Abstract
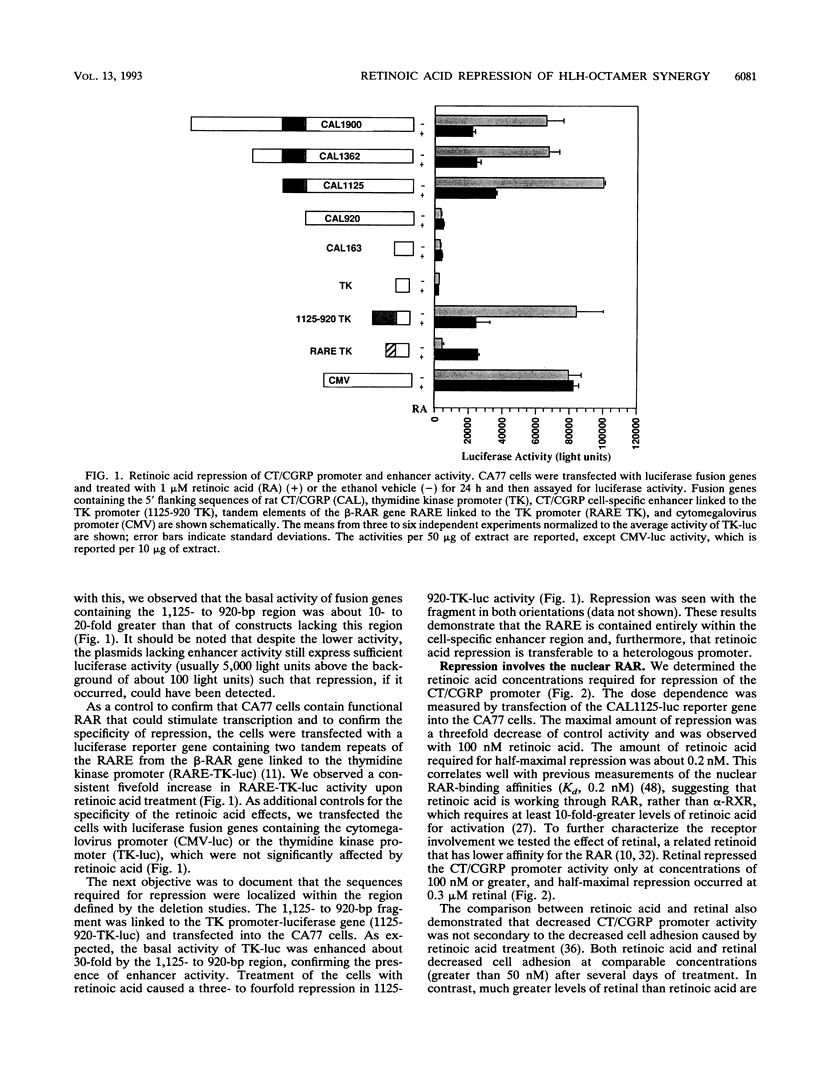
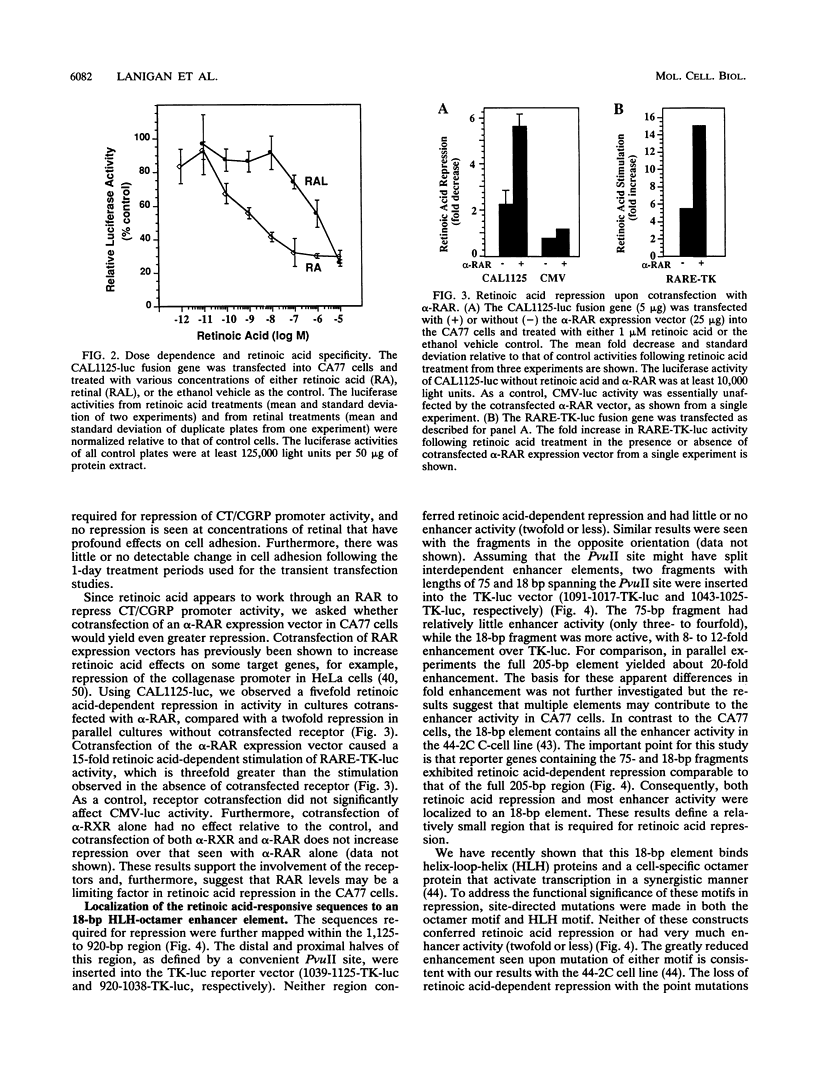
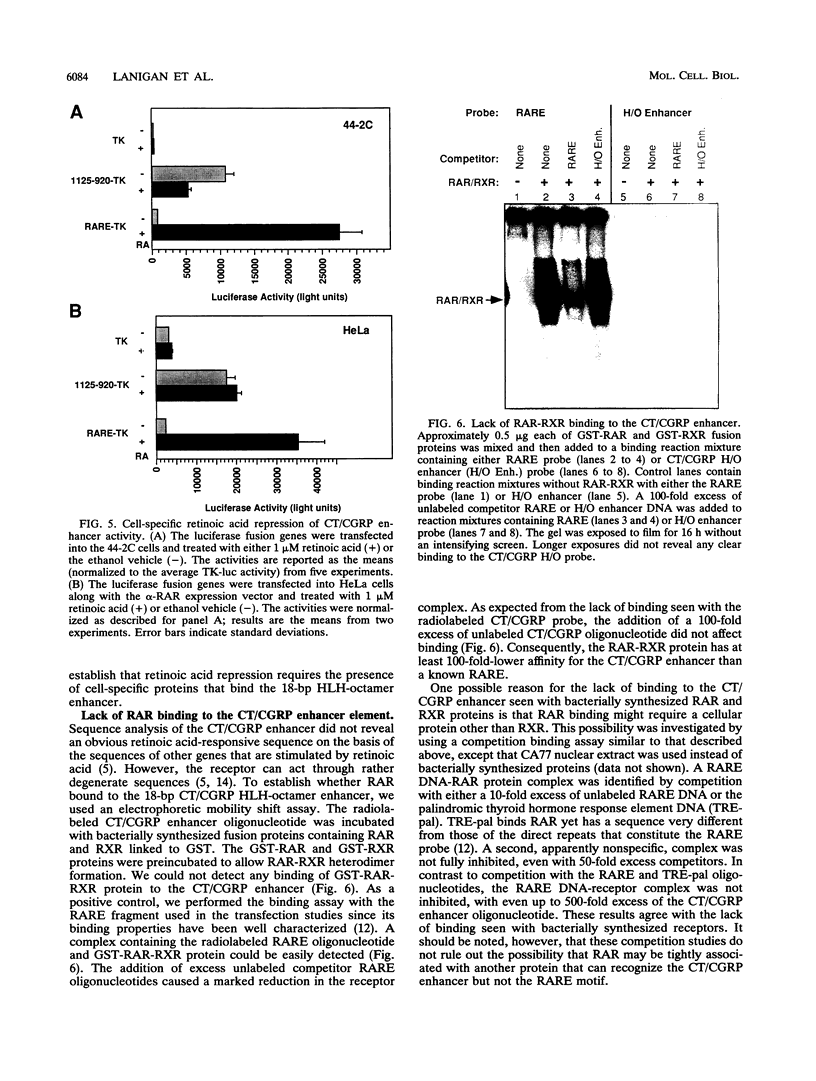
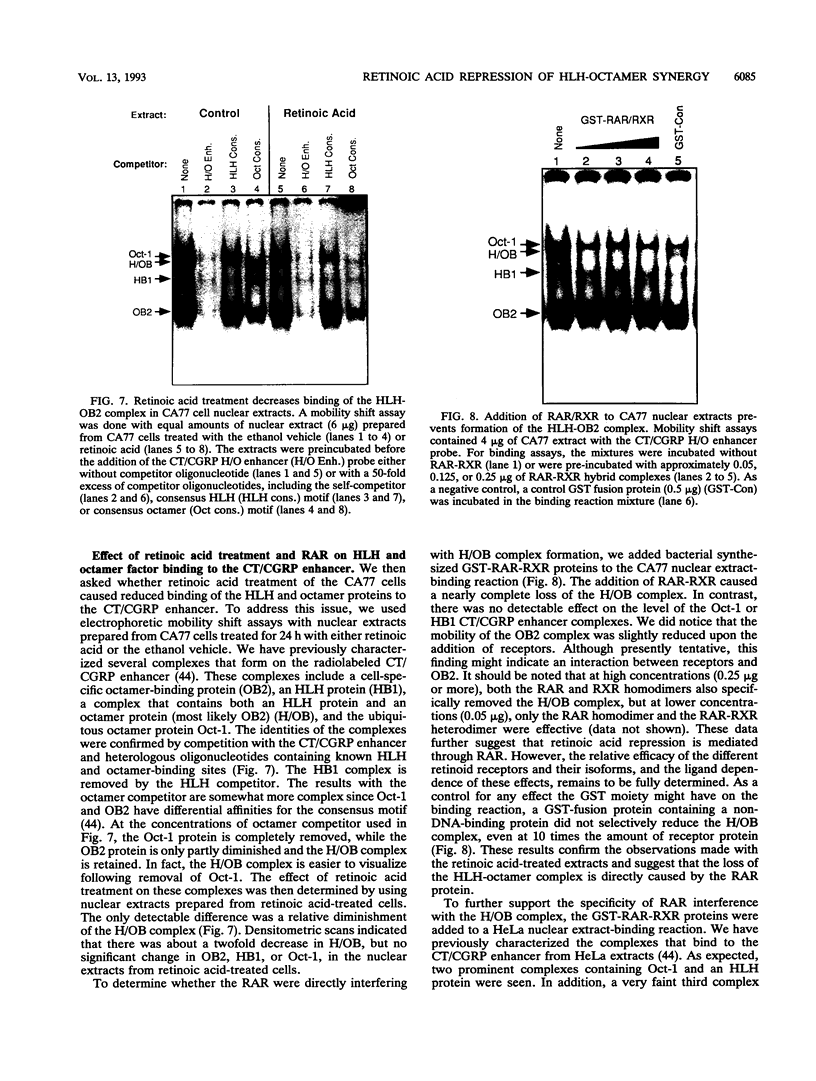
We have investigated the mechanism underlying repression of calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide (CT/CGRP) gene expression by retinoic acid. Retinoic acid treatment of the CA77 thyroid C-cell line decreased CT/CGRP promoter activity two- to threefold, which correlates well with the decrease in calcitonin and CGRP mRNA levels. Repression is mediated through the nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RAR) on the basis of the retinoid specificity, the sensitivity of repression (half-maximal repression at 0.2 nM), and the additional repression caused by cotransfection of an alpha-RAR expression vector. The sequences required for retinoic acid repression were localized to an 18-bp element containing cell-specific enhancer activity. The enhancer binds helix-loop-helix (HLH) and octamer transcription factors that act synergistically to activate transcription. Retinoic acid repression requires both these factors since mutations in either motif resulted in the loss of repression. Furthermore, repression was observed only in cell lines containing enhancer activity. We have used electrophoretic mobility shift assays to show that repression does not involve direct DNA binding of RAR or RAR-retinoid X receptor heterodimers. Instead, repression appears to involve interactions with the stimulatory enhancer factors. Following retinoic acid treatment, there was a specific decrease in an enhancer complex containing both HLH and octamer proteins. Formation of the HLH-octamer complex was also specifically blocked by the addition of exogenous RAR-retinoid X receptor protein. These results demonstrate that RAR can repress CT/CGRP gene transcription by interfering with combinatorial activation by cell-specific HLH and octamer proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball D. W., Compton D., Nelkin B. D., Baylin S. B., de Bustros A. Human calcitonin gene regulation by helix-loop-helix recognition sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):117–123. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Transcriptional control by nuclear receptors. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2044–2051. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.2010057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Kalff M., Franke S., Scheidereit C., Beato M. Ubiquitous transcription factor OTF-1 mediates induction of the MMTV promoter through synergistic interaction with hormone receptors. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90240-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca L. M. Retinoids and their receptors in differentiation, embryogenesis, and neoplasia. FASEB J. 1991 Nov;5(14):2924–2933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencker L., Annerwall E., Busch C., Eriksson U. Localization of specific retinoid-binding sites and expression of cellular retinoic-acid-binding protein (CRABP) in the early mouse embryo. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):343–352. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felli M. P., Vacca A., Meco D., Screpanti I., Farina A. R., Maroder M., Martinotti S., Petrangeli E., Frati L., Gulino A. Retinoic acid-induced down-regulation of the interleukin-2 promoter via cis-regulatory sequences containing an octamer motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4771–4778. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Multiple cell type-specific proteins differentially regulate target sequence recognition by the alpha retinoic acid receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Lipkin S. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Positive and negative regulation of gene transcription by a retinoic acid-thyroid hormone receptor heterodimer. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussler M., Sidell N., Kelly M., Donaldson C., Altman A., Mangelsdorf D. Specific high-affinity binding and biologic action of retinoic acid in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5525–5529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. G., Santon J. B., Glass C. K., Gill G. N. Ligand-activated thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors inhibit growth factor receptor promoter expression. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1165–1175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90393-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutoh E., Strömstedt P. E., Poellinger L. Functional interference between the ubiquitous and constitutive octamer transcription factor 1 (OTF-1) and the glucocorticoid receptor by direct protein-protein interaction involving the homeo subdomain of OTF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4960–4969. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafyatis R., Kim S. J., Angel P., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Karin M., Wilder R. L. Interleukin-1 stimulates and all-trans-retinoic acid inhibits collagenase gene expression through its 5' activator protein-1-binding site. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jul;4(7):973–980. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-7-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langille R. M., Paulsen D. F., Solursh M. Differential effects of physiological concentrations of retinoic acid in vitro on chondrogenesis and myogenesis in chick craniofacial mesenchyme. Differentiation. 1989 May;40(2):84–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay R. M., Harmar A. J. Nerve growth factor regulates expression of neuropeptide genes in adult sensory neurons. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):362–364. doi: 10.1038/337362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin S. M., Nelson C. A., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. A negative retinoic acid response element in the rat oxytocin promoter restricts transcriptional stimulation by heterologous transactivation domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1209–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Fujii H., Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A novel B cell-derived coactivator potentiates the activation of immunoglobulin promoters by octamer-binding transcription factors. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90352-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Hunt P., Eriksson U., Kuroiwa A., Krumlauf R., Summerbell D. Retinoic acid-binding protein, rhombomeres and the neural crest. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):35–43. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naveh-Many T., Silver J. Regulation of calcitonin gene transcription by vitamin D metabolites in vivo in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):270–273. doi: 10.1172/JCI113305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson R. C., Mader S., Nagpal S., Leid M., Rochette-Egly C., Chambon P. Negative regulation of the rat stromelysin gene promoter by retinoic acid is mediated by an AP1 binding site. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4443–4454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazawa H., Okamoto K., Ishino F., Ishino-Kaneko T., Takeda S., Toyoda Y., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. The oct3 gene, a gene for an embryonic transcription factor, is controlled by a retinoic acid repressible enhancer. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2997–3005. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peleg S., Abruzzese R. V., Cote G. J., Gagel R. F. Transcription of the human calcitonin gene is mediated by a C cell-specific enhancer containing E-box-like elements. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1750–1757. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Mermod J. J., Amara S. G., Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E., Rivier J., Vale W. W., Evans R. M. Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):129–135. doi: 10.1038/304129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe A., Eager N. S., Brickell P. M. A member of the RXR nuclear receptor family is expressed in neural-crest-derived cells of the developing chick peripheral nervous system. Development. 1991 Mar;111(3):771–778. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.3.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberte E., Dolle P., Chambon P., Morriss-Kay G. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. II. Their differential pattern of transcription during early morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):45–60. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo A. F., Lanigan T. M., Sullivan B. E. Neuronal properties of a thyroid C-cell line: partial repression by dexamethasone and retinoic acid. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Feb;6(2):207–218. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.2.1569964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R. Octamania: the POU factors in murine development. Trends Genet. 1991 Oct;7(10):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90422-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Evans R. M. Cross-coupling of signal transduction pathways: zinc finger meets leucine zipper. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90259-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Yang N., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1217–1226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90397-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Yang N., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid is a negative regulator of AP-1-responsive genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6092–6096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Thomas L., Lott I., Bronner-Fraser M. Effects of isotretinoin on the behavior of neural crest cells in vitro. Dev Biol. 1987 Sep;123(1):276–281. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90449-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolarsky-Fredman L., Leff S. E., Klein E. S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Yeakley J., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific enhancer in the rat-calcitonin/CGRP gene is active in both neural and endocrine cell types. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):497–504. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tverberg L. A., Russo A. F. Cell-specific glucocorticoid repression of calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide transcription. Localization to an 18-base pair basal enhancer element. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17567–17573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tverberg L. A., Russo A. F. Regulation of the calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide gene by cell-specific synergy between helix-loop-helix and octamer-binding transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15965–15973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., van Oosterhout J. A., van der Vliet P. C. The Oct-1 POU domain mediates interactions between Oct-1 and other POU proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):542–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J. W., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. POU-domain proteins Pit-1 and Oct-1 interact to form a heteromeric complex and can cooperate to induce expression of the prolactin promoter. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1309–1320. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland S., Döbbeling U., Rusconi S. Interference and synergism of glucocorticoid receptor and octamer factors. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2513–2521. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Zhang X. K., Graupner G., Tzukerman M., Sakamoto B., Karin M., Pfahl M. Antagonism between retinoic acid receptors and AP-1: implications for tumor promotion and inflammation. New Biol. 1991 Dec;3(12):1206–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N., Schüle R., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Characterization of DNA binding and retinoic acid binding properties of retinoic acid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3559–3563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBustros A., Baylin S. B., Levine M. A., Nelkin B. D. Cyclic AMP and phorbol esters separately induce growth inhibition, calcitonin secretion, and calcitonin gene transcription in cultured human medullary thyroid carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8036–8041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





