Abstract
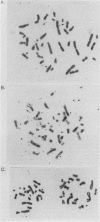
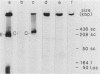
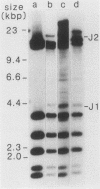
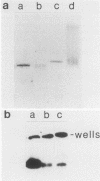
In a previous study (G. M. Wahl, B. Robert de Saint Vincent, and M. L. De Rose, Nature (London) 307:516-520, 1984), we used gene transfer of a CAD cosmid to demonstrate that gene position profoundly affects amplification frequency. One transformant, T5, amplified the donated CAD genes at a frequency at least 100-fold higher than did the other transformants analyzed. The CAD genes in T5 and two drug-resistant derivatives were chromosomally located. In this report, we show that a subclone of T5 gives rise to an extrachromosomal molecule (CAD episome) containing the donated CAD genes. Gel electrophoresis indicated that the CAD episome is approximately 250 to 300 kilobase pairs, and a variety of methods showed that it is a covalently closed circle. We show that the CAD episome replicates semiconservatively and approximately once per cell cycle. Since the CAD cosmid, which comprises most of the CAD episome, does not replicate autonomously when transfected into cells, our results indicate that either the process which generated the episome resulted in a cellular origin of DNA replication being linked to the CAD sequences or specific rearrangements within the episome generated a functional origin. The implications of these results for mechanisms of gene amplification and the genesis of minute chromosomes are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair G. M., Stallings R. L., Nairn R. S., Siciliano M. J. High-frequency structural gene deletion as the basis for functional hemizygosity of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5961–5964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Roth J. Spontaneous tandem genetic duplications in Salmonella typhimurium arise by unequal recombination between rRNA (rrn) cistrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3113–3117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshir F., Giulotto E., Zieg J., Brison O., Liao W. S., Stark G. R. Structure of amplified DNA in different Syrian hamster cell lines resistant to N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2076–2088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaban-Malenbaum G., Gilbert F. Double minute chromosomes and the homogeneously staining regions in chromosomes of a human neuroblastoma cell line. Science. 1977 Nov 18;198(4318):739–741. doi: 10.1126/science.71759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker P. E. Double minutes in human tumor cells. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1982 Feb;5(1):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(82)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker P. E., Drwinga H. L., Hittelman W. N., Maddox A. M. Double minutes replicate once during S phase of the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Dec;130(2):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Haase A. T. Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Selegue J. E., Heintz N. H. Isolation of the origin of replication associated with the amplified Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7790–7794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins K. D., Stark G. R. Aspartate transcarbamylase. Interaction with the transition state analogue N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6599–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. K. Double minutes and homogeneously staining regions: gene amplification in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:21–59. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Perle M. A., Latt S. A. High resolution analysis of the timing of replication of specific DNA sequences during S phase of mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4753–4774. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M., Fried M. Large inverted duplications are associated with gene amplification. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Medveczky P., Sairenji T., Mulder C. Detection of circular and linear herpesvirus DNA molecules in mammalian cells by gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey E. P., Santi D. V. Stable amplified DNA in drug-resistant Leishmania exists as extrachromosomal circles. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):535–540. doi: 10.1126/science.3726545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N. Unstable expression and amplification of a transfected oncogene in confluent and subconfluent cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1456–1464. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Björck E., Bjursell G., Lindahl T. Sequence complexity of circular Epstein-Bar virus DNA in transformed cells. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):11–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.11-19.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber D. A., Schimke R. T. Unstable amplification of an altered dihydrofolate reductase gene associated with double-minute chromosomes. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamkalo B. A., Farnham P. J., Johnston R., Schimke R. T. Ultrastructural features of minute chromosomes in a methotrexate-resistant mouse 3T3 cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1126–1130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Milbrandt J. D., Greisen K. S., Hamlin J. L. Cloning of the initiation region of a mammalian chromosomal replicon. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):439–441. doi: 10.1038/302439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell N., Belli T. A., Zaczkiewicz L. T., Belli J. A. High-level, unstable adriamycin resistance in a Chinese hamster mutant cell line with double minute chromosomes. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):4023–4029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. S., Potter S. S. L1 sequences in HeLa extrachromosomal circular DNA: evidence for circularization by homologous recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1989–1993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Schimke R. T. Amplification and loss of dihydrofolate reductase genes in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1069–1076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyama R., Matsui H., Oishi M. A repetitive DNA family (Sau3A family) in human chromosomes: extrachromosomal DNA and DNA polymorphism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4665–4669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S. Carcinogen-mediated amplification of viral DNA sequences in simian virus 40-transformed Chinese hamster embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6144–6148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani B. D., Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in a single cell cycle in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1901–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Carnright D. V. Biochemical genetic analysis of pyrimidine biosynthesis in mammalian cells: I. Isolation of a mutant defective in the early steps of de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Sep;3(5):483–495. doi: 10.1007/BF01539120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini S., Dailey L., Basilico C. Amplification and excision of integrated polyoma DNA sequences require a functional origin of replication. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):943–949. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Wigler M. Genetic and physical linkage of exogenous sequences in transformed cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Léopold P., Vailly J., Cuzin F. Germ line transmission of autonomous genetic elements in transgenic mouse strains. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90876-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Ripley S., Henderson A. S., Axel R. Transforming DNA integrates into the host chromosome. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sherwood S. W., Hill A. B., Johnston R. N. Overreplication and recombination of DNA in higher eukaryotes: potential consequences and biological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C. W., Krolewski J. J., Rush M. G. Selective trapping of circular double-stranded DNA molecules in solidifying agarose. Plasmid. 1982 May;7(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Mahowald A. P. A chromosome inversion alters the pattern of specific DNA replication in Drosophila follicle cells. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90374-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C. The organization and amplification of two chromosomal domains containing Drosophila chorion genes. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. Phorbol ester dramatically increases incidence of methotrexate-resistant mouse cells: possible mechanisms and relevance to tumor promotion. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Robert de Saint Vincent B., DeRose M. L. Effect of chromosomal position on amplification of transfected genes in animal cells. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):516–520. doi: 10.1038/307516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Vitto L., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Single-copy and amplified CAD genes in Syrian hamster chromosomes localized by a highly sensitive method for in situ hybridization. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):308–319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z. Y., Veldman G. M., Cowie A., Carr A., Schaffhausen B., Kamen R. Construction and functional characterization of polyomavirus genomes that separately encode the three early proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):170–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.170-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Cicco D. V., Spradling A. C. Localization of a cis-acting element responsible for the developmentally regulated amplification of Drosophila chorion genes. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90525-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Vincent B. R., Delbrück S., Eckhart W., Meinkoth J., Vitto L., Wahl G. The cloning and reintroduction into animal cells of a functional CAD gene, a dominant amplifiable genetic marker. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90410-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Vincent B. R., Wahl G. M. Homologous recombination in mammalian cells mediates formation of a functional gene from two overlapping gene fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2002–2006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]