Abstract
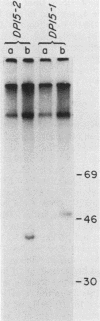
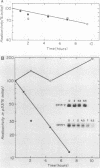
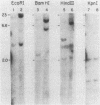
The p53 gene is rearranged in an erythroleukemic cell line (DP15-2) transformed by Friend retrovirus. Here, we characterize the mutation and identify a deletion of approximately equal to 3.0 kilobases that removes exon 2 coding sequences. The gene is expressed in DP15-2 cells and results in synthesis of a 44,000-dalton protein that is missing the N-terminal amino acid residues of p53. The truncated protein is unusually stable and accumulates to high levels intracellularly. Moreover, it appears to have undergone a change in conformation as revealed by epitope mapping studies. This study represents the first description of an altered p53 gene product arising by mutation during neoplastic progression and identifies a region in the p53 protein molecule that plays a role in determining p53 stability in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker A., Gold M. Isolation of the bacteriophage lambda A-gene protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):581–585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Dori R., Resnitzki D., Kimchi A. Reduction in p53 synthesis during differentiation of Friend-erythroleukemia cells. Correlation with the commitment to terminal cell division. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 17;162(2):384–389. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80792-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benchimol S., Pim D., Crawford L. Radioimmunoassay of the cellular protein p53 in mouse and human cell lines. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1055–1062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01296.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz B., Zakut-Houri R., Givol D., Oren M. Analysis of the gene coding for the murine cellular tumour antigen p53. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2179–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Viral oncogenes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes B cells and B cell precursors in mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):269–279. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. The 53,000-dalton cellular protein and its role in transformation. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;25:1–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo A. B., Jay G., Appella E., Dubois G. C., Law L. W., Old L. J. Detection of a transformation-related antigen in chemically induced sarcomas and other transformed cells of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2420–2424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Oren M. Overproduction of p53 antigen makes established cells highly tumorigenic. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):158–160. doi: 10.1038/316158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. DNA as substrate for packaging into bacteriophage lambda, in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):93–106. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Chumakov P., Currie G. A. The cellular oncogene p53 can be activated by mutagenesis. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):816–818. doi: 10.1038/317816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Currie G. A. Cellular immortalization by a cDNA clone encoding the transformation-associated phosphoprotein p53. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):651–654. doi: 10.1038/312651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Redmond S., Wade-Evans A. Cloning and expression analysis of full length mouse cDNA sequences encoding the transformation associated protein p53. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5609–5626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelekar A., Cole M. D. Tumorigenicity of fibroblast lines expressing the adenovirus E1a, cellular p53, or normal c-myc genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. The SV40 A gene product is required for the production of a 54,000 MW cellular tumor antigen. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):308–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90554-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Banks L., Pim D., Crawford L. Analysis of human p53 proteins and mRNA levels in normal and transformed cells. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):665–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Harlow E. Association of a murine 53,000-dalton phosphoprotein with simian virus 40 large-T antigen in transformed cells. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):213–224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.213-224.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Avignolo C., Baserga R. Role of the p53 protein in cell proliferation as studied by microinjection of monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):276–281. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Baserga R. Expression of the p53 protein during the cell cycle of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Sep;160(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Nelson D., DeLeo A. B., Old L. J., Baserga R. Microinjection of monoclonal antibody to protein p53 inhibits serum-induced DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6309–6312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Milner S. SV40-53K antigen: a possible role for 53K in normal cells. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):785–788. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora P. T., Chandrasekaran K., McFarland V. W. An embryo protein induced by SV40 virus transformation of mouse cells. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):722–724. doi: 10.1038/288722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat M., Cheng A., Kimura N., Bernstein A., Benchimol S. Rearrangements of the cellular p53 gene in erythroleukaemic cells transformed by Friend virus. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):633–636. doi: 10.1038/314633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Post-translational regulation of the 54K cellular tumor antigen in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):101–110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M. The p53 cellular tumor antigen: gene structure, expression and protein properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 12;823(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(85)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Michalovitz D., Ben-Zeev A., Oren M. Specific interaction between the p53 cellular tumour antigen and major heat shock proteins. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):182–184. doi: 10.1038/320182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Alpers J. D., Nowell P. C., Hoover R. G. Sequential expression of protooncogenes during lectin-stimulated mitogenesis of normal human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Growth regulation of a cellular tumour antigen, p53, in nontransformed cells. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):199–201. doi: 10.1038/308199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Oren M., Levine A. J. Two distinct mechanisms regulate the levels of a cellular tumor antigen, p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2143–2150. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Boss M. A., Baltimore D. Increased concentration of an apparently identical cellular protein in cells transformed by either Abelson murine leukemia virus or other transforming agents. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):336–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.336-346.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Witte O. N., Coffman R., Baltimore D. Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced tumors elicit antibodies against a host cell protein, P50. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):547–555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.547-555.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S. K., Scolnick E. M. Expression of a transformation-related protein (p53) in the malignant stage of Friend virus-induced diseases. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1022–1026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1022-1026.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Ho Y. S., Williams J., Levine A. J. Adenovirus E1b-58kd tumor antigen and SV40 large tumor antigen are physically associated with the same 54 kd cellular protein in transformed cells. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen D. W., Real F. X., DeLeo A. B., Old L. J., Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Protein p53 and inducer-mediated erythroleukemia cell commitment to terminal cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5919–5922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Wallis J., Levine A. J. Identification of the p53 protein domain involved in formation of the simian virus 40 large T-antigen-p53 protein complex. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):574–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.574-583.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. The molecular genetics of cellular oncogenes. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:553–612. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade-Evans A., Jenkins J. R. Precise epitope mapping of the murine transformation-associated protein, p53. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):699–706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The action of oncogenes in the cytoplasm and nucleus. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):770–776. doi: 10.1126/science.2997917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Rotter V. Reconstitution of p53 expression in a nonproducer Ab-MuLV-transformed cell line by transfection of a functional p53 gene. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Rotter V. Inactivation of p53 gene expression by an insertion of Moloney murine leukemia virus-like DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1402–1410. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Rotter V. Major deletions in the gene encoding the p53 tumor antigen cause lack of p53 expression in HL-60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):790–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.444-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakut-Houri R., Oren M., Bienz B., Lavie V., Hazum S., Givol D. A single gene and a pseudogene for the cellular tumour antigen p53. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):594–597. doi: 10.1038/306594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]