Abstract
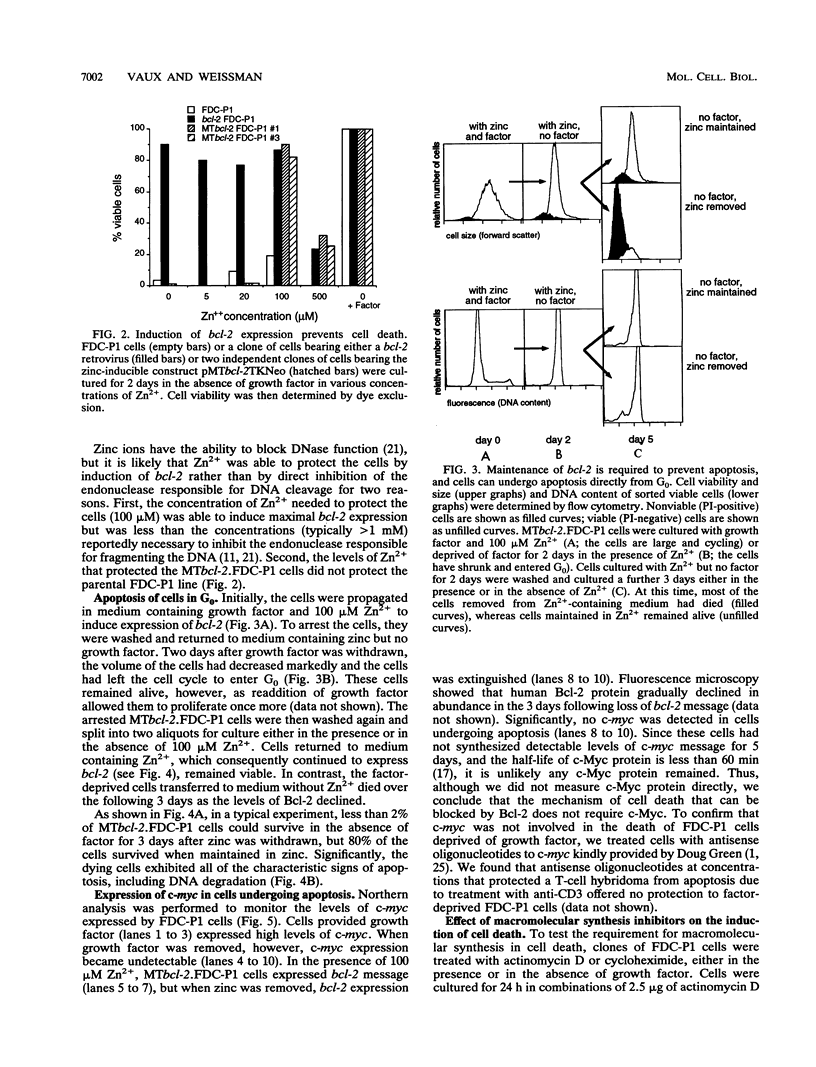
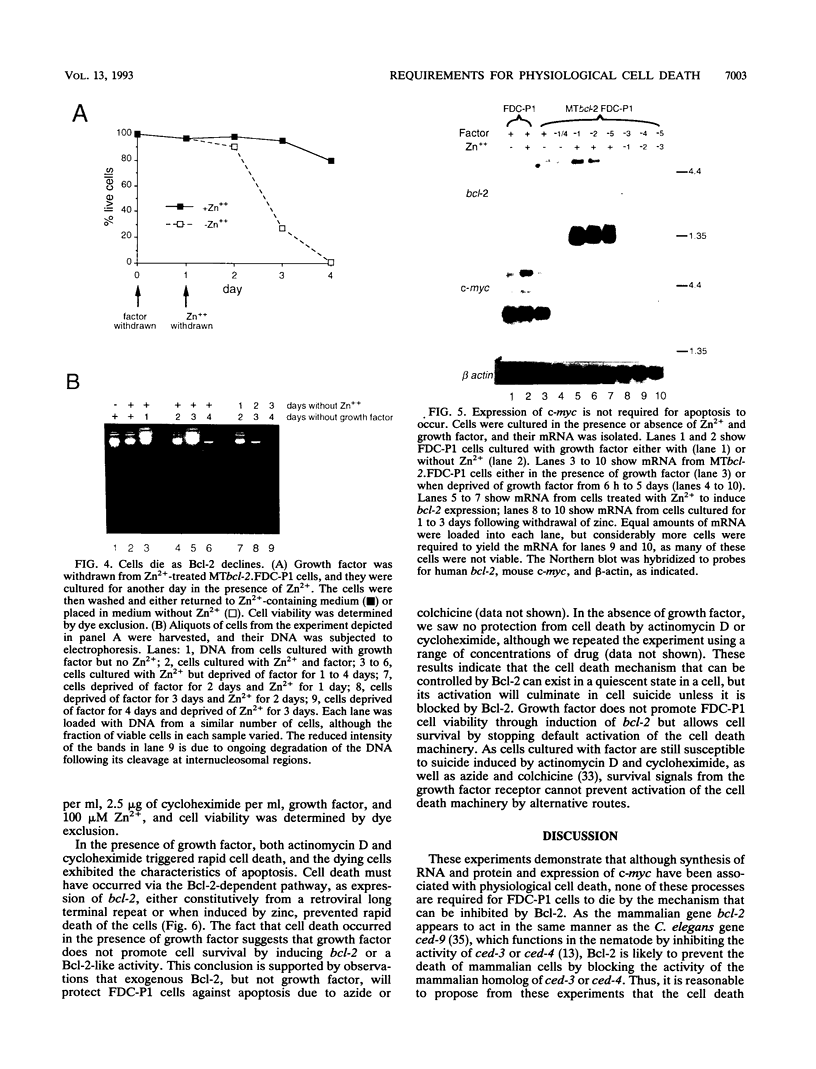
Expression of c-myc and macromolecular synthesis have been associated with physiological cell death. We have studied their requirement for the death of factor (interleukin-3)-dependent cells (FDC-P1) bearing an inducible bcl-2 expression construct. FDC-P1 cells expressing bcl-2 turned off expression of c-myc when deprived of interleukin-3 but remained viable as long as bcl-2 was maintained. A subsequent decline in Bcl-2 allowed the cells to undergo apoptosis directly from G0, in the absence of detectable c-myc expression. Thus c-myc expression may lead to apoptosis in some cases but is not directly involved in the mechanism of physiological cell death that can be controlled by Bcl-2. The macromolecular synthesis inhibitors actinomycin D and cycloheximide triggered rapid cell death of FDC-P1 cells in the presence of interleukin-3, but the cells could be protected by Bcl-2. Thus, the cell death machinery can exist in a quiescent state and can be activated by mechanisms that do not require synthesis of RNA or protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bissonnette R. P., Echeverri F., Mahboubi A., Green D. R. Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):552–554. doi: 10.1038/359552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Smith S. D., Sklar J. Cloning and structural analysis of cDNAs for bcl-2 and a hybrid bcl-2/immunoglobulin transcript resulting from the t(14;18) translocation. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Cole M. D. Constitutive c-myc oncogene expression blocks mouse erythroleukaemia cell differentiation but not commitment. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):760–763. doi: 10.1038/320760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter T. G., Glynn J. M., Echeverri F., Green D. R. The induction of apoptosis by chemotherapeutic agents occurs in all phases of the cell cycle. Anticancer Res. 1992 May-Jun;12(3):773–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Garland J., Scott D., Scolnick E., Metcalf D. Growth of factor-dependent hemopoietic precursor cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1036–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Gilman M. Z., Maruyama M., Weinberg R. A. c-myc and c-fos expression in differentiating mouse primary keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2853–2857. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. M., Horvitz H. R. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanidi A., Harrington E. A., Evan G. I. Cooperative interaction between c-myc and bcl-2 proto-oncogenes. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):554–556. doi: 10.1038/359554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flieger D., Riethmüller G., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W. Zn++ inhibits both tumor necrosis factor-mediated DNA fragmentation and cytolysis. Int J Cancer. 1989 Aug 15;44(2):315–319. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia I., Martinou I., Tsujimoto Y., Martinou J. C. Prevention of programmed cell death of sympathetic neurons by the bcl-2 proto-oncogene. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):302–304. doi: 10.1126/science.1411528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner M. O., Ellis R. E., Horvitz H. R. Caenorhabditis elegans gene ced-9 protects cells from programmed cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):494–499. doi: 10.1038/356494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Hapel A. J., Ihle J. N. Constitutive production of a unique lymphokine (IL 3) by the WEHI-3 cell line. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2393–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B., Huang Q., Isaacs J. T., Reed J. C., Griffin D. E., Hardwick J. M. Conversion of lytic to persistent alphavirus infection by the bcl-2 cellular oncogene. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):739–742. doi: 10.1038/361739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. K., Chou C. K. In vitro apoptosis in the human hepatoma cell line induced by transforming growth factor beta 1. Cancer Res. 1992 Jan 15;52(2):385–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. c-myc and c-myb protein degradation: effect of metabolic inhibitors and heat shock. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2504–2512. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. P., Schmidt R. E., DiStefano P. S., Lowry O. H., Carter J. G., Johnson E. M., Jr Inhibitors of protein synthesis and RNA synthesis prevent neuronal death caused by nerve growth factor deprivation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):829–844. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Nicotera P., Hartzell P., Bellomo G., Wyllie A. H., Orrenius S. Glucocorticoids activate a suicide process in thymocytes through an elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Feb 15;269(1):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan P., Robertson D., Amos T. A., Dyer M. J., Mason D. Y., Greaves M. F. Ultrastructural localization of bcl-2 protein. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Dec;40(12):1819–1825. doi: 10.1177/40.12.1453000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peitsch M. C., Polzar B., Stephan H., Crompton T., MacDonald H. R., Mannherz H. G., Tschopp J. Characterization of the endogenous deoxyribonuclease involved in nuclear DNA degradation during apoptosis (programmed cell death). EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):371–377. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05666.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Lazdins I., Danks D. M., Mercer J. F. Cloning and sequencing of a sheep metallothionein cDNA. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 17;143(3):507–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Tse A. G., Cordell J. L., Pulford K. A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Expression of the bcl-2 oncogene protein is not specific for the 14;18 chromosomal translocation. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Glynn J. M., Guilbert L. J., Cotter T. G., Bissonnette R. P., Green D. R. Role for c-myc in activation-induced apoptotic cell death in T cell hybridomas. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):212–214. doi: 10.1126/science.1378649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Bath M. L., Cory S. Novel primitive lymphoid tumours induced in transgenic mice by cooperation between myc and bcl-2. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):331–333. doi: 10.1038/348331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Cory S. bcl-2 transgene inhibits T cell death and perturbs thymic self-censorship. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):889–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. W. A rapid single step staining technique for DNA analysis by flow microfluorimetry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Sep;28(9):1021–1024. doi: 10.1177/28.9.6157714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Analysis of the structure, transcripts, and protein products of bcl-2, the gene involved in human follicular lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y. Stress-resistance conferred by high level of bcl-2 alpha protein in human B lymphoblastoid cell. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1331–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Obermiller P. S., Eckhart W., Apgar J. R., Berger N. A., Meyers J. Genome digestion is a dispensable consequence of physiological cell death mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3060–3069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Cory S., Adams J. M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):440–442. doi: 10.1038/335440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L. Toward an understanding of the molecular mechanisms of physiological cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):786–789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Weissman I. L., Kim S. K. Prevention of programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans by human bcl-2. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1955–1957. doi: 10.1126/science.1470921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner A. J., Small M. B., Hay N. Myc-mediated apoptosis is blocked by ectopic expression of Bcl-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2432–2440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring P. DNA fragmentation induced in macrophages by gliotoxin does not require protein synthesis and is preceded by raised inositol triphosphate levels. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14476–14480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., Smith C. A., Spooncer E., Dexter T. M., Taylor D. R. Haemopoietic colony stimulating factors promote cell survival by suppressing apoptosis. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):76–79. doi: 10.1038/343076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]