Abstract
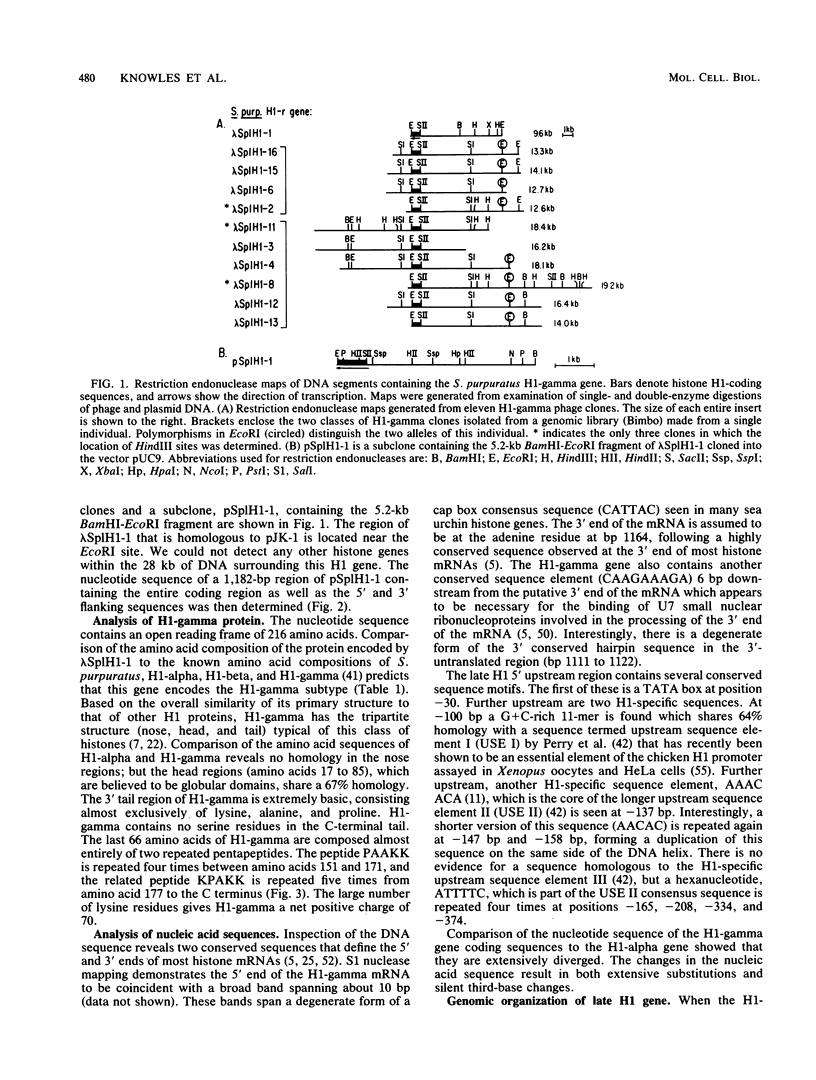
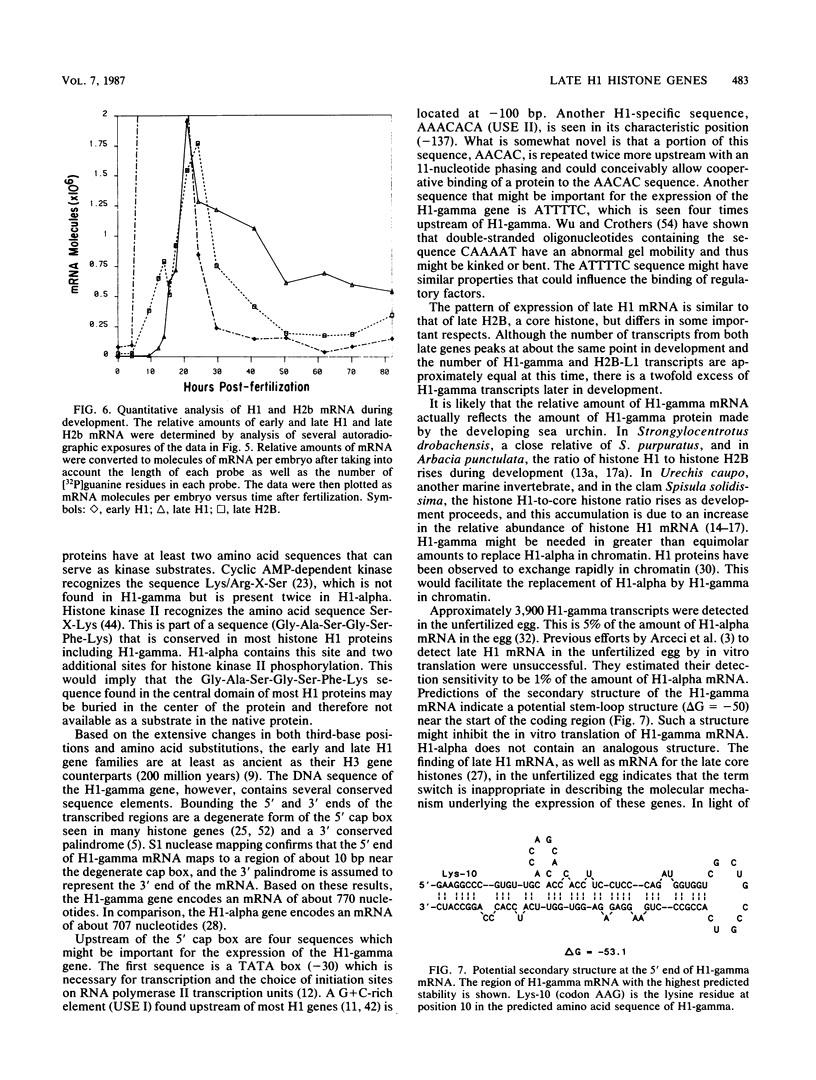
We cloned and characterized the gene encoding H1-gamma, a late histone subtype of the sea urchin species Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. The predicted primary sequence of H1-gamma is 216 amino acids in length and has a net charge of +70, which is high for a somatic H1 histone. The H1-gamma gene appears to be a unique sequence gene that is not tightly linked to the core histone genes. The 770-base-pair transcribed region of the H1-gamma gene is bordered on the 5' side by two previously described H1-specific sequence elements and on the 3' side by a hairpin loop structure and CAGA box sequences. We detected 3,900 stored maternal H1-gamma mRNA transcripts per egg. The number of H1-gamma transcripts per embryo rises by 9.5 h postfertilization, but the maximum rate of accumulation (4,300 molecules per min per embryo) occurs in the late-blastula-stage embryo between 14 and 21 h after fertilization. The number of H1-gamma mRNA molecules peaks 21 h after fertilization when there are 2.0 X 10(6) molecules per embryo (a 500-fold increase) and then decreases over the next 3.25 h to 1.3 million molecules per embryo. Between 24 and 82 h after fertilization the number of H1-gamma transcripts declines steadily (210 molecules per min per embryo) to reach approximately 5.4 X 10(5) H1-gamma mRNAs by 82 h postfertilization. Surprisingly, the number of late H1 mRNA molecules per embryo is greater than the number of late H2B mRNA molecules beginning at the early gastrula stage of development.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angerer L. M., DeLeon D. V., Angerer R. C., Showman R. M., Wells D. E., RafF R. A. Delayed accumulation of maternal histone mRNA during sea urchin oogenesis. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arceci R. J., Gross P. R. Histone variants and chromatin structure during sea urchin development. Dev Biol. 1980 Nov;80(1):186–209. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arceci R. J., Senger D. R., Gross P. R. The programmed switch in lysine-rich histone synthesis at gastrulation. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Cetta A., Davidson E. H. The single-copy DNA sequence polymorphism of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1175–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Cole R. D. Species and organ specificity in very lysine-rich histones. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4500–4505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Maxson R., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. Orphons: dispersed genetic elements derived from tandem repetitive genes of eucaryotes. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):651–663. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Maxson R., Kedes L. H. Histone gene expression during sea urchin embryogenesis: isolation and characterization of early and late messenger RNAs of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus by gene-specific hybridization and template activity. Dev Biol. 1979 Nov;73(1):153–173. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Nocente-McGrath C., Lieber T., Holt C., Knowles J. A. Sea urchin (lytechinus pictus) late-stage histone H3 and H4 genes: characterization and mapping of a clustered but nontandemly linked multigene family. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. H., Newrock K. M., Zweidler A. Stage-specific switches in histone synthesis during embryogenesis of the sea urchin. Science. 1975 Dec 5;190(4218):994–997. doi: 10.1126/science.1237932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles L. S., Wells J. R. An H1 histone gene-specific 5' element and evolution of H1 and H5 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):585–594. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton D., Chalkley R. High-resolution electrophoretic analysis of the histones from embryos and sperm of Arbacia punctulata. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Jun;72(2):502–508. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks R. R., Davis F. C. Histone messenger RNA synthesis and accumulation during early development in the echiuroid worm, Urechis caupo. Dev Biol. 1985 May;109(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90352-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks R. R., Davis F. C. Regulation of histone synthesis during early Urechis caupo (echiura) development. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli F., Baglioni C. Maternal messenger RNA and histone synthesis in embryos of the surf clam Spisula solidissima. Dev Biol. 1975 Apr;43(2):254–263. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli F., Baglioni C. Regulation of maternal mRNA translation in developing embryos of the surf clam Spisula solidissima. Nature. 1977 Oct 6;269(5628):529–531. doi: 10.1038/269529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gineitis A. A., Stankeviciute J. V., Vorob'ev V. I. Chromatin proteins from normal, vegetalized, and animalized sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1976 Sep;52(2):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Hatching in the sea urchin Lytechinus pictus is accompanied by a shift in histone H4 gene activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4135–4139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Schedl P., Kedes L. Sequence analysis and evolution of sea urchin (Lytechinus pictus and Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) histone H4 messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):351–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. F., Wilt F. H. The program of Hl histone synthesis in S. purpuratus embryos and the control of its timing. J Exp Zool. 1982 Nov 1;223(3):245–256. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402230306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. G., Chapman G. E., Moss T., Bradbury E. M. Studies on the role and mode of operation of the very-lysine-rich histone H1 in eukaryote chromatin. The three structural regions of the histone H1 molecule. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):45–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto E., Takeda M., Nishizuka Y., Hamana K., Iwai K. Studies on the sites in histones phosphorylated by adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent and guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6287–6293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Hendricks M. B., Hemminki K., Weinberg E. S. Histone gene switch in the sea urchin embryo. Identification of late embryonic histone messenger ribonucleic acids and the control of their synthesis. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2707–2716. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumeyer J. F., Weinberg E. S. Sequence, organization and expression of late embryonic H3 and H4 histone genes from the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4557–4576. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles J. A., Childs G. J. Temporal expression of late histone messenger RNA in the sea urchin Lytechinus pictus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2411–2415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S., Sures I., Kedes L. The nucleotide and amino acid coding sequence of a gene for H1 histone that interacts with euchromatin. The early embryonic H1 gene of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9438–9443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber T., Weisser K., Childs G. Analysis of histone gene expression in adult tissues of the sea urchins Strongylocentrotus purpuratus and Lytechinus pictus: tissue-specific expression of sperm histone genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2602–2612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louters L., Chalkley R. Exchange of histones H1, H2A, and H2B in vivo. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3080–3085. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauron A., Kedes L., Hough-Evans B. R., Davidson E. H. Accumulation of individual histone mRNAs during embryogenesis of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1982 Dec;94(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90359-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R. E., Jr, Wilt F. H. Accumulation of the early histone messenger RNAs during the development of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1982 Dec;94(2):435–440. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R. E., Jr, Wilt F. H. The rate of synthesis of histone mRNA during the development of sea urchin embryos (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus). Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 30;83(2):380–386. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90485-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R., Cohn R., Kedes L., Mohun T. Expression and organization of histone genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:239–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R., Mohun T., Gormezano G., Childs G., Kedes L. Distinct organizations and patterns of expression of early and late histone gene sets in the sea urchin. Nature. 1983 Jan 13;301(5896):120–125. doi: 10.1038/301120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newrock K. M., Cohen L. H., Hendricks M. B., Donnelly R. J., Weinberg E. S. Stage-specific mRNAs coding for subtypes of H2A and H2B histones in the sea urchin embryo. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock S. L., McIver C. M., Monahan J. J. Transformation of E. coli using homopolymer-linked plasmid chimeras. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 28;655(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pehrson J. R., Cohen L. H. Embryonal histone H1 subtypes of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus: purification, characterization, and immunological comparison with H1 subtypes of the adult. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6761–6764. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Thomsen G. H., Roeder R. G. Genomic organization and nucleotide sequence of two distinct histone gene clusters from Xenopus laevis. Identification of novel conserved upstream sequence elements. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):479–499. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romhányi T., Seprödi J., Antoni F., Mészáros G., Faragó A. Specific substrate for histone kinase II: a synthetic nonapeptide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 4;827(2):144–149. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Baglioni C., Gross P. R. Histone mRNA and histone synthesis during embryogenesis. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):36–38. doi: 10.1038/247036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Gross P. R. Histones and histone synthesis in sea urchin development. Dev Biol. 1974 Feb;36(2):286–298. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale R. L., Aronson A. I. Chromatin-associated proteins of the developing sea urchin embryo. II. Acid-soluble proteins. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland W. N., Strickland M., Brandt W. F., Von Holt C., Lehmann A., Wittmann-Liebold B. The primary structure of histone H1 from sperm of the sea urchin Parechinus angulosus. 2. Sequence of the C-terminal CNBr peptide and the entire primary structure. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;104(2):567–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Galli G., Busslinger M., Birnstiel M. L. The cDNA sequences of the sea urchin U7 small nuclear RNA suggest specific contacts between histone mRNA precursor and U7 RNA during RNA processing. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2801–2807. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. Genomic organization, DNA sequence, and expression of chicken embryonic histone genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):9005–9016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Levy S., Kedes L. H. Leader sequences of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus histone mRNAs start at a unique heptanucleotide common to all five histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. S., Hendricks M. B., Hemminki K., Kuwabara P. E., Farrelly L. A. Timing and rates of synthesis of early histone mRNA in the embryo of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):117–129. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younghusband H. B., Sturm R., Wells J. R. Mutagenesis of conserved 5' elements and transcription of a chicken H1 histone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):635–644. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]