P. General repression of enhanson activity by the adenovirus-2 E1A proteins. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):137–150. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Habener J. F. Angiotensinogen gene-inducible enhancer-binding protein 1, a member of a new family of large nuclear proteins that recognize nuclear factor kappa B-binding sites through a zinc finger motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2887–2895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. F., Fisher F., Goding C. R., Jones N. C. Mutational analysis of the adenovirus E1a gene: the role of transcriptional regulation in transformation. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2053–2060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Handa H., Fujisawa-Sehara A., Hiromasa T., Yamane M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Repression of cytochrome P-450c gene expression by cotransfection with adenovirus E1a DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1989 May 15;181(3):539–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. W., Corrigan M., Yaciuk P., Whelan J., Moran E. Analysis of E1A-mediated growth regulation functions: binding of the 300-kilodalton cellular product correlates with E1A enhancer repression function and DNA synthesis-inducing activity. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4421–4427. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4421-4427.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. W., Ziff E. B. Repression of insulin gene expression by adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1164–1170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers H. T., van Dam H., Pronk G. J., Bos J. L., Van der Eb A. J. Adenovirus E1A represses transcription of the cellular JE gene. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1470–1473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1470-1473.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga O., Yaegashi T., Lowe J., Dobbs L., Padmanabhan R. Sequence analysis in the E1 region of adenovirus type 4 DNA. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):418–433. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90204-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Kern F. G., Basilico C., Ziff E. B. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress expression from polyomavirus early and late promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4019–4025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a ras cooperation activity is separate from its positive and negative transcription regulatory functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2177–2183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ventura A. M., Arens M. Q., Srinivasan A., Chinnadurai G. Silencing of human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat expression by an adenovirus E1a mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1310–1314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. G., Draetta G., Moran E. E1A induces phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein independently of direct physical association between the E1A and retinoblastoma products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4253–4265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. A., Muscat G. E., Kedes L. Adenovirus E1A products suppress myogenic differentiation and inhibit transcription from muscle-specific promoters. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):553–557. doi: 10.1038/332553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaciuk P., Moran E. Analysis with specific polyclonal antiserum indicates that the E1A-associated 300-kDa product is a stable nuclear phosphoprotein that undergoes cell cycle phase-specific modification. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5389–5397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Kieran M., Le Bail O., Israël A., Kourilsky P. Purification of KBF1, a common factor binding to both H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3317–3324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02652.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. S., Weigel R., Hiebert S., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A-mediated negative control of genes activated during F9 differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3109–3113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. DNA binding of purified transcription factor NF-kappa B. Affinity, specificity, Zn2+ dependence, and differential half-site recognition. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):252–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Offringa R., Meijer I., Stein B., Smits A. M., Herrlich P., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J. Differential effects of the adenovirus E1A oncogene on members of the AP-1 transcription factor family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5857–5864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Offringa R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L., Jones N. C., van der Eb A. J. The repression of the growth factor-inducible genes JE, c-myc and stromelysin by adenovirus E1A is mediated by conserved region 1. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1207–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]