Abstract
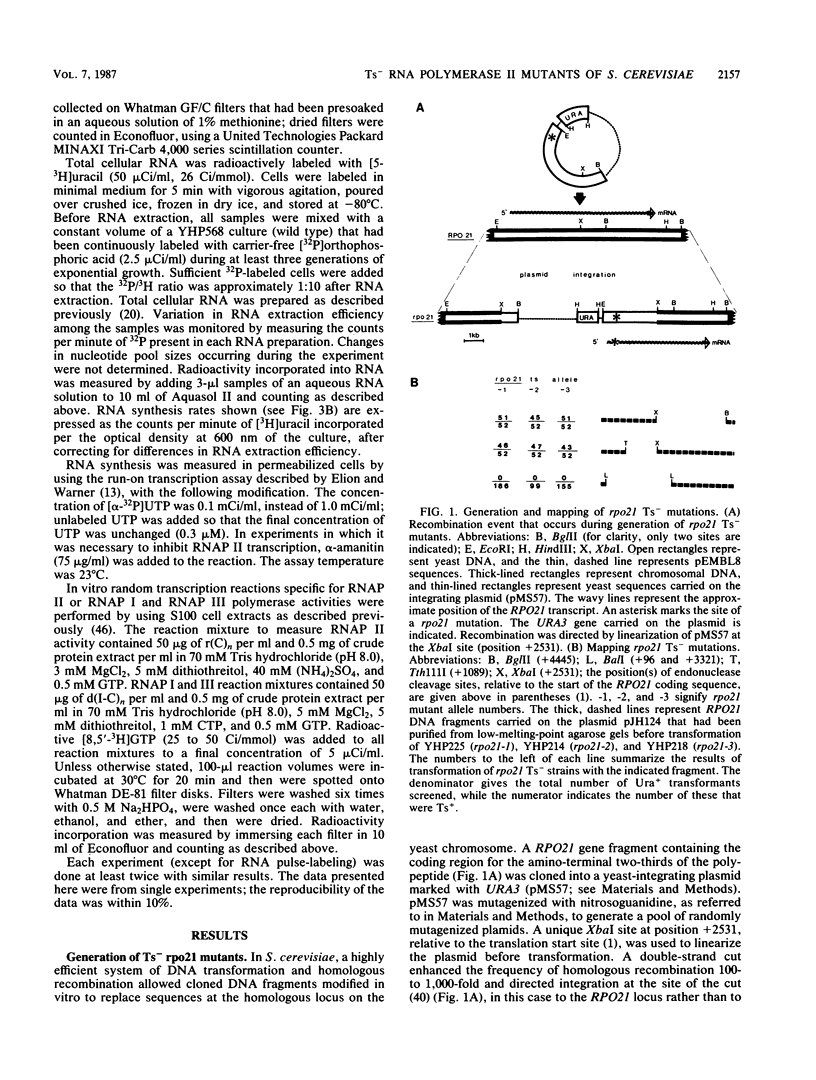
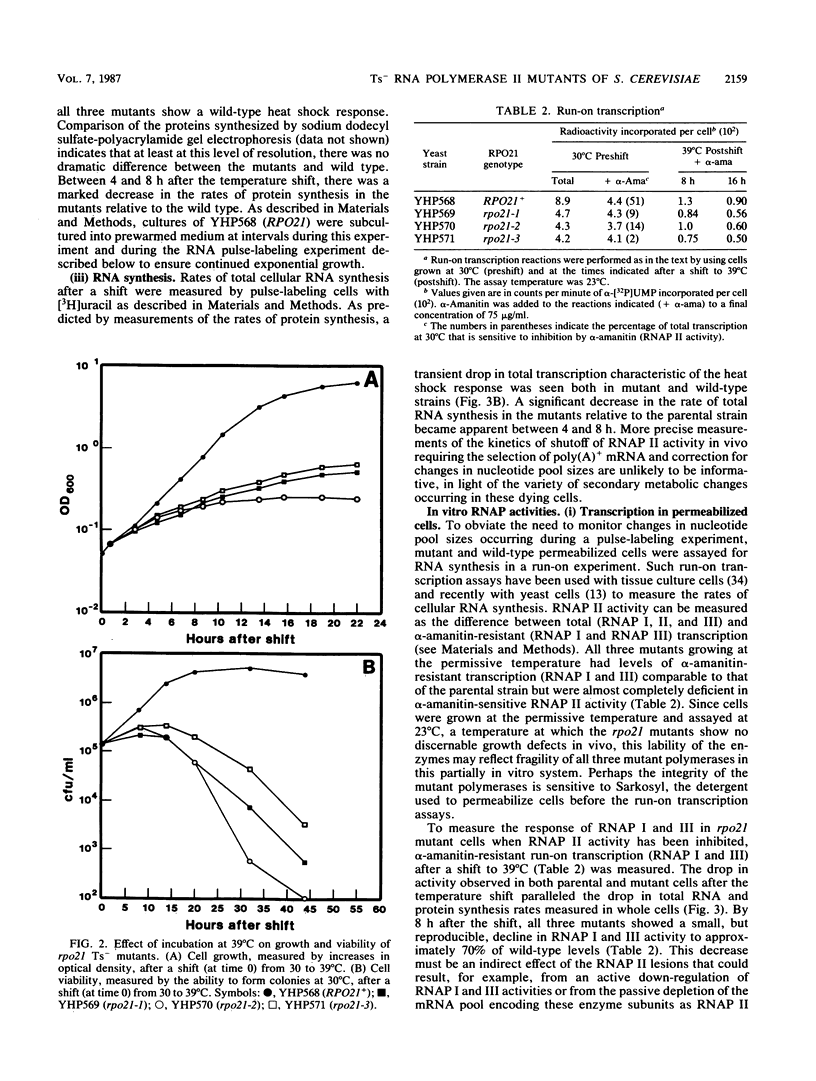
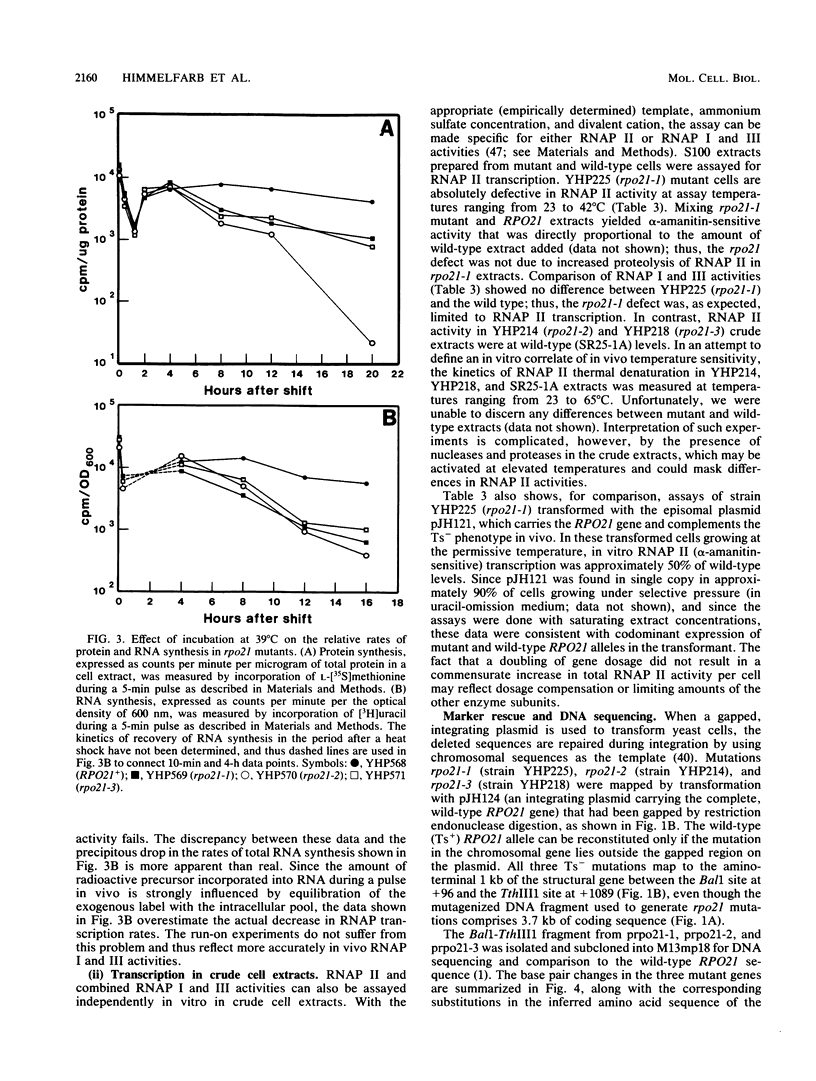
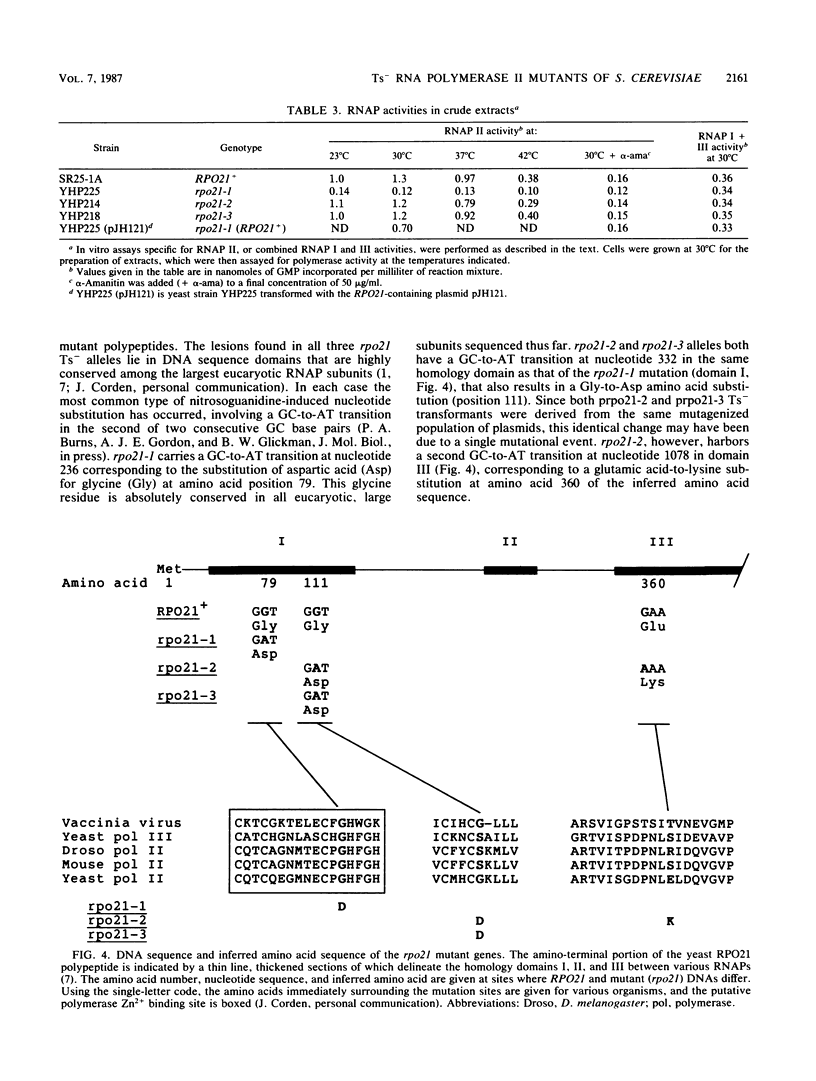
Three independent, recessive, temperature-sensitive (Ts-) conditional lethal mutations in the largest subunit of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) have been isolated after replacement of a portion of the wild-type gene (RPO21) by a mutagenized fragment of the cloned gene. Measurements of cell growth, viability, and total RNA and protein synthesis showed that rpo21-1, rpo21-2, and rpo21-3 mutations caused a slow shutoff of RNAP II activity in cells shifted to the nonpermissive temperature (39 degrees C). Each mutant displayed a distinct phenotype, and one of the mutant enzymes (rpo21-1) was completely deficient in RNAP II activity in vitro. RNAP I and RNAP III in vitro activities were not affected. These results were consistent with the notion that the genetic lesions affect RNAP II assembly or holoenzyme stability. DNA sequencing revealed that in each case the mutations involved nonconservative amino acid substitutions, resulting in charge changes. The lesions harbored by all three rpo21 Ts- alleles lie in DNA sequence domains that are highly conserved among genes that encode the largest subunits of RNAP from a variety of eucaryotes; one mutation lies in a possible Zn2+ binding domain.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs J., Searles L. L., Greenleaf A. L. Structure of the eukaryotic transcription apparatus: features of the gene for the largest subunit of Drosophila RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Moss B. Homology between RNA polymerases of poxviruses, prokaryotes, and eukaryotes: nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of vaccinia virus genes encoding 147-kDa and 22-kDa subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3141–3145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bréant B., Huet J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Analysis of yeast RNA polymerases with subunit-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11968–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhler J. M., Huet J., Davies K. E., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Immunological studies of yeast nuclear RNA polymerases at the subunit level. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9949–9954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V. L., Whitmore G. F., Siminovitch L. Mammalian cells with altered forms of RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3119–3123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., Khalili K., Zandomeni R., Weinmann R. The gene encoding the large subunit of human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15204–15210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Thomas M., Cameron J., St John T. P., Scherer S., Padgett R. A. Rapid DNA isolations for enzymatic and hybridization analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):404–411. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2089–2097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk K. H., Mazus B., Ulpino L., Vallee B. L. Euglena gracilis DNA dependent RNA polymerase II: a zinc metalloenzyme. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4468–4475. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen J. D., Tropak M., An G. Mutations in the rpIJ leader of Escherichia coli that abolish feedback regulation. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90455-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda R., Ishihama A. Subunits of RNA polymerase in function and structure; Maturation in vitro of core enzyme from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 15;87(3):523–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Borsett L. M., Jiamachello P. F., Coulter D. E. Alpha-amanitin-resistant D. melanogaster with an altered RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Fields D. A., Bautz E. K. Characterization of a ts beta' mutant RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Sep 23;147(3):337–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00582886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guialis A., Morrison K. E., Ingles C. J. Regulated synthesis of RNA polymerase II polypeptides in Chinese hamster ovary cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4171–4176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelfarb H. J., Maicas E., Friesen J. D. Isolation of the SUP45 omnipotent suppressor gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and characterization of its gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):816–822. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Spot-immunodetection of conserved determinants in eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Study with antibodies to yeast RNA polymerases subunits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2613–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J., Himmelfarb H. J., Shales M., Greenleaf A. L., Friesen J. D. Identification, molecular cloning, and mutagenesis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J. Temperature-sensitive RNA polymerase II mutations in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):405–409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gniazdowski M., Mandel J. L., Jr, Gissinger F., Chambon P. Alpha-amanitin: a specific inhibitor of one of two DNA-pendent RNA polymerase activities from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. A new mapping method employing a meiotic rec-mutant of yeast. Genetics. 1982 Mar;100(3):387–412. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroute F., Huet J., Exinger F. Dominant and semidominant mutations leading to thermosensitivity of ribonucleic acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):847–854. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.847-854.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattke H., Weser U. Yeast RNA-polymerase B: A zinc protein. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jun 15;65(3):288–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Xuong N. H., Geiduschek E. P. A response of protein synthesis to temperature shift in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5222–5225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Xuong N. H., Geiduschek E. P. Quantitative analysis of the heat shock response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):311–327. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.311-327.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollis D. L., Brick P., Hamlin R., Xuong N. G., Steitz T. A. Structure of large fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I complexed with dTMP. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):762–766. doi: 10.1038/313762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Multiple, tandem plasmid integration in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):747–749. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Monastyrskaya G. S., Gubanov V. V., Guryev S. O., Salomatina I. S., Shuvaeva T. M., Lipkin V. M., Sverdlov E. D. The primary structure of E. coli RNA polymerase, Nucleotide sequence of the rpoC gene and amino acid sequence of the beta'-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):4035–4044. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Segall J. Characterization and mutational analysis of a cluster of three genes expressed preferentially during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2443–2451. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petranyi P., Jendrisak J. J., Burgess R. R. RNA polymerase II from wheat germ contains tightly bound zinc. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 7;74(3):1031–1038. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91621-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva M., Memet S., Micouin J. Y., Huet J., Treich I., Dassa J., Young R., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Isolation of structural genes for yeast RNA polymerases by immunological screening. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1554–1558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruet A., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A specific assay for yeast RNA polymerases in crude cell extracts. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct;90(2):325–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruet A., Sentenac A., Fromageot P., Winsor B., Lacroute F. A mutation of the B220 subunit gene affects the structural and functional properties of yeast RNA polymerase B in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6450–6455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. D., Hall B. D. Transcription in yeast: alpha-amanitin sensitivity and other properties which distinguish between RNA polymerases I and III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1029–1033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles L. L., Jokerst R. S., Bingham P. M., Voelker R. A., Greenleaf A. L. Molecular cloning of sequences from a Drosophila RNA polymerase II locus by P element transposon tagging. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Novick P., Botstein D. Construction and genetic characterization of temperature-sensitive mutant alleles of the yeast actin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4889–4893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thonart P., Bechet J., Hilger F., Burny A. Thermosensitive mutations affecting ribonucleic acid polymerases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):25–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.25-32.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Morris R. W., Faras A., Levinson W., Rutter W. J. Are all nucleotidyl transferases metalloenzymes? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):1036–1041. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks J. R., Coulter D. E., Greenleaf A. L. Immunological studies of RNA polymerase II using antibodies to subunits of Drosophila and wheat germ enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5884–5892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsor B., Lacroute F., Ruet A., Sentenac A. Isolation and characterisation of a strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae deficient in in vitro RNA polymerase B(II) activity. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jun 7;173(2):145–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00330304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


