Abstract
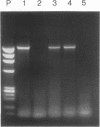
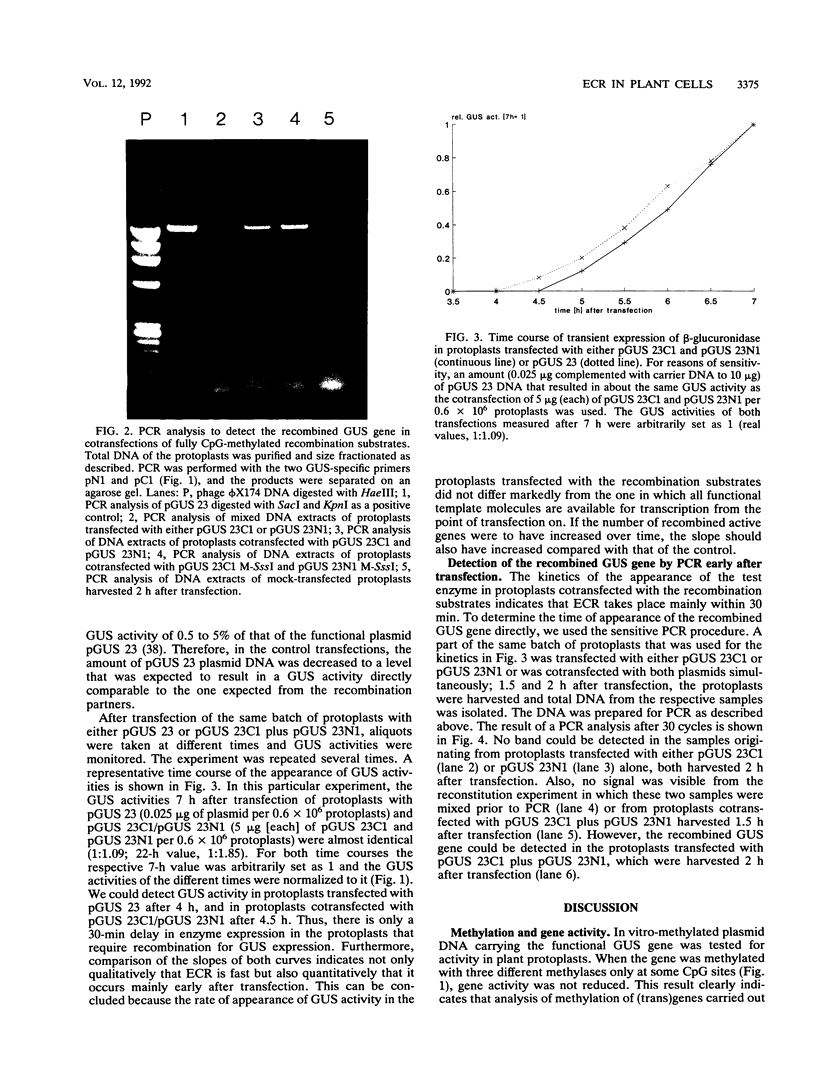
Using a sensitive transient assay, we investigated extrachromosomal homologous DNA recombination (ECR) in plant cells. As the plant genome is highly C methylated, we addressed the question of whether CpG methylation has an influence on DNA recombination efficiencies. Whereas the expression level of the fully CpG-methylated DNA molecules was reduced drastically, we found no significant changes in ECR efficiencies between two partly CpG-methylated plasmids or between one fully CpG-methylated and one nonmethylated plasmid. Using a modified polymerase chain reaction analysis, we were able to detect recombination between two fully CpG-methylated plasmids. Furthermore, we characterized the kinetics of the ECR reaction. Cotransfection of plasmids carrying truncated copies of the beta-glucuronidase (GUS) gene resulted in enzyme activity with a delay of only half an hour compared with that of the plasmid carrying the functional marker gene. This indicates that the ECR reaction itself requires no more than 30 min. By polymerase chain reaction, we were able to detect the recombined GUS gene as early as 2 h after transfection. This result and the time course of the transient GUS activity indicate that ECR occurs mainly early after transfection. The biological significance of this finding is discussed, and properties of ECR and intrachromosomal recombination are compared.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayares D., Chekuri L., Song K. Y., Kucherlapati R. Sequence homology requirements for intermolecular recombination in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5199–5203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur M., Potrykus I., Paszkowski J. Intermolecular homologous recombination in plants. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):492–500. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilang R., Peterhans A., Bogucki A., Paszkowski J. Single-stranded DNA as a recombination substrate in plants as assessed by stable and transient recombination assays. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):329–336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag R. J., Waldman A. S., Liskay R. M. Homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:199–225. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyes J., Bird A. DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A. Controlling-element events at the shrunken locus in maize. Genetics. 1981 May;98(1):143–156. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomet P. S. Cytosine methylation in gene-silencing mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;3(3):438–443. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W., Toth M., Kochanek S., Achten S., Freisem-Rabien U., Behn-Krappa A., Orend G. Eukaryotic DNA methylation: facts and problems. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell R. B., O'Dell M. Variation and inheritance of cytosine methylation patterns in wheat at the high molecular weight glutenin and ribosomal RNA gene loci. Dev Suppl. 1990:15–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Thomas K., Capecchi M. R. Nonreciprocal exchanges of information between DNA duplexes coinjected into mammalian cell nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):59–69. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal S., Pisan B., Hohn T., Grimsley N., Hohn B. Agroinfection of transgenic plants leads to viable cauliflower mosaic virus by intermolecular recombination. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):525–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90455-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal S., Pisan B., Hohn T., Grimsley N., Hohn B. Genomic homologous recombination in planta. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1571–1578. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07677.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierl A., Lütticke S., Saedler H. TnpA product encoded by the transposable element En-1 of Zea mays is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4045–4053. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershkovitz M., Gruenbaum Y., Renbaum P., Razin A., Loyter A. Effect of CpG methylation on gene expression in transfected plant protoplasts. Gene. 1990 Oct 15;94(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. L., Lieber M. R. CpG methylated minichromosomes become inaccessible for V(D)J recombination after undergoing replication. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):315–325. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05054.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inamdar N. M., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. CpG methylation inhibits binding of several sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins from pea, wheat, soybean and cauliflower. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;17(1):111–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00036811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. Altered gene expression in plants due to trans interactions between homologous genes. Trends Biotechnol. 1990 Dec;8(12):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(90)90220-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Saluz H. P., Pawlak A. Estradiol down regulates the binding activity of an avian vitellogenin gene repressor (MDBP-2) and triggers a gradual demethylation of the mCpG pair of its DNA binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5771–5775. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebeurier G., Hirth L., Hohn B., Hohn T. In vivo recombination of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2932–2936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. Y., Lund P., Lowe K., Dunsmuir P. Homologous recombination in plant cells after Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):415–425. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J., Bird A. DNA methylation and chromatin structure. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80795-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Intermolecular recombination between DNAs introduced into mouse L cells is mediated by a nonconservative pathway that leads to crossover products. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):103–112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn F., Heidmann I., Saedler H., Meyer P. Epigenetic changes in the expression of the maize A1 gene in Petunia hybrida: role of numbers of integrated gene copies and state of methylation. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jul;222(2-3):329–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00633837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liskay R. M., Letsou A., Stachelek J. L. Homology requirement for efficient gene conversion between duplicated chromosomal sequences in mammalian cells. Genetics. 1987 Jan;115(1):161–167. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyznik L. A., McGee J. D., Tung P. Y., Bennetzen J. L., Hodges T. K. Homologous recombination between plasmid DNA molecules in maize protoplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Nov;230(1-2):209–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00290670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Characterization of recombination intermediates from DNA injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes: evidence for a nonconservative mechanism of homologous recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3278–3287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Involvement of single-stranded tails in homologous recombination of DNA injected into Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3268–3277. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzke M. A., Matzke A. J. Differential inactivation and methylation of a transgene in plants by two suppressor loci containing homologous sequences. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 May;16(5):821–830. doi: 10.1007/BF00015074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messeguer R., Ganal M. W., Steffens J. C., Tanksley S. D. Characterization of the level, target sites and inheritance of cytosine methylation in tomato nuclear DNA. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 May;16(5):753–770. doi: 10.1007/BF00015069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offringa R., de Groot M. J., Haagsman H. J., Does M. P., van den Elzen P. J., Hooykaas P. J. Extrachromosomal homologous recombination and gene targeting in plant cells after Agrobacterium mediated transformation. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3077–3084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07504.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paszkowski J., Baur M., Bogucki A., Potrykus I. Gene targeting in plants. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4021–4026. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington S. L., Wilson J. H. Gene targeting in Chinese hamster ovary cells is conservative. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9498–9502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterhans A., Schlüpmann H., Basse C., Paszkowski J. Intrachromosomal recombination in plants. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3437–3445. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchta H., Hohn B. A transient assay in plant cells reveals a positive correlation between extrachromosomal recombination rates and length of homologous overlap. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2693–2700. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchta H., Hohn B. The mechanism of extrachromosomal homologous DNA recombination in plant cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Nov;230(1-2):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00290641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M. M. Intermolecular homologous recombination between transfected sequences in mammalian cells is primarily nonconservative. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3561–3565. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U. DNA methylation and chromatin structure: a view from below. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90193-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staiger D., Kaulen H., Schell J. A CACGTG motif of the Antirrhinum majus chalcone synthase promoter is recognized by an evolutionarily conserved nuclear protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6930–6934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenger D. C., Revington G. N., Stevenson M. C., Bisaro D. M. Replicational release of geminivirus genomes from tandemly repeated copies: evidence for rolling-circle replication of a plant viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8029–8033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Rothstein R. Elevated recombination rates in transcriptionally active DNA. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman A. S., Liskay R. M. Differential effects of base-pair mismatch on intrachromosomal versus extrachromosomal recombination in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5340–5344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber H., Ziechmann C., Graessmann A. In vitro DNA methylation inhibits gene expression in transgenic tobacco. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4409–4415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07891.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz U., Schell J., Czernilofsky A. P. Recombination of selectable marker DNA in Nicotiana tabacum. DNA. 1987 Jun;6(3):245–253. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng H., Wilson J. H. Gene targeting in normal and amplified cell lines. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):170–173. doi: 10.1038/344170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]