Abstract
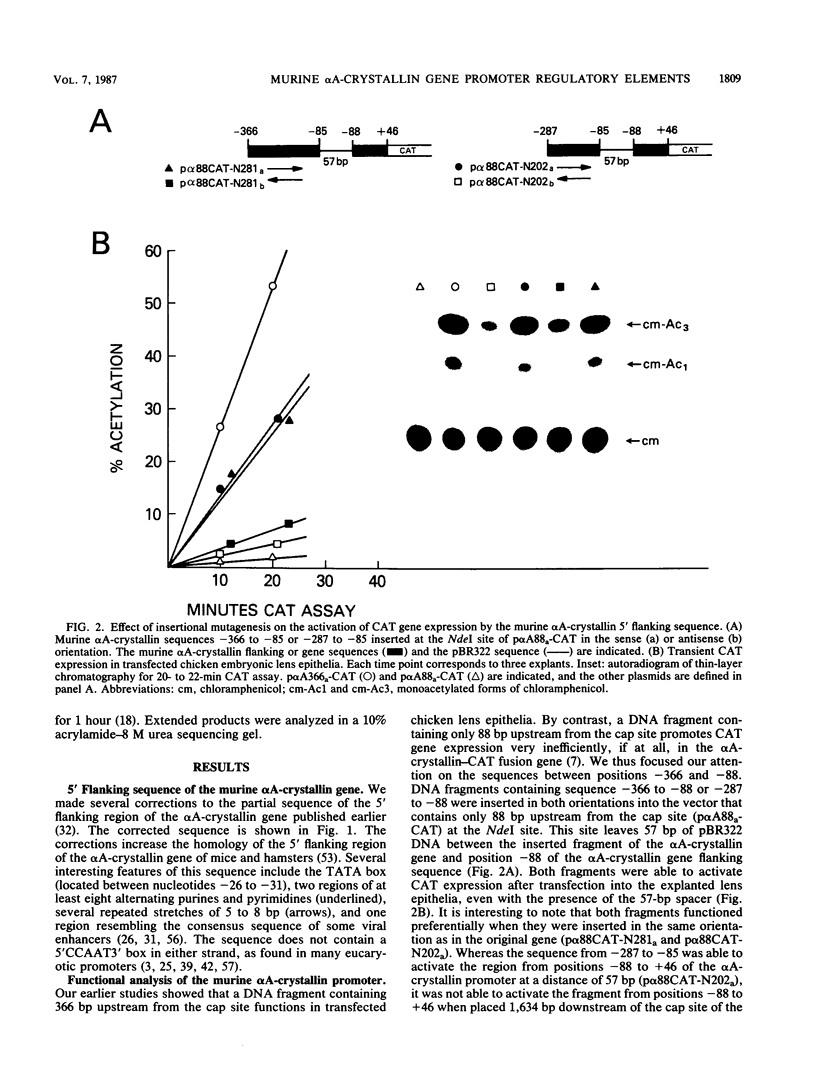
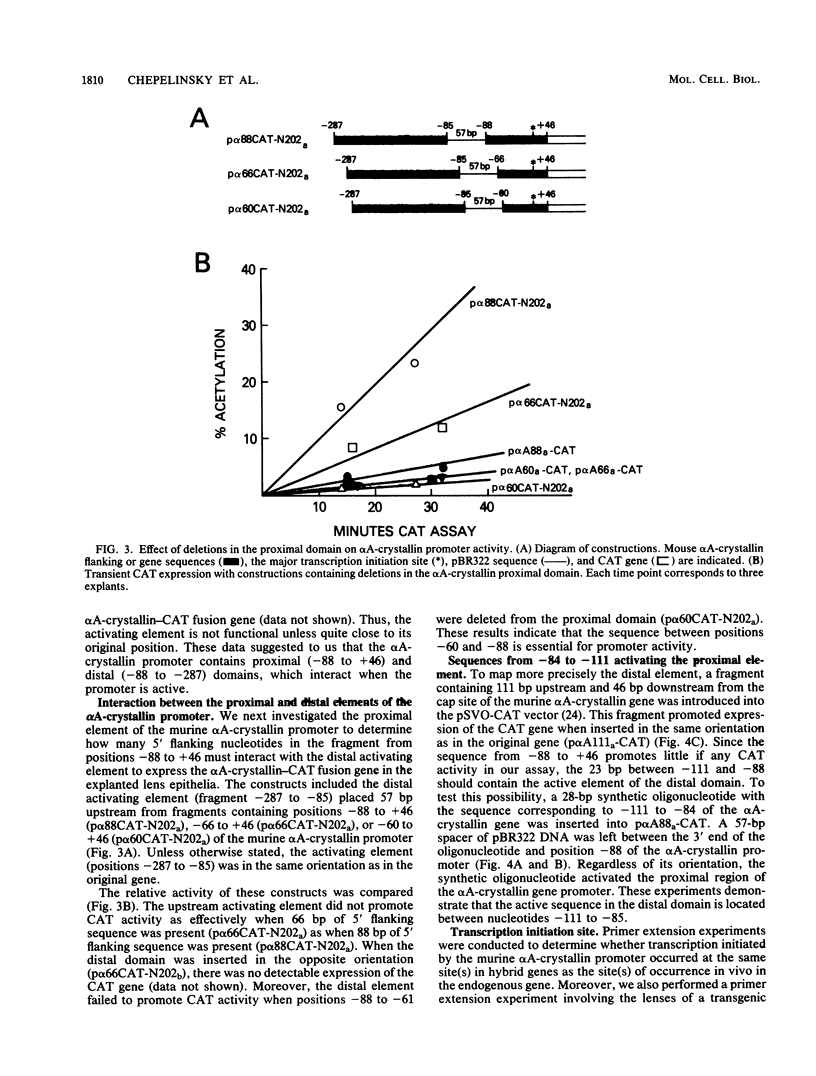
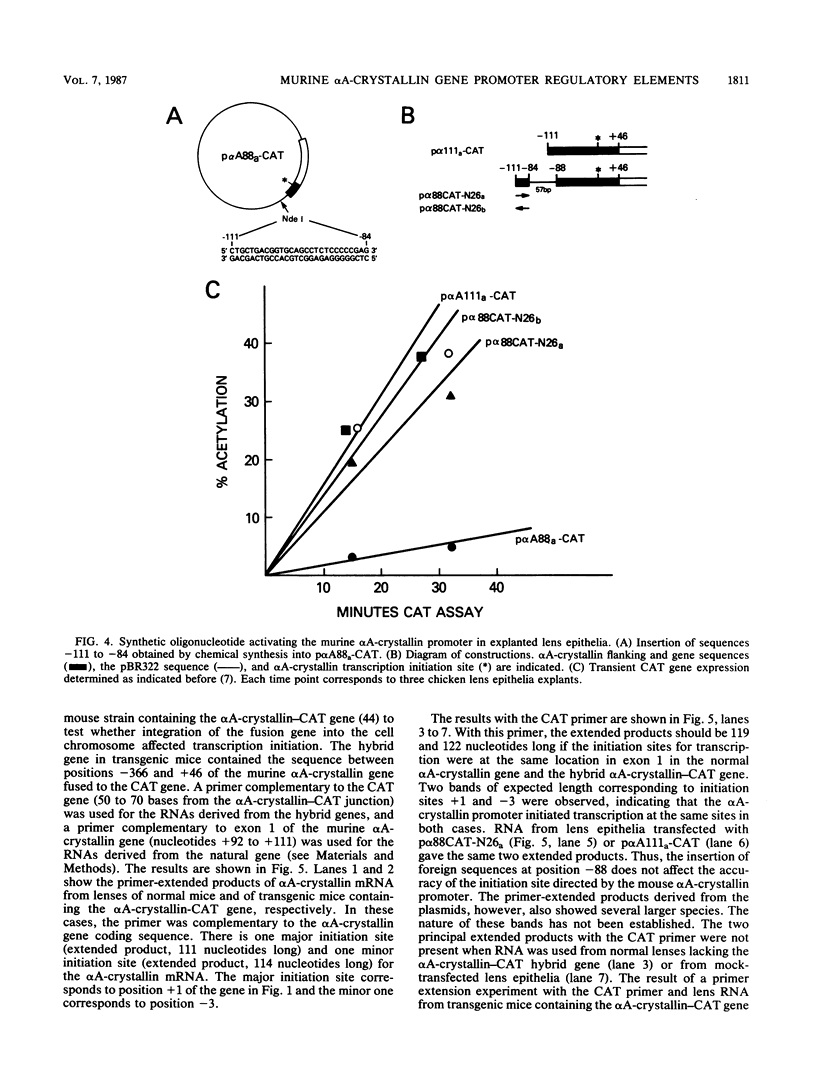
Previous experiments have indicated that 5' flanking DNA sequences (nucleotides-366 to +46) are capable of regulating the lens-specific transcription of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene. Here we have analyzed these 5' regulatory sequences by transfecting explanted embryonic chicken lens epithelia with different alpha A-crystallin-CAT (chloramphenicol acetyltransferase) hybrid genes (alpha A-crystallin promoter sequences fused to the bacterial CAT gene in the pSVO-CAT expression vector). The results indicated the presence of a proximal (-88 to +46) and a distal (-111 to -88) domain which must interact for promoter function. Deletion experiments showed that the sequence between -88 and -60 was essential for function of the proximal domain in the explanted epithelia. A synthetic oligonucleotide containing the sequence between -111 and -84 activated the proximal domain when placed in either orientation 57 base pairs upstream from position -88 of the alpha A-crystallin-CAT hybrid gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ares M., Jr, Mangin M., Weiner A. M. Orientation-dependent transcriptional activator upstream of a human U2 snRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1560–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman Y., Rice D., Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Two regulatory elements for immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7041–7045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Heat shock regulatory elements function as an inducible enhancer in the Xenopus hsp70 gene and when linked to a heterologous promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90789-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendal H. Lens proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;12(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238209105849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrás T., Nickerson J. M., Chepelinsky A. B., Piatigorsky J. Structural and functional evidence for differential promoter activity of the two linked delta-crystallin genes in the chicken. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):445–452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulet A. M., Erwin C. R., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific enhancers in the rat exocrine pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3599–3603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chepelinsky A. B., King C. R., Zelenka P. S., Piatigorsky J. Lens-specific expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene promoted by 5' flanking sequences of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene in explanted chicken lens epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2334–2338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dente L., Cortese R. Cell-specific expression of a transfected human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Meselson M. Separate regulatory elements for the heat-inducible and ovarian expression of the Drosophila hsp26 gene. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):737–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Casey J. W. Two elements in the bovine leukemia virus long terminal repeat that regulate gene expression. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1437–1440. doi: 10.1126/science.3006241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps J., Meijlink F., Verma I. M. Identification of a transcriptional enhancer element upstream from the proto-oncogene fos. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1174–1177. doi: 10.1126/science.3865371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Coen D. M., McKnight S. L. Promoter domains required for expression of plasmid-borne copies of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in virus-infected mouse fibroblasts and microinjected frog oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1940–1947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J., Stafford J., Queen C. An immunoglobulin promoter displays cell-type specificity independently of the enhancer. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):423–425. doi: 10.1038/315423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Bich-Thuy L. T., Stafford J., Queen C. Synergism between immunoglobulin enhancers and promoters. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):383–385. doi: 10.1038/322383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal T. V., Shimada T., Baur A. W., Nienhuis A. W. Contribution of promoter to tissue-specific expression of the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1102–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.2994213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P. Magic enhancers? DNA. 1984;3(1):1–5. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Kondoh H., Yasuda K., Soma G., Ikawa Y., Okada T. S. Tissue-specific regulation of a chicken delta-crystallin gene in mouse cells: involvement of the 5' end region. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2201–2207. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg D., Tsui L. C., Gorin M., Breitman M. L. Characterization of the human beta-crystallin gene Hu beta A3/A1 reveals ancestral relationships among the beta gamma-crystallin superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12420–12427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., Chamberlain J. S., Buskin J. N., Johnson J. E., Hauschka S. D. Transcriptional regulation of the muscle creatine kinase gene and regulated expression in transfected mouse myoblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2855–2864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Piatigorsky J. Alternative RNA splicing of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene: protein-coding information within an intron. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):707–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Piatigorsky J. Alternative splicing of alpha A-crystallin RNA. Structural and quantitative analyses of the mRNAs for the alpha A2- and alpha Ains-crystallin polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1822–1826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok S., Tsui L. C., Shinohara T., Piatigorsky J., Gold R., Breitman M. Analysis of the mouse gamma-crystallin gene family: assignment of multiple cDNAs to discrete genomic sequences and characterization of a representative gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4517–4529. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakin S. O., Breitman M. L., Tsui L. C. Structural and evolutionary relationships among five members of the human gamma-crystallin gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1408–1414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Yasuda K., Kondoh H., Okada T. S. DNA sequences responsible for tissue-specific expression of a chicken alpha-crystallin gene in mouse lens cells. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2589–2595. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03975.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek P. A., Chepelinsky A. B., Khillan J. S., Piatigorsky J., Westphal H. Lens-specific expression and developmental regulation of the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene driven by the murine alpha A-crystallin promoter in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J. Gene expression and genetic engineering in the lens. Friedenwald lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Jan;28(1):9–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J. Lens crystallins and their gene families. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):620–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax-Jeuken Y., Quax W., van Rens G., Khan P. M., Bloemendal H. Complete structure of the alpha B-crystallin gene: conservation of the exon-intron distribution in the two nonlinked alpha-crystallin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5819–5823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. The yeast his3 promoter contains at least two distinct elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7385–7389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Kingston R. E., Morimoto R. I. Human HSP70 promoter contains at least two distinct regulatory domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):629–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaan J. The appearance of alpha-crystallin in relation to cell cycle phase in the embryonic mouse lens. Dev Biol. 1983 Mar;96(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90320-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Dunnen J. T., Moormann R. J., Cremers F. P., Schoenmakers J. G. Two human gamma-crystallin genes are linked and riddled with Alu-repeats. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Dunnen J. T., Moormann R. J., Lubsen N. H., Schoenmakers J. G. Concerted and divergent evolution within the rat gamma-crystallin gene family. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90379-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Dunnen J. T., Moormann R. J., Lubsen N. H., Schoenmakers J. G. Intron insertions and deletions in the beta/gamma-crystallin gene family: the rat beta B1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2855–2859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel R., Hendriks W., Quax W., Bloemendal H. Complete structure of the hamster alpha A crystallin gene. Reflection of an evolutionary history by means of exon shuffling. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




