Abstract
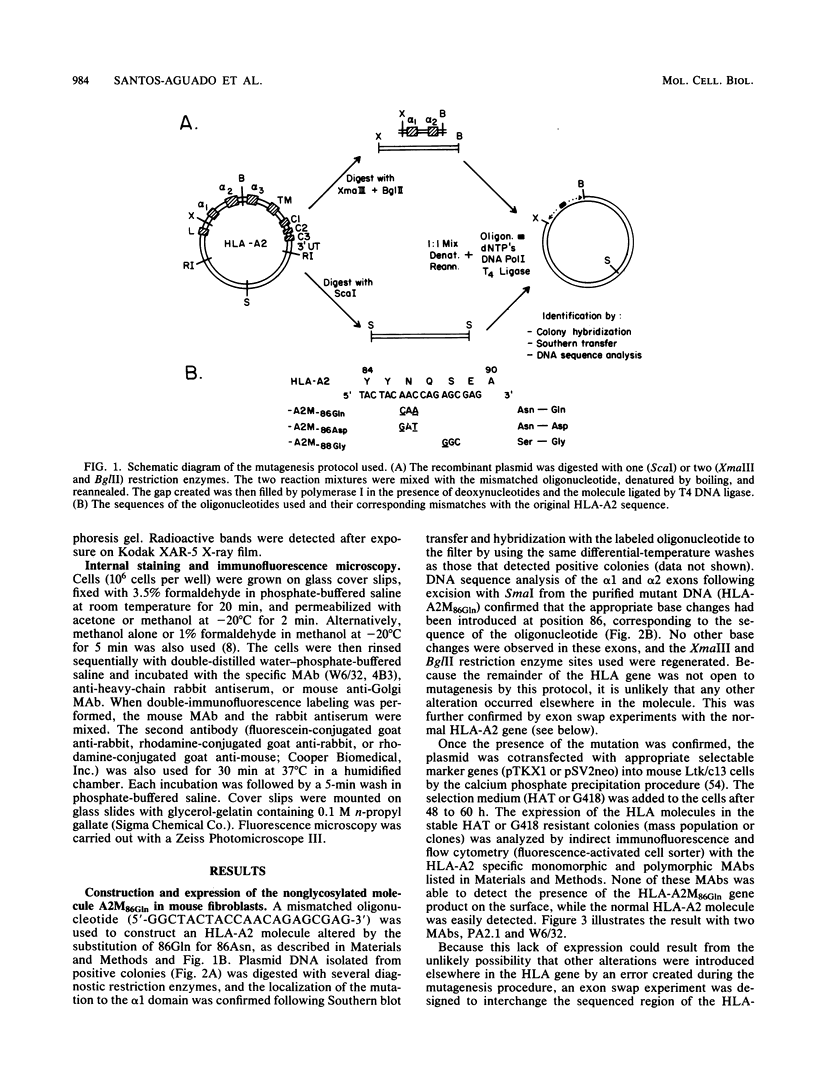
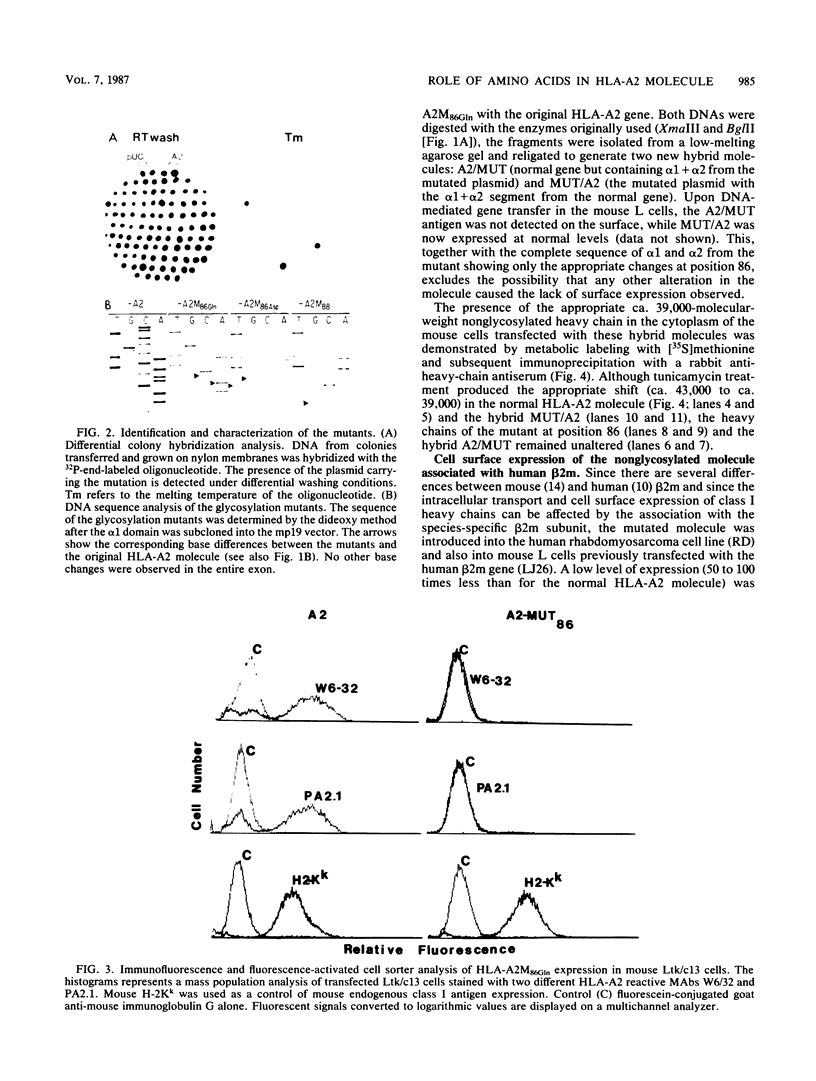
The role of the single carbohydrate moiety present on the HLA-A2 molecule was studied by introducing several amino acid substitutions (by site-directed mutagenesis of the HLA-A2 gene) in the consensus glycosylation sequence Asn-X-Ser. Two different amino acid substitutions of the asparagine residue at position 86 (glutamine and aspartic acid) resulted in the synthesis of ca. 39,000-molecular-weight nonglycosylated heavy chains that were detected in the cytoplasm but not on the surface of mouse L-cell transfectants. However, a low level of surface expression was detected following transfection of human (rhabdomyosarcoma) cells or mouse L cells containing human beta 2-microglobulin. The defect in surface expression was not due to the absence of the glycan moiety, since the substitution of a glycine for a serine at amino acid 88 did not have the same drastic effect in the presence of human beta 2-microglobulin. These and other data suggest that the asparagine residue may play a critical role in the conformation of the HLA heavy chain and its interaction with beta 2-microglobulin. Immunofluorescence microscopy following permeabilization of the transfectants demonstrated that the unglycosylated HLA heavy chains are sequestered in an unidentified cellular compartment that is different from the Golgi structure.
Full text
PDF

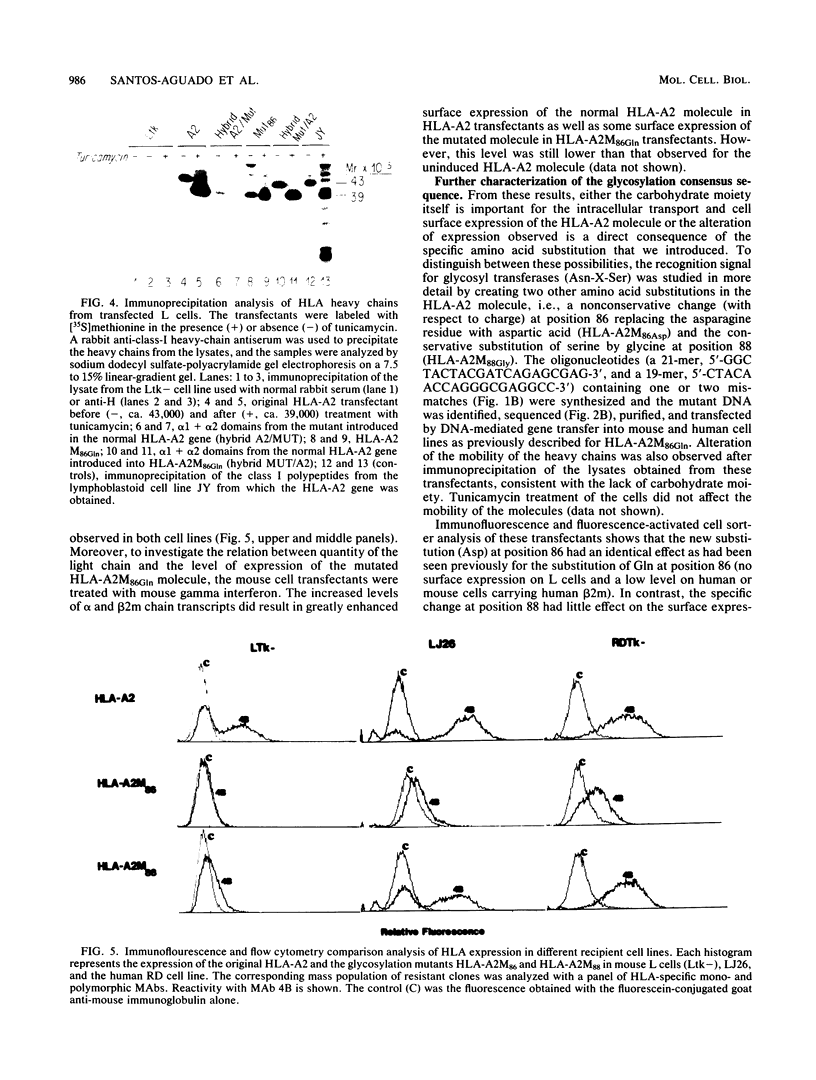

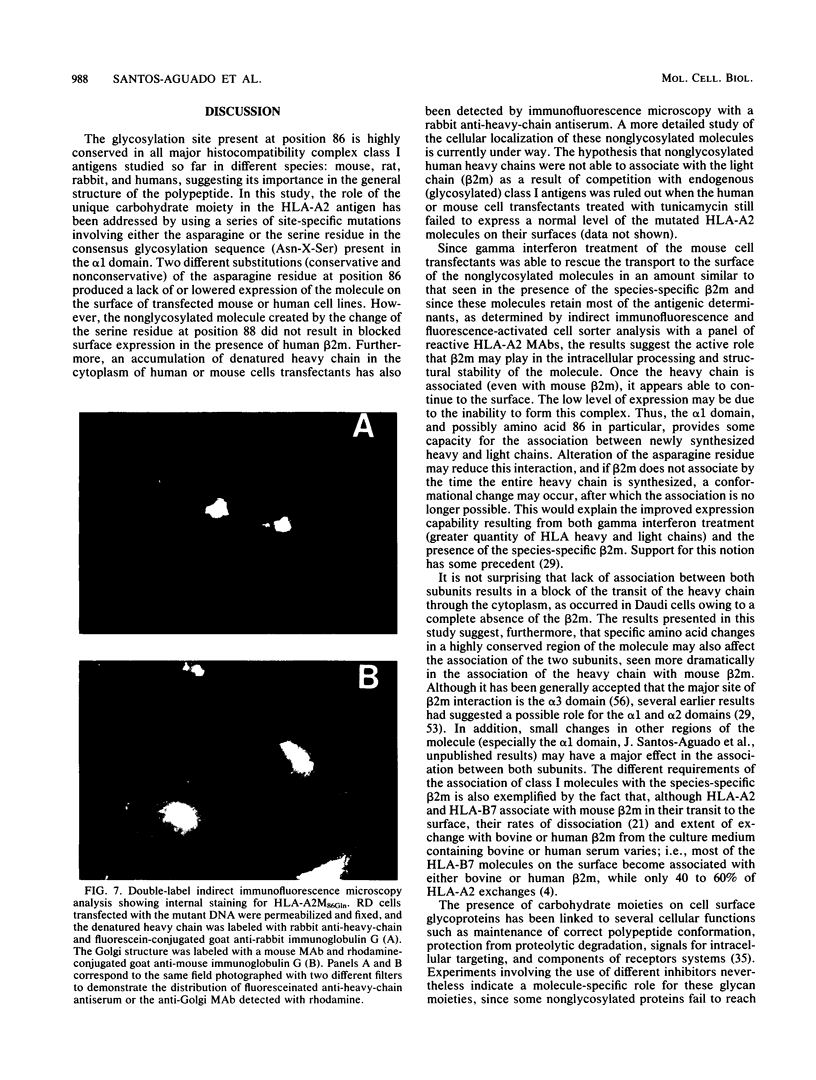


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Rose J. K. Structural requirements of a membrane-spanning domain for protein anchoring and cell surface transport. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J. A., Kamarck M. E., Biro P. A., Weissman S. M., Ruddle F. H. Identification of human genomic clones coding the major histocompatibility antigens HLA-a2 and HLA-B7 by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6327–6331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernabeu C., Maziarz R., Murre C., Terhorst C. beta 2-Microglobulin from serum associates with several class I antigens expressed on the surface of mouse L-cells. Mol Immunol. 1985 Aug;22(8):955–960. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernabeu C., van de Rijn M., Lerch P. G., Terhorst C. P. Beta 2-microglobulin from serum associates with MHC class I antigens on the surface of cultured cells. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):642–645. doi: 10.1038/308642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Matlin K., Bause E., Legler G., Peyrieras N., Ploegh H. Inhibition of N-linked oligosaccharide trimming does not interfere with surface expression of certain integral membrane proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):551–556. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01845.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Frischauf A., Lehrach H. An integrated and simplified approach to cloning into plasmids and single-stranded phages. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:78–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Wang J. L., Berggård I., Peterson P. A. The complete amino acid sequence of beta 2-microglobulin. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4811–4822. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F., Wagner M., Smiley J. R., Summers W. C. Construction and characterization of a recombinant plasmid encoding the gene for the thymidine kinase of Herpes simplex type 1 virus. Gene. 1979 Nov;7(3-4):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier P., Fontecilla-Camps J. C., Bucchini D., Caillol D. H., Jordan B. R., Lemonnier F. A. Altered structure of HLA class I heavy chains associated with mouse beta-2 microglobulin. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(4):321–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00430798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Pellegrino M. A. Assignment of the major histocompatibility complex to a region of the short arm of human chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1147–1151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gates F. T., 3rd, Coligan J. E., Kindt T. J. Complete amino acid sequence of murine beta 2-microglobulin: structural evidence for strain-related polymorphism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):554–558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R., Leavitt R., Kornfeld S., Schlesinger S. Synthesis and infectivity of vesicular stomatitis virus containing nonglycosylated G protein. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Jones E. A., Van Heyningen V., Solomon E., Bobrow M., Miggiano V., Bodmer W. F. The beta2-microglobulin gene is on chromosome 15 and not in the HL-A region. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):267–269. doi: 10.1038/254267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. Glycosylation allows cell-surface transport of an anchored secretory protein. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamarck M. E., Barbosa J. A., Ruddle F. H. Somatic cell genetic analysis of HLA-A, B, C and human beta 2-microglobulin expression. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 May;8(3):385–402. doi: 10.1007/BF01538895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavathas P., Herzenberg L. A. Stable transformation of mouse L cells for human membrane T-cell differentiation antigens, HLA and beta 2-microglobulin: selection by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):524–528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefford R. F., Calabi F., Fearnley I. M., Burrone O. R., Milstein C. Serum beta 2-microglobulin binds to a T-cell differentiation antigen and increases its expression. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):641–642. doi: 10.1038/308641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Assembly and maturation of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens in vivo. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):979–991. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90210-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancet D., Parham P., Strominger J. L. Heavy chain of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens is conformationally labile: a possible role for beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3844–3848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Parham P., Rust N., Brodsky F. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes an antigenic determinant shared by HLA A2 and B17. Hum Immunol. 1980 Sep;1(2):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(80)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J., Appella E., Zhao H., Forman J., Ozato K. Expression and function of a nonglycosylated major histocompatibility class I antigen. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):856–871. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Parent J. B., White S. L. Carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins. A re-evaluation of their function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 12;650(4):209–232. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Kissonerghis A. M., Lodish H. F. Biosynthesis of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9678–9684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Alpert B. N., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Carbohydrate moiety of HLA antigens. Antigenic properties and amino acid sequences around the site of glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7555–7567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibody to a human histocompatibility alloantigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):397–399. doi: 10.1038/276397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Brodsky F. M. Partial purification and some properties of BB7.2. A cytotoxic monoclonal antibody with specificity for HLA-A2 and a variant of HLA-A28. Hum Immunol. 1981 Dec;3(4):277–299. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. C., Strominger J. L. Subunit interactions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5543–5550. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Cannon L. E., Strominger J. L. Cell-free translation of the mRNAs for the heavy and light chains of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2273–2277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Stominger J. L. Biosynthesis and cell surface localization of nonglycosylated human histocompatibility antigens. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):270–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesney-Huneeus V., Wiley M. H., Siperstein M. D. Essential role for mevalonate synthesis in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Berissi H., Weissenbach J., Maroteaux L., Fellous M., Revel M. The beta2-microglobulin mRNA in human Daudi cells has a mutated initiation codon but is still inducible by interferon. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):239–243. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sege K., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Role of beta2-microglobulin in the intracellular processing of HLA antigens. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4523–4530. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinsson L., Peterson P. A. Beta 2-microglobulin induces intracellular transport of human class I transplantation antigen heavy chains in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):226–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Evans G. A., Appella E., Ozato K. In vitro mutagenesis of a mouse MHC class I gene for the examination of structure-function relationships. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):623–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear B. T., Kornbluth J., Strominger J. L., Wilson D. B. Evidence for a shared HLA-A intralocus determinant defined by monoclonal antibody 131. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1802–1810. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trägårdh L., Wiman K., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Fragmentation of the human transplantation antigen heavy chain by limited proteolysis, acid cleavage, and cyanogen bromide treatment. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1322–1328. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. Y., Morishima Y., Collins N. H., Alton T., Pollack M. S., Yunis E. J., Dupont B. Comparison of one-dimensional IEF patterns for serologically detectable HLA-A and B allotypes. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(3):217–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00364765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama K., Nathenson S. G. Intramolecular organization of Class I H-2 MHC antigens; localization of the alloantigenic determinants and the beta 2 m binding site to different regions of the H-2 Kb glycoprotein. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1419–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]