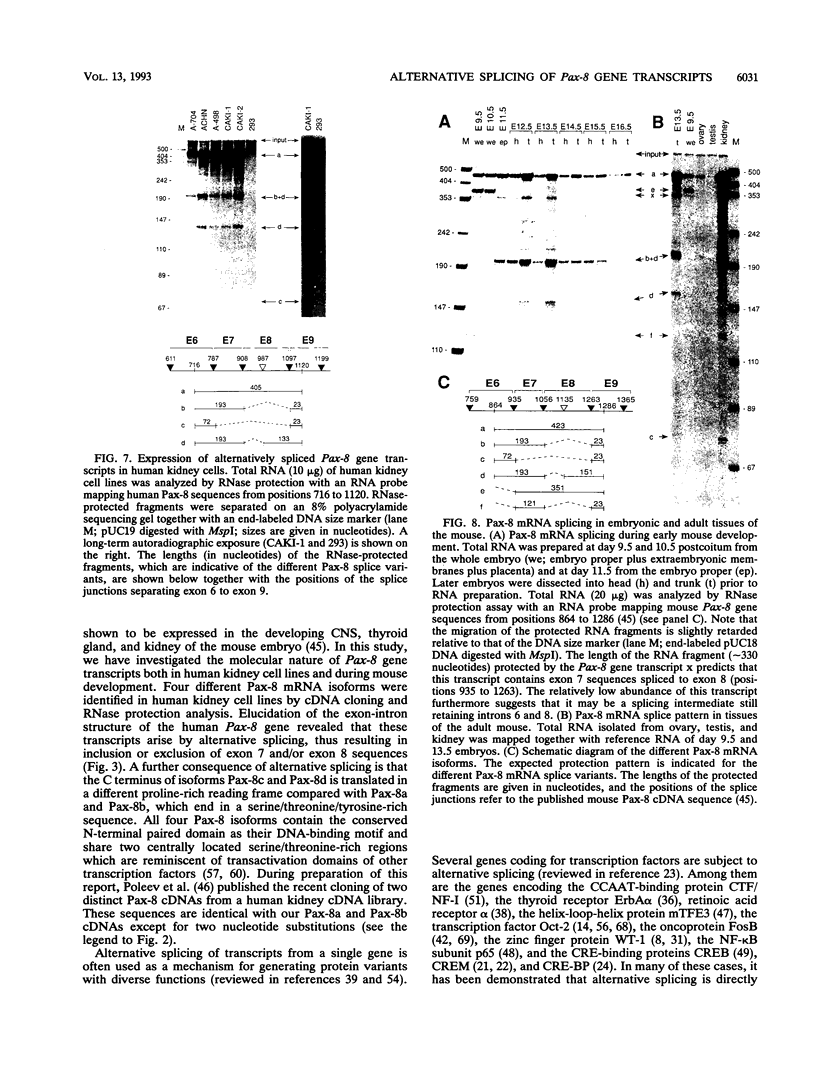
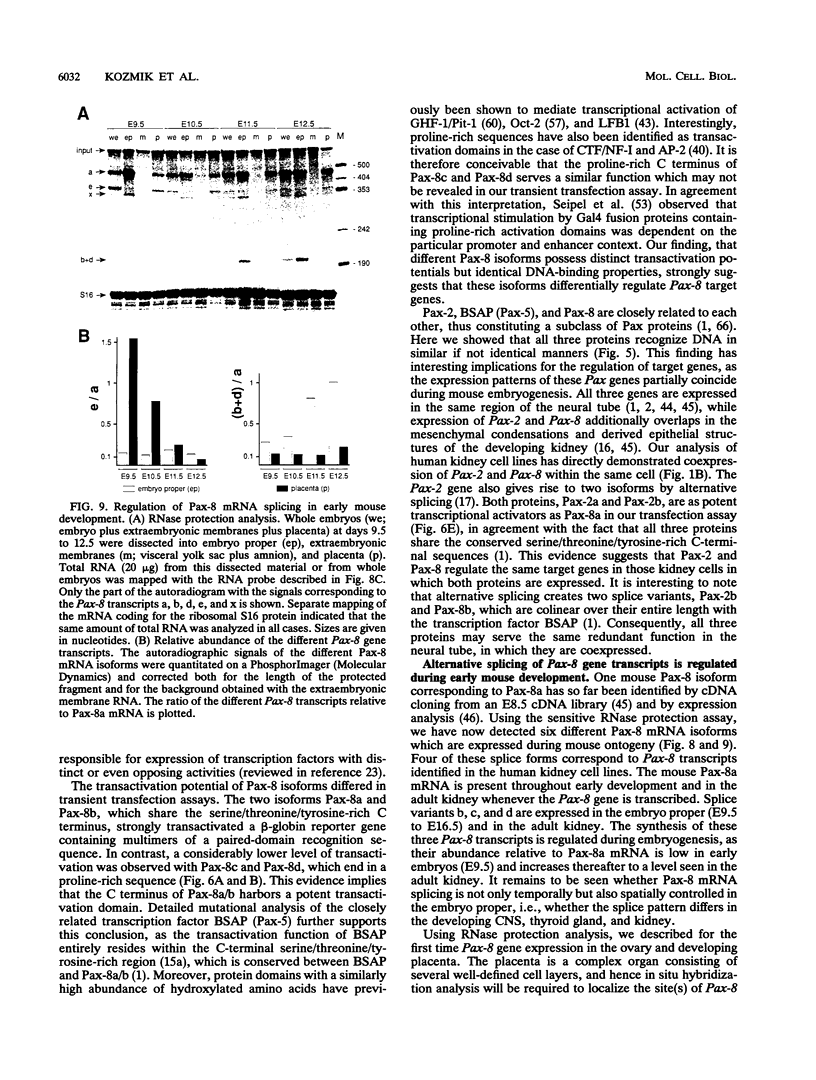
Abstract
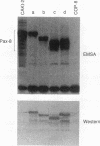
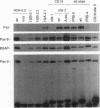
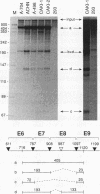
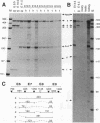
Pax-8, a member of the paired box-containing gene family, was shown to be coexpressed with Pax-2 in several human kidney carcinoma cell lines. Four different Pax-8 mRNA isoforms, a to d, were cloned from one of these cell lines by polymerase chain reaction amplification, and the Pax-8 gene was isolated from a human cosmid library. Analysis of the exon-intron structure of Pax-8 revealed that the four mRNA isoforms arise by alternative splicing, resulting in inclusion or exclusion of exon 7 and/or exon 8 sequences. All four Pax-8 proteins retain the paired domain as their DNA-binding motif and recognize DNA in the same manner as do the closely related Pax-2 and BSAP (Pax-5) proteins. The Pax-8a and Pax-8b isoforms end in a serine/threonine/tyrosine-rich sequence, while the C terminus of Pax-8c and Pax-8d is translated in a different, proline-rich reading frame. Transient transfection experiments revealed that Pax-8 isoforms a and b, but not c and d, strongly stimulate transcription from a promoter containing six copies of a paired-domain recognition sequence. The same four mRNA variants were also detected by RNase protection analysis in the mouse embryo and adult kidney, thus indicating evolutionary conservation of Pax-8 mRNA splicing. A different splice pattern was observed in the developing placenta, which expresses two new variants, Pax-8e and Pax-8f, instead of transcripts b to d. Expression of these mRNAs is high at embryonic day 9.5 and is gradually reduced until Pax-8a is the predominant transcript in the 12.5-day placenta. In the embryo, however, the synthesis of mRNAs b to d is initially low and then increases relative to that of Pax-8a. Hence, alternative splicing of Pax-8 gene transcripts not only generates six different Pax-8 variants but is also temporally and spatially regulated during early mouse development.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams B., Dörfler P., Aguzzi A., Kozmik Z., Urbánek P., Maurer-Fogy I., Busslinger M. Pax-5 encodes the transcription factor BSAP and is expressed in B lymphocytes, the developing CNS, and adult testis. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1589–1607. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano M., Gruss P. Pax-5 is expressed at the midbrain-hindbrain boundary during mouse development. Mech Dev. 1992 Nov;39(1-2):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90023-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. T., Hoth C. F., Amos J. A., da-Silva E. O., Milunsky A. An exonic mutation in the HuP2 paired domain gene causes Waardenburg's syndrome. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):637–638. doi: 10.1038/355637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balling R., Deutsch U., Gruss P. undulated, a mutation affecting the development of the mouse skeleton, has a point mutation in the paired box of Pax 1. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):531–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Vitelli L., Kemler I., Busslinger M. Developmental and tissue-specific regulation of a novel transcription factor of the sea urchin. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):663–675. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Widenhorn K., Vitelli L., Busslinger M. A novel B-cell lineage-specific transcription factor present at early but not late stages of differentiation. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):849–859. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner S., Bopp D., Burri M., Noll M. Structure of two genes at the gooseberry locus related to the paired gene and their spatial expression during Drosophila embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1247–1267. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickmore W. A., Oghene K., Little M. H., Seawright A., van Heyningen V., Hastie N. D. Modulation of DNA binding specificity by alternative splicing of the Wilms tumor wt1 gene transcript. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):235–237. doi: 10.1126/science.1321494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp D., Burri M., Baumgartner S., Frigerio G., Noll M. Conservation of a large protein domain in the segmentation gene paired and in functionally related genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1033–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90818-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp D., Jamet E., Baumgartner S., Burri M., Noll M. Isolation of two tissue-specific Drosophila paired box genes, Pox meso and Pox neuro. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3447–3457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call K. M., Glaser T., Ito C. Y., Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Haber D. A., Rose E. A., Kral A., Yeger H., Lewis W. H. Isolation and characterization of a zinc finger polypeptide gene at the human chromosome 11 Wilms' tumor locus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90601-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Fritsch R., Fickenscher H., Deutsch U., Goulding M., Gruss P. The molecular basis of the undulated/Pax-1 mutation. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):873–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90434-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch U., Dressler G. R., Gruss P. Pax 1, a member of a paired box homologous murine gene family, is expressed in segmented structures during development. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90577-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Deutsch U., Chowdhury K., Nornes H. O., Gruss P. Pax2, a new murine paired-box-containing gene and its expression in the developing excretory system. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):787–795. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Douglass E. C. Pax-2 is a DNA-binding protein expressed in embryonic kidney and Wilms tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1179–1183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrich E., Craig A., Poustka A., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. A family of cosmid vectors with the multi-copy R6K replication origin. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein D. J., Vekemans M., Gros P. Splotch (Sp2H), a mutation affecting development of the mouse neural tube, shows a deletion within the paired homeodomain of Pax-3. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90503-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Mellström B., Benusiglio E., Sassone-Corsi P. Developmental switch of CREM function during spermatogenesis: from antagonist to activator. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):80–84. doi: 10.1038/355080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Sassone-Corsi P. More is better: activators and repressors from the same gene. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90178-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNEBERG H. Genetical studies on the skeleton of the mouse. XXII. The development of Danforth's short-tail. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1958 Mar;6(1):124–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos K., Morgan B. A., Moore D. D. Functionally distinct isoforms of the CRE-BP DNA-binding protein mediate activity of a T-cell-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):747–757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessler M., Poustka A., Cavenee W., Neve R. L., Orkin S. H., Bruns G. A. Homozygous deletion in Wilms tumours of a zinc-finger gene identified by chromosome jumping. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):774–778. doi: 10.1038/343774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser T., Walton D. S., Maas R. L. Genomic structure, evolutionary conservation and aniridia mutations in the human PAX6 gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):232–239. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluecksohn-Schoenheimer S. The Morphological Manifestations of a Dominant Mutation in Mice Affecting Tail and Urogenital System. Genetics. 1943 Jul;28(4):341–348. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.4.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding M. D., Chalepakis G., Deutsch U., Erselius J. R., Gruss P. Pax-3, a novel murine DNA binding protein expressed during early neurogenesis. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1135–1147. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08054.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Walther C. Pax in development. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):719–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90281-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber D. A., Buckler A. J., Glaser T., Call K. M., Pelletier J., Sohn R. L., Douglass E. C., Housman D. E. An internal deletion within an 11p13 zinc finger gene contributes to the development of Wilms' tumor. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1257–1269. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90690-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D. Pax in our time. Curr Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):342–344. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90186-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Favor J., Hogan B. L., Ton C. C., Saunders G. F., Hanson I. M., Prosser J., Jordan T., Hastie N. D., van Heyningen V. Mouse small eye results from mutations in a paired-like homeobox-containing gene. Nature. 1991 Dec 19;354(6354):522–525. doi: 10.1038/354522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan T., Hanson I., Zaletayev D., Hodgson S., Prosser J., Seawright A., Hastie N., van Heyningen V. The human PAX6 gene is mutated in two patients with aniridia. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):328–332. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jostes B., Walther C., Gruss P. The murine paired box gene, Pax7, is expressed specifically during the development of the nervous and muscular system. Mech Dev. 1990 Dec;33(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(90)90132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Brent G. A., Larsen P. R., Chin W. W., Moore D. D. Inhibition of thyroid hormone action by a non-hormone binding c-erbA protein generated by alternative mRNA splicing. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):659–661. doi: 10.1038/337659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozmik Z., Wang S., Dörfler P., Adams B., Busslinger M. The promoter of the CD19 gene is a target for the B-cell-specific transcription factor BSAP. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2662–2672. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy P., Krust A., Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Kastner P., Dierich A., Chambon P. Multiple isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor alpha are generated by alternative splicing and differential induction by retinoic acid. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):59–69. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown M. Alternative mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:133–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell R., Friedman T. B., Moeljopawiro S., Hartono, Soewito, Asher J. H., Jr A frameshift mutation in the HuP2 paired domain of the probable human homolog of murine Pax-3 is responsible for Waardenburg syndrome type 1 in an Indonesian family. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):243–247. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.4.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Nathans D. A naturally occurring truncated form of FosB that inhibits Fos/Jun transcriptional activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):751–759. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90504-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Monaci P., Tomei L., De Francesco R., Nuzzo M., Stunnenberg H., Cortese R. A myosin-like dimerization helix and an extra-large homeodomain are essential elements of the tripartite DNA binding structure of LFB1. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1225–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90687-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nornes H. O., Dressler G. R., Knapik E. W., Deutsch U., Gruss P. Spatially and temporally restricted expression of Pax2 during murine neurogenesis. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):797–809. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plachov D., Chowdhury K., Walther C., Simon D., Guenet J. L., Gruss P. Pax8, a murine paired box gene expressed in the developing excretory system and thyroid gland. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):643–651. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poleev A., Fickenscher H., Mundlos S., Winterpacht A., Zabel B., Fidler A., Gruss P., Plachov D. PAX8, a human paired box gene: isolation and expression in developing thyroid, kidney and Wilms' tumors. Development. 1992 Nov;116(3):611–623. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Cohn L., Calame K. A dominant negative form of transcription activator mTFE3 created by differential splicing. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):94–97. doi: 10.1126/science.1840705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Narayanan R., Klement J. F., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Functional characterization of the NF-kappa B p65 transcriptional activator and an alternatively spliced derivative. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):444–454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert S., Cole T. J., Boshart M., Schmid E., Schütz G. Multiple mRNA isoforms of the transcription activator protein CREB: generation by alternative splicing and specific expression in primary spermatocytes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1503–1512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05195.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W. Different activation domains stimulate transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4961–4968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:527–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton P., Weith A., Urbánek P., Kozmik Z., Busslinger M. Chromosomal localization of seven PAX genes and cloning of a novel family member, PAX-9. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):292–298. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoykova A. S., Sterrer S., Erselius J. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Gruss P. Mini-Oct and Oct-2c: two novel, functionally diverse murine Oct-2 gene products are differentially expressed in the CNS. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):541–558. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90282-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Read A. P., Newton V. E., Harris R., Balling R., Gruss P., Strachan T. Waardenburg's syndrome patients have mutations in the human homologue of the Pax-3 paired box gene. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):635–636. doi: 10.1038/355635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Read A. P., Newton V. E., Patton M., Gruss P., Harris R., Strachan T. Mutations in the PAX3 gene causing Waardenburg syndrome type 1 and type 2. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):26–30. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theill L. E., Castrillo J. L., Wu D., Karin M. Dissection of functional domains of the pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):945–948. doi: 10.1038/342945a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Harris E., Desplan C. The paired box encodes a second DNA-binding domain in the paired homeo domain protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):594–604. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall C., La Mantia G., Thacker C. M., Favaloro J., Kamen R. A region of the polyoma virus genome between the replication origin and late protein coding sequences is required in cis for both early gene expression and viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6231–6250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitelli L., Kemler I., Lauber B., Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M. Developmental regulation of micro-injected histone genes in sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):54–63. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther C., Gruss P. Pax-6, a murine paired box gene, is expressed in the developing CNS. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1435–1449. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther C., Guenet J. L., Simon D., Deutsch U., Jostes B., Goulding M. D., Plachov D., Balling R., Gruss P. Pax: a murine multigene family of paired box-containing genes. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Gerster T., Müller M. M., Schaffner G., Schaffner W. OVEC, a versatile system to study transcription in mammalian cells and cell-free extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6787–6798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Priess A., Annweiler A., Zwilling S., Oeler B. Multiple Oct2 isoforms are generated by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):43–51. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisdom R., Yen J., Rashid D., Verma I. M. Transformation by FosB requires a trans-activation domain missing in FosB2 that can be substituted by heterologous activation domains. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):667–675. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannini M., Francis-Lang H., Plachov D., Di Lauro R. Pax-8, a paired domain-containing protein, binds to a sequence overlapping the recognition site of a homeodomain and activates transcription from two thyroid-specific promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4230–4241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]