Abstract
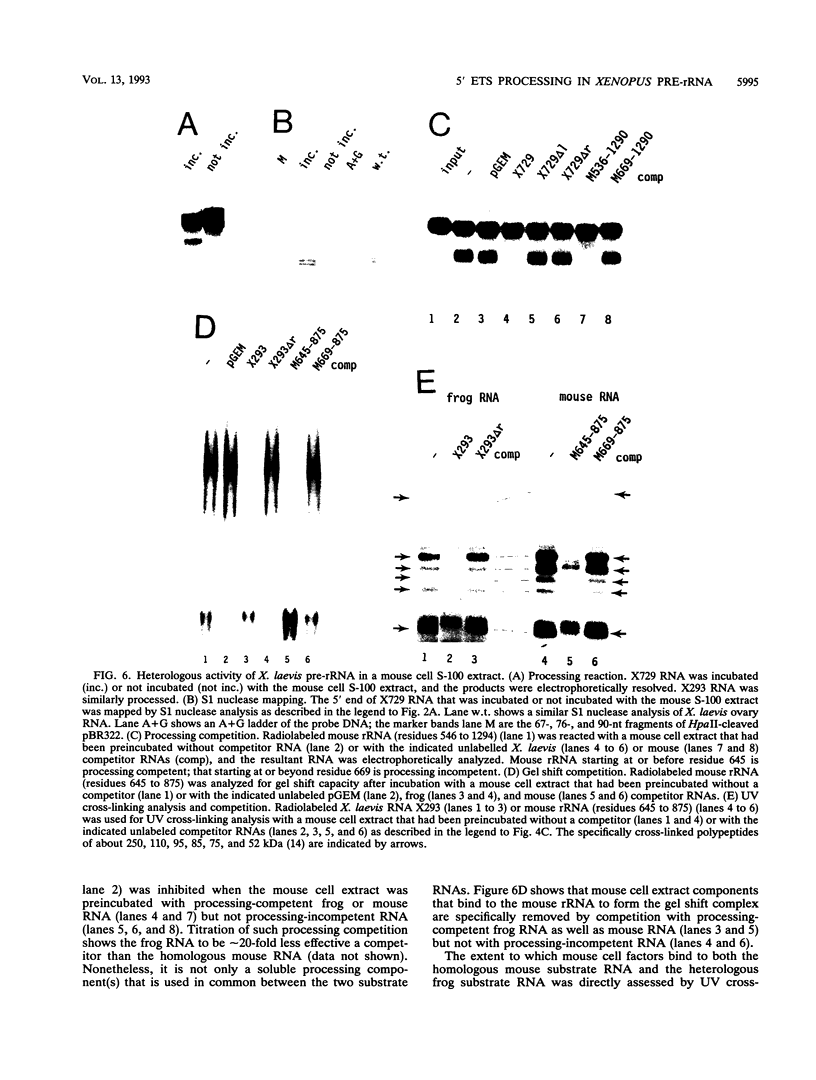
A processing site has been identified within the 5' external transcribed spacer (ETS) of Xenopus laevis and X. borealis pre-RNAs, and this in vivo processing can be reproduced in vitro. It involves a stable and specific association of the pre-rRNA with factors in the cell extract, including at least four RNA-contacting polypeptides, yielding a distinct complex that sediments at 20S. Processing also requires the U3 small nuclear RNA. This processing, at residue +105 of the 713-nucleotide X. laevis 5' ETS, is highly reminiscent of the initial processing cleavage of mouse pre-rRNA within its 3.5-kb 5' ETS, previously thought to be mammal specific. The frog and mouse processing signals share a short essential sequence motif, and mouse factors can faithfully process the frog pre-rRNA. This conservation suggests that this 5' ETS processing site serves an evolutionarily selective function.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach R., Allet B., Crippa M. Sequence organization of the spacer in the ribosomal genes of Xenopus clivii and Xenopus borealis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5311–5330. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. F., Harberd N. P., Jarvis M. G., Flavell R. B. Structure and evolution of the intergenic region in a ribosomal DNA repeat unit of wheat. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90434-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltrame M., Tollervey D. Identification and functional analysis of two U3 binding sites on yeast pre-ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1531–1542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05198.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum B., Pierron G., Seebeck T., Braun R. Processing in the external transcribed spacer of ribosomal RNA from Physarum polycephalum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3153–3166. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourbon H., Michot B., Hassouna N., Feliu J., Bachellerie J. P. Sequence and secondary structure of the 5' external transcribed spacer of mouse pre-rRNA. DNA. 1988 Apr;7(3):181–191. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N., Kass S., Sollner-Webb B. Nucleotide sequence determining the first cleavage site in the processing of mouse precursor rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):629–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N., Kass S., Sollner-Webb B. Sequence organization and RNA structural motifs directing the mouse primary rRNA-processing event. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):458–467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsheit A. B., Davidson N., Brown D. D. An electron microscope heteroduplex study of the ribosomal DNAs of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90375-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara H., Ishikawa H. Structure of the Bombyx mori rDNA: initiation site for its transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1245–1258. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong J. C., Forbes J., Robertson M., Maden B. E. The external transcribed spacer and preceding region of Xenopus borealis rDNA: comparison with the corresponding region of Xenopus laevis rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8183–8196. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney T., Jr Characterization of mouse 45S ribosomal RNA subspecies suggests that the first processing cleavage occurs 600 +/- 100 nucleotides from the 5' end and the second 500 +/- 100 nucleotides from the 3' end of a 13.9 kb precursor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4905–4919. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Ares M., Jr Depletion of U3 small nucleolar RNA inhibits cleavage in the 5' external transcribed spacer of yeast pre-ribosomal RNA and impairs formation of 18S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4231–4239. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass S., Craig N., Sollner-Webb B. Primary processing of mammalian rRNA involves two adjacent cleavages and is not species specific. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2891–2898. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass S., Sollner-Webb B. The first pre-rRNA-processing event occurs in a large complex: analysis by gel retardation, sedimentation, and UV cross-linking. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4920–4931. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass S., Tyc K., Steitz J. A., Sollner-Webb B. The U3 small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein functions in the first step of preribosomal RNA processing. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):897–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90338-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maser R. L., Calvet J. P. U3 small nuclear RNA can be psoralen-cross-linked in vivo to the 5' external transcribed spacer of pre-ribosomal-RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6523–6527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen M. D., Hunter B., Phillips R. L., Rubenstein I. The structure of the maize ribosomal DNA spacer region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4953–4968. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. An RNA polymerase I termination site can stimulate the adjacent ribosomal gene promoter by two distinct mechanisms in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1240–1251. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. L., Jr, Beatty B. R. Visualization of nucleolar genes. Science. 1969 May 23;164(3882):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3882.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougey E. B., O'Reilly M., Osheim Y., Miller O. L., Jr, Beyer A., Sollner-Webb B. The terminal balls characteristic of eukaryotic rRNA transcription units in chromatin spreads are rRNA processing complexes. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1609–1619. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Windle J. J., Mougey E. B., Sollner-Webb B. The Xenopus ribosomal DNA 60- and 81-base-pair repeats are position-dependent enhancers that function at the establishment of the preinitiation complex: analysis in vivo and in an enhancer-responsive in vitro system. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5093–5104. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piller K. J., Baerson S. R., Polans N. O., Kaufman L. S. Structural analysis of the short length ribosomal DNA variant from Pisum sativum L. cv. Alaska. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3135–3145. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Sollner-Webb B., Wahn H. L. Sites of transcription initiation in vivo on Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino R., Gerbi S. A. In vivo disruption of Xenopus U3 snRNA affects ribosomal RNA processing. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2299–2308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino R., Gerbi S. A. Preribosomal RNA processing in Xenopus oocytes does not include cleavage within the external transcribed spacer as an early step. Biochimie. 1991 Jun;73(6):805–812. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90060-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., McKnight S. L. Accurate transcription of cloned Xenopus rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: demonstration by S1 nuclease mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3391–3405. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroke I. L., Weiner A. M. The 5' end of U3 snRNA can be crosslinked in vivo to the external transcribed spacer of rat ribosomal RNA precursors. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):497–512. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutiphong J., Matzura C., Niles E. G. Characterization of a crude selective PolI transcription system from Tetrahymena pyriformis. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6319–6326. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Henderson S. L., Dougherty K. M., Wejksnora P. J., Sollner-Webb B. An RNA polymerase I promoter located in the CHO and mouse ribosomal DNA spacers: functional analysis and factor and sequence requirements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1513–1525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. M., Giles N. H. Structure of a Neurospora RNA polymerase I promoter defined by transcription in vitro with homologous extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4311–4332. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Secondary structure maps of ribosomal RNA. II. Processing of mouse L-cell ribosomal RNA and variations in the processing pathway. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Secondary structure maps of ribosomal RNA and DNA. I. Processing of Xenopus laevis ribosomal RNA and structure of single-stranded ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):379–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]