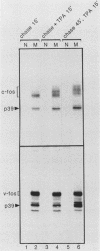
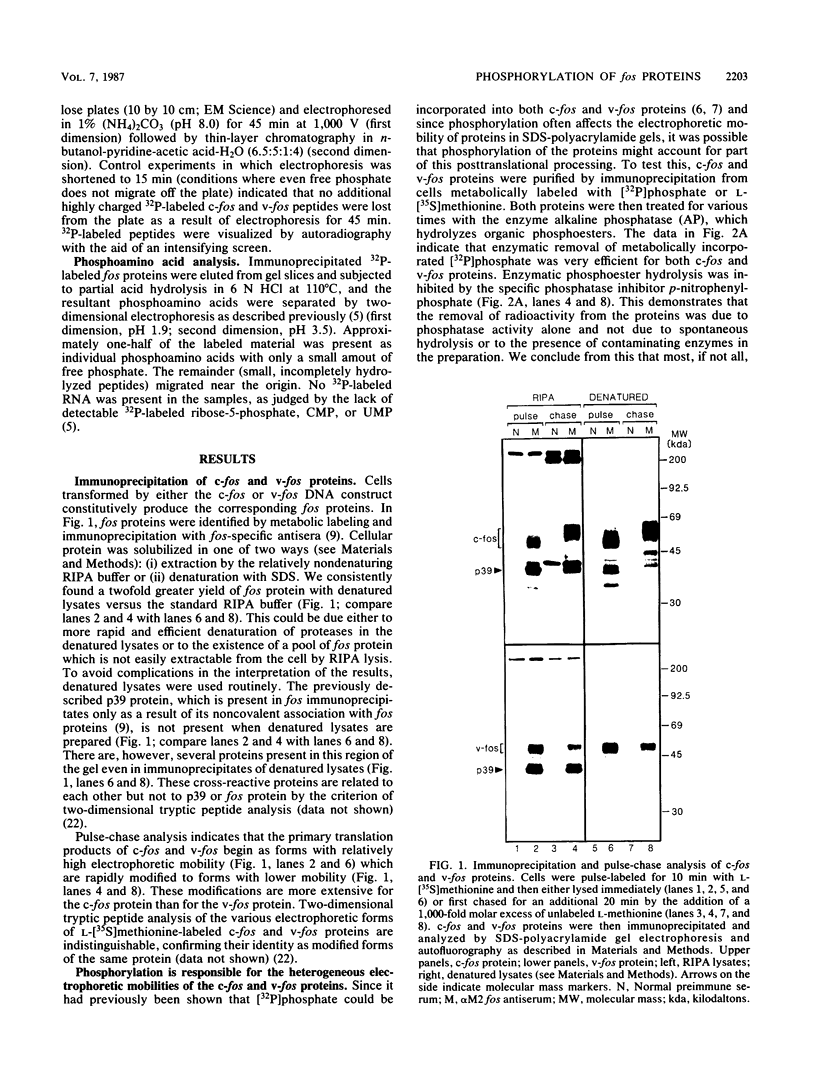
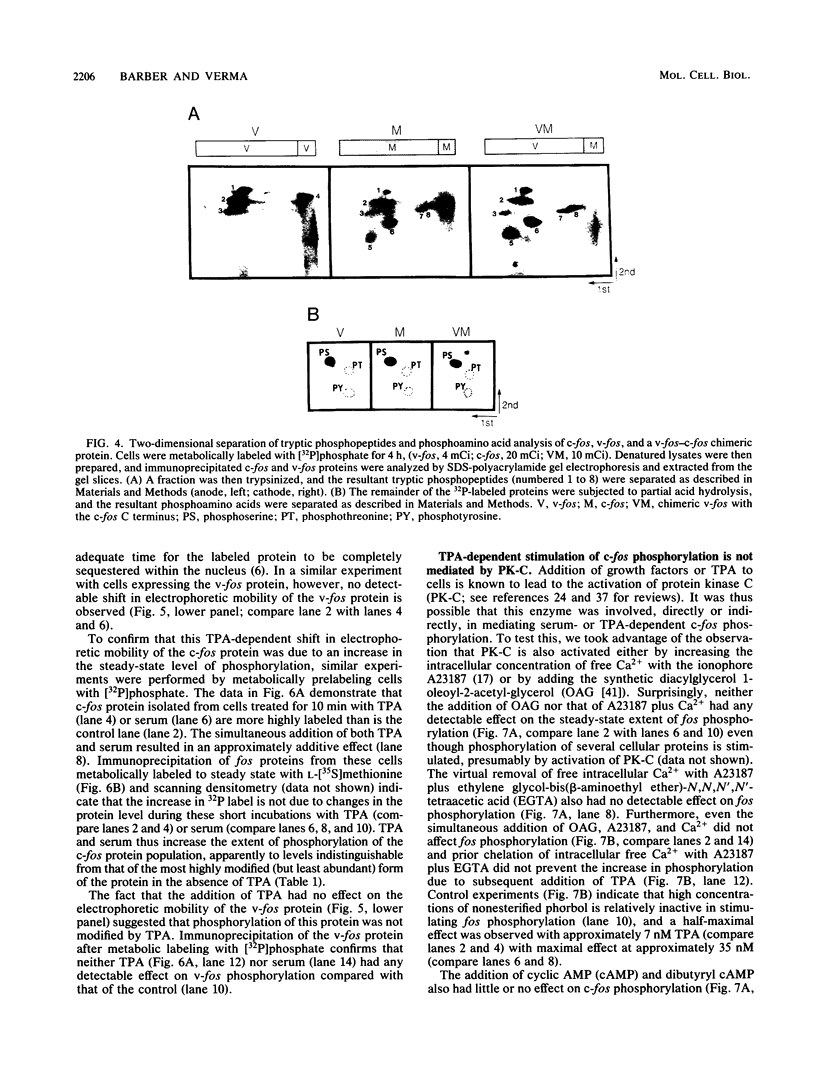
Abstract
We have investigated the covalent modification of the proteins encoded by the murine fos proto-oncogene (c-fos) and that of the corresponding gene product of FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus (v-fos). Both proteins are posttranslationally processed in the cell, resulting in forms with lower electrophoretic mobilities than that of the initial translation product on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Treatment with alkaline phosphatase indicates that most, if not all, of this electrophoretic shift is due to phosphoesterification of both proteins. These phosphoryl groups stoichiometrically modify the v-fos and c-fos proteins on serine residues and turn over rapidly in vivo in the presence of protein kinase inhibitors (half-life, less than 15 min). Direct quantitative comparison of steady-state labeling studies with L-[35S]methionine and [32P]phosphate reveals that the c-fos protein is four- to fivefold more highly phosphorylated than the v-fos protein is. Comparison of tryptic fragments from [32P]phosphate-labeled proteins indicates that although the two proteins have several tryptic phosphopeptides in common, the c-fos protein contains unique major tryptic phosphopeptides that the v-fos protein lacks. These unique sites of c-fos phosphorylation have been tentatively localized to the carboxy-terminal 20 amino acid residues of the protein. Phosphorylation of the c-fos protein, but not the v-fos protein, can be stimulated at least fivefold in vivo by the addition of either 12-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate or serum. This increase in the steady-state degree of phosphorylation of c-fos appears to be independent of protein kinase C since phosphorylation is Ca2+ and diacylglycerol independent. The possible role of phosphorylation of these proteins in cellular transformation is discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard O., Cory S., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Adams J. M. Sequence of the murine and human cellular myc oncogenes and two modes of myc transcription resulting from chromosome translocation in B lymphoid tumours. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2375–2383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A. P., Byus C. V., Slaga T. J. Phosphorylation of histones is stimulated by phorbol esters in quiescent Reuber H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9421–9425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Miller A. D., Zokas L., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins: a comparative analysis. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Teich N. M. Candidate product of the FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus oncogene: characterization of a 55,000-dalton phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Teich N. M. Identification of a 39,000-dalton protein in cells transformed by the FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins are complexed with a 39,000-dalton cellular protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Glass D. B., Krebs E. G. Optimal spatial requirements for the location of basic residues in peptide substrates for the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4240–4245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel M. P., Biskis B. O., Jinkins P. B. Virus induction of osteosarcomas in mice. Science. 1966 Feb 11;151(3711):698–701. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3711.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., King W. C., Nist C., Mitchell C. D., Ross R. Early changes in phosphatidylinositol and arachidonic acid metabolism in quiescent swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12329–12335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by v-myc and c-myc oncogenes: identification and localization in acute leukemia virus transformants and bursal lymphoma cell lines. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassauer M., Scheidtmann K. H., Walter G. Mapping of phosphorylation sites in polyomavirus large T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):805–816. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.805-816.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf J. L., Lee M. H., Sultzman L. A., Kriz R. W., Loomis C. R., Hewick R. M., Bell R. M. Cloning and expression of multiple protein kinase C cDNAs. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90874-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Smith J. B., Berkow R. L. Bryostatin, an activator of the calcium phospholipid-dependent protein kinase, blocks phorbol ester-induced differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells HL-60. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1334–1338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutter D., Caldwell A. B., Morin M. J. Dissociation of protein kinase C activation from phorbol ester-induced maturation of HL-60 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5979–5984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Skelly H., Botteri F., van der Putten H., Barber J. R., Verma I. M., Leffert H. L. Proto-oncogene expression in regenerating liver is simulated in cultures of primary adult rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7929–7933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Schatzman R. C., Turner R. S., Mazzei G. J. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase: a major protein phosphorylation system. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 May;35(2-3):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Huebner R. J. Studies of FBJ osteosarcoma virus in tissue culture. I. Biologic characteristics of the "C"-type viruses. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Aug;51(2):525–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacConnell W. P., Verma I. M. Expression of FBJ-MSV oncogene (fos) product in bacteria. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90504-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Deana A. D., Pinna L. A. A study with model substrates of the structure of the sites phosphorylated by rat liver casein kinase TS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 13;662(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijlink F., Curran T., Miller A. D., Verma I. M. Removal of a 67-base-pair sequence in the noncoding region of protooncogene fos converts it to a transforming gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4987–4991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Curran T., Verma I. M. c-fos protein can induce cellular transformation: a novel mechanism of activation of a cellular oncogene. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Henning-Chubb C., Huberman E., Verma I. M. c-fos expression is neither sufficient nor obligatory for differentiation of monomyelocytes to macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Zokas L., Schreiber R. D., Verma I. M. Rapid induction of the expression of proto-oncogene fos during human monocytic differentiation. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Todd J. A., Hesketh T. R., Metcalfe J. C. c-fos and c-myc gene activation, ionic signals, and DNA synthesis in thymocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8158–8162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Slamon D. J., Tremblay J. M., Cline M. J., Verma I. M. Differential expression of cellular oncogenes during pre- and postnatal development of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):640–644. doi: 10.1038/299640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patskan G. J., Baxter C. S. Specific stimulation of histone H2B and H4 phosphorylation in mouse lymphocytes by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):12899–12903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quade K. Transformation of mammalian cells by avian myelocytomatosis virus and avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90569-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Hayman M. J., Bister K. Phosphorylation of specific sites in the gag-myc polyproteins encoded by MC29-type viruses correlates with their transforming ability. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1111–1116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Rodriguez-Pena A., Coombs M., Sinnett-Smith J. Diacylglycerol stimulates DNA synthesis and cell division in mouse 3T3 cells: role of Ca2+-sensitive phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5748–5752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Rodriguez-Pena M., Smith K. A. Phorbol esters, phospholipase C, and growth factors rapidly stimulate the phosphorylation of a Mr 80,000 protein in intact quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7244–7248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambucetti L. C., Curran T. The Fos protein complex is associated with DNA in isolated nuclei and binds to DNA cellulose. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1417–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.3491427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambucetti L. C., Schaber M., Kramer R., Crowl R., Curran T. The fos gene product undergoes extensive post-translational modification in eukaryotic but not in prokaryotic cells. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Raynor R. L., Kuo J. F. N-(6-Aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide(W-7), a calmodulin antagonist, also inhibits phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 4;755(1):144–147. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Echle B., Walter G. Simian virus 40 large T antigen is phosphorylated at multiple sites clustered in two separate regions. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):116–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.116-133.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoyama C., Frunzio R., Liau G., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. Transcriptional activation encoded by the v-fos gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara O., Knecht M., Catt K. J. Differential actions of phorbol ester and diacylglycerol on inhibition of granulosa cell maturation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):468–474. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90930-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Chou W., Rodgers K. Phosphorylation downregulates the DNA-binding activity of simian virus 40 T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):888–894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.888-894.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto A. S., Ponticelli A., Berk A. J., Gaynor R. B. Genetic mapping of a major site of phosphorylation in adenovirus type 2 E1A proteins. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):14–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.14-22.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Curran T., Müller R., Verma I. M. Analysis of FBJ-MuSV provirus and c-fos (mouse) gene reveals that viral and cellular fos gene products have different carboxy termini. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1241–1255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heuverswyn H., Van de Voorde A., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., De Winne P., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of simian virus 40 DNA: structure of the middle segment of the HindII + III restriction fragment B (sixth part of the T antigen gene) and codon usage. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):199–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Phosphorylation patterns of tumour antigens in cells lytically infected or transformed by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):28–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.28-44.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. J., Edlin G. Phosphate transport, nucleotide pools, and ribonucleic acid synthesis in growing and in density-inhibited 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1828–1833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Straaten F., Müller R., Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a human c-onc gene: deduced amino acid sequence of the human c-fos protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3183–3187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]