Abstract
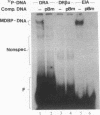
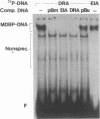
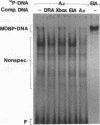
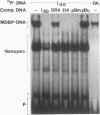
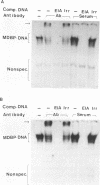
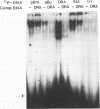
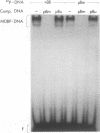
A mammalian protein called RFX or NF-X binds to the X box (or X1 box) in the promoters of a number of major histocompatibility (MHC) class II genes. In this study, RFX was shown to have the same DNA-binding specificity as methylated DNA-binding protein (MDBP), and its own cDNA was found to contain a binding site for MDBP in the leader region. MDBP is a ubiquitous mammalian protein that binds to certain DNA sequences preferentially when they are CpG methylated and to other related sequences, like the X box, irrespective of DNA methylation. MDBP from HeLa and Raji cells formed DNA-protein complexes with X-box oligonucleotides that coelectrophoresed with those containing standard MDBP sites. Furthermore, MDBP and X-box oligonucleotides cross-competed for the formation of these DNA-protein complexes. DNA-protein complexes obtained with MDBP sites displayed the same partial supershifting with an antiserum directed to the N terminus of RFX seen for complexes containing an X-box oligonucleotide. Also, the in vitro-transcribed-translated product of a recombinant RFX cDNA bound specifically to MDBP ligands and displayed the DNA methylation-dependent binding of MDBP. RFX therefore contains MDBP activity and thereby also EF-C, EP, and MIF activities that are indistinguishable from MDBP and that bind to methylation-independent sites in the transcriptional enhancers of polyomavirus and hepatitis B virus and to an intron of c-myc.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson G., Peterlin B. M. NF-X2 that binds to the DRA X2-box is activator protein 1. Expression cloning of c-Jun. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3456–3462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asiedu C. K., Supakar P. C., Ehrlich M. End-filling of an oligonucleotide duplex containing an MDBP site in the human HSP70 promoter inhibits protein-DNA complex formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):927–933. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90980-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Levy R., Faktor O., Berger I., Shaul Y. Cellular factors that interact with the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1804–1809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Mathis D. Regulation of major histocompatibility complex class-II genes: X, Y and other letters of the alphabet. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:681–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothby M., Liou H. C., Glimcher L. H. Differences in DNA sequence specificity among MHC class II X box binding proteins. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):1005–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calman A. F., Peterlin B. M. Evidence for a trans-acting factor that regulates the transcription of class II major histocompatibility complex genes: genetic and functional analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8830–8834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Baumhueter S., Crabtree G. R. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7937–7941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikstein R., Faktor O., Ben-Levy R., Shaul Y. Functional organization of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3683–3689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M., Ehrlich K. C. Effect of DNA methylation on the binding of vertebrate and plant proteins to DNA. EXS. 1993;64:145–168. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9118-9_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Lubon H., Fleckenstein B., Hennighausen L. Binding of transcription factors and creation of a large nucleoprotein complex on the human cytomegalovirus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3658–3662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa S. L., Boss J. M. Two B cell factors bind the HLA-DRA X box region and recognize different subsets of HLA class II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6269–6276. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa S. L., Sloan J. H., Reith W., Mach B., Boss J. M. Regulatory factor-X binding to mutant HLA-DRA promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1243–1249. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrero Sanchez C., Reith W., Silacci P., Mach B. The DNA-binding defect observed in major histocompatibility complex class II regulatory mutants concerns only one member of a family of complexes binding to the X boxes of class II promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4076–4083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges-Garcia Y., Hagerman P. J. Cytosine methylation can induce local distortions in the structure of duplex DNA. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 25;31(33):7595–7599. doi: 10.1021/bi00148a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. H., Wang R., Gama-Sosa M. A., Shenoy S., Ehrlich M. A protein from human placental nuclei binds preferentially to 5-methylcytosine-rich DNA. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):293–295. doi: 10.1038/308293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen S., Banerjee R., Zelent A., Price P., Acs G. Identification of protein-binding sites in the hepatitis B virus enhancer and core promoter domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5159–5165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan R., Zhang X. Y., Supakar P. C., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Human methylated DNA-binding protein. Determinants of a pBR322 recognition site. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14374–14383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouskoff V., Mantovani R. M., Candéias S. M., Dorn A., Staub A., Lisowska-Grospierre B., Griscelli C., Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J. NF-X, a transcription factor implicated in MHC class II gene regulation. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3197–3204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima G. K., Itoh-Lindstrom Y., Ting J. P. Activation of the HLA-DRA gene in primary human T lymphocytes: novel usage of TATA and the X and Y promoter elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5610–5619. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Karlsson O., Edlund T. A beta-cell-specific protein binds to the two major regulatory sequences of the insulin gene enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4228–4231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostapchuk P., Scheirle G., Hearing P. Binding of nuclear factor EF-C to a functional domain of the hepatitis B virus enhancer region. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2787–2797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterlin B. M., Andersson G., Lötscher E., Tsang S. Transcriptional regulation of HLA class-II genes. Immunol Res. 1990;9(3):164–177. doi: 10.1007/BF02918176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugliatti L., Derré J., Berger R., Ucla C., Reith W., Mach B. The genes for MHC class II regulatory factors RFX1 and RFX2 are located on the short arm of chromosome 19. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1307–1310. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90052-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Barras E., Satola S., Kobr M., Reinhart D., Sanchez C. H., Mach B. Cloning of the major histocompatibility complex class II promoter binding protein affected in a hereditary defect in class II gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4200–4204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Herrero-Sanchez C., Kobr M., Silacci P., Berte C., Barras E., Fey S., Mach B. MHC class II regulatory factor RFX has a novel DNA-binding domain and a functionally independent dimerization domain. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1528–1540. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Moore T. L., Brown A. M., Ting J. P. Class II box consensus sequences in the HLA-DR alpha gene: transcriptional function and interaction with nuclear proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):50–56. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supakar P. C., Weist D., Zhang D. L., Inamdar N., Zhang X. Y., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Methylated DNA-binding protein is present in various mammalian cell types. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8029–8044. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supakar P. C., Zhang X. Y., Githens S., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. How different DNA sequences are recognized by a DNA-binding protein: effects of partial proteolysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8611–8629. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. Y., Nakanishi M., Peterlin B. M. B-cell-specific and interferon-gamma-inducible regulation of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8598–8602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. Y., Nakanishi M., Peterlin B. M. Mutational analysis of the DRA promoter: cis-acting sequences and trans-acting factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):711–719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voliva C. F., Aronheim A., Walker M. D., Peterlin B. M. B-cell factor 1 is required for optimal expression of the DRA promoter in B cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2383–2390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. Y., Zhang X. Y., Ehrlich M. A human DNA-binding protein is methylation-specific and sequence-specific. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1599–1614. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann L. M., Perry R. P. Characterization of the expressed gene and several processed pseudogenes for the mouse ribosomal protein L30 gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2518–2528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright K. L., Ting J. P. In vivo footprint analysis of the HLA-DRA gene promoter: cell-specific interaction at the octamer site and up-regulation of X box binding by interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7601–7605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Fukushige S., Semba K., Sukegawa J., Miyajima N., Matsubara K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. The yes-related cellular gene lyn encodes a possible tyrosine kinase similar to p56lck. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):237–243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajac-Kaye M., Gelmann E. P., Levens D. A point mutation in the c-myc locus of a Burkitt lymphoma abolishes binding of a nuclear protein. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1776–1780. doi: 10.1126/science.2454510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajac-Kaye M., Levens D. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of a 138-kDa myc intron factor to a regulatory element in the first intron of the c-myc gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4547–4551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Asiedu C. K., Supakar P. C., Ehrlich M. Increasing the activity of affinity-purified DNA-binding proteins by adding high concentrations of nonspecific proteins. Anal Biochem. 1992 Mar;201(2):366–374. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Asiedu C. K., Supakar P. C., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Binding sites in mammalian genes and viral gene regulatory regions recognized by methylated DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6253–6260. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Inamdar N. M., Supakar P. C., Wu K., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Three MDBP sites in the immediate-early enhancer-promoter region of human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):865–869. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90631-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Supakar P. C., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Related sites in human and herpesvirus DNA recognized by methylated DNA-binding protein from human placenta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1459–1474. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Supakar P. C., Wu K. Z., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. An MDBP site in the first intron of the human c-myc gene. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 1;50(21):6865–6869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]