Abstract
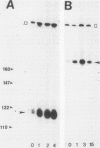
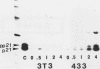
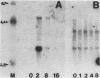
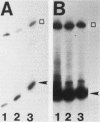
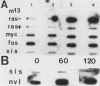
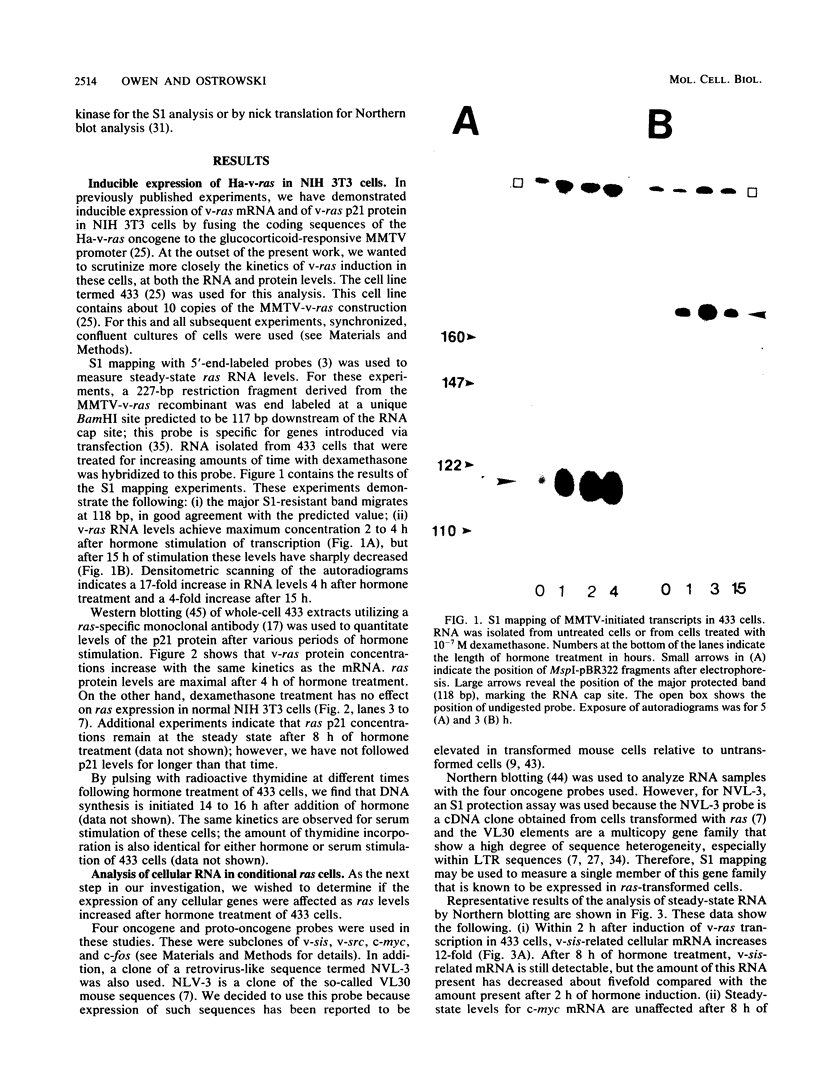
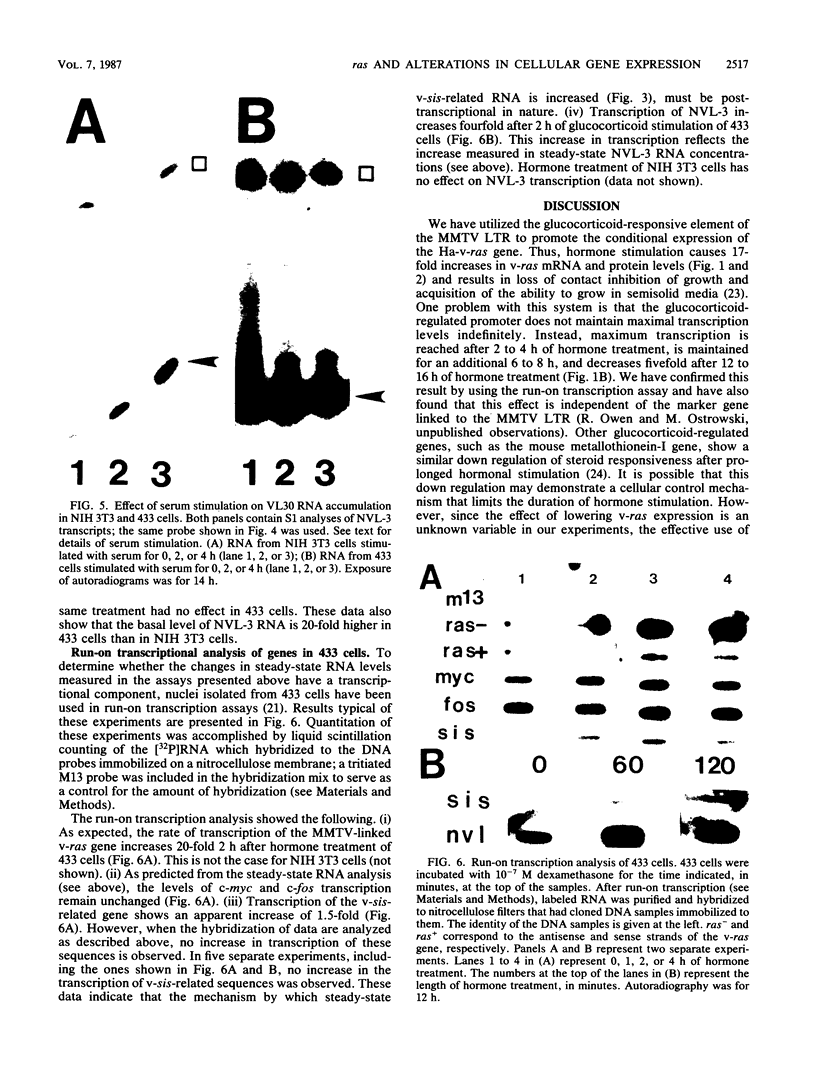
Hormone treatment of NIH 3T3 cells that contain recombinant fusions between the mouse mammary virus long terminal repeat and the v-ras gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus results in conditional expression of the ras p21 gene product. Levels of ras mRNA and p21 are maximal after 2 to 4 h of hormone treatment. Analysis of cellular RNA by Northern blotting and nuclease S1 protection assays indicates that the expression of two cellular RNA species increases with kinetics similar to v-ras: v-sis-related RNA and retrovirus-related VL30 RNA. Run-on transcription in isolated nuclei shows that the increase in v-sis-related RNA is not dependent on transcription and therefore must arise by a post-transcriptional mechanism. The increase in VL30 expression is a transcriptional effect. Hormone treatment of normal NIH 3T3 cells has no effect on the expression of these DNA sequences. These results suggest that v-ras stimulation of autocrine factors may play a role in transformation of cells by this gene and also suggest a reverse genetic strategy to determine the nucleic acid sequences and cellular factors involved in the regulation of gene expression that is observed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anzano M. A., Roberts A. B., De Larco J. E., Wakefield L. M., Assoian R. K., Roche N. S., Smith J. M., Lazarus J. E., Sporn M. B. Increased secretion of type beta transforming growth factor accompanies viral transformation of cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):242–247. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K., Frolik C. A., Roberts A. B., Miller D. M., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor-beta controls receptor levels for epidermal growth factor in NRK fibroblasts. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Viral oncogenes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., Dani C., Chambard J. C., Franchi A., Pouyssegur J., Jeanteur P. c-myc gene is transcribed at high rate in G0-arrested fibroblasts and is post-transcriptionally regulated in response to growth factors. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):443–445. doi: 10.1038/317443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Vogel A., Ross R. Production of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecules and reduced expression of platelet-derived growth factor receptors accompany transformation by a wide spectrum of agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. T., Norton J. D., Avery R. J. A novel approach to cloning transcriptionally active retrovirus-like genetic elements from mouse cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6243–6254. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney M. G., Elder P. K., Steffen D. L., Getz M. J. Evidence for an early evolutionary origin and locus polymorphism of mouse VL30 DNA sequences. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):511–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.511-518.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney M. G., Schmidt L. J., Getz M. J. Organization and expression of endogenous virus-like (VL30) DNA sequences in nontransformed and chemically transformed mouse embryo cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1982 Feb;42(2):569–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Larco J. E., Preston Y. A., Todaro G. J. Properties of a sarcoma-growth-factor-like peptide from cells transformed by a temperature-sensitive sarcoma virus. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Oct;109(1):143–152. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041090116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Ellis R. W., Shih T. Y., Oroszlan S., Shapiro B., Maizel J., Lowy D., Scolnick E. Nucleotide sequence of the p21 transforming protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):934–936. doi: 10.1126/science.6287572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Gross M., Kamata T., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. Microinjection of the oncogene form of the human H-ras (T-24) protein results in rapid proliferation of quiescent cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. N., Schmidt L. J., Hodgson C. P., Moses H. L., Getz M. J. Polyadenylylated RNA complementary to a mouse retrovirus-like multigene family is rapidly and specifically induced by epidermal growth factor stimulation of quiescent cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7317–7321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Picard D., Schaffner W. During B-cell differentiation enhancer activity and transcription rate of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes are high before mRNA accumulation. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14101–14110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Activation of cellular genes by avian RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5351–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager L. J., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of mouse liver metallothionein-I gene by glucocorticoids. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):340–342. doi: 10.1038/291340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. L., Ostrowski M. C., Berard D., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of the Ha-MuSV p21 gene conferred by sequences from mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., Itin A. Patterns of genomic distribution and sequence heterogeneity of a murine "retrovirus-like" multigene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.50-58.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., Shaul Y., Kaminchik J., Aviv H. Heterogeneity of "virus-like" genes encoding retrovirus-associated 30S RNA and their organization within the mouse genome. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90629-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leys E. J., Crouse G. F., Kellems R. E. Dihydrofolate reductase gene expression in cultured mouse cells is regulated by transcript stabilization in the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):180–187. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Curran T., Verma I. M. c-fos protein can induce cellular transformation: a novel mechanism of activation of a cellular oncogene. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch G. H., Potter E., Nicolaisen A. K., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Epidermal growth factor rapidly stimulates prolactin gene transcription. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):192–194. doi: 10.1038/300192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton J. D., Connor J., Avery R. J. Unusual long terminal repeat sequence of a retrovirus transmissible mouse (VL 30) genetic element: identification of functional domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3445–3460. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski M. C., Huang A. L., Kessel M., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Modulation of enhancer activity by the hormone responsive regulatory element from mouse mammary tumor virus. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1891–1899. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski M. C., Richard-Foy H., Wolford R. G., Berard D. S., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of transcription at an amplified, episomal promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2045–2057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines E. W., Ross R. Purification of human platelet-derived growth factor. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:749–773. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Devare S. G., Aaronson S. A. Molecular cloning of integrated simian sarcoma virus: genome organization of infectious DNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Vass W. C., Howk R. S., Duesberg P. H. Defective retrovirus-like 30S RNA species of rat and mouse cells are infectious if packaged by type C helper virus. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):964–972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.964-972.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Sordat B., Schibler U. Developmental coordination of alpha-amylase and psp gene expression during mouse parotid gland differentiation is controlled posttranscriptionally. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Saragosti S., Botchan M. Isolation of cellular genes differentially expressed in mouse NIH 3T3 cells and a simian virus 40-transformed derivative: growth-specific expression of VL30 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2590–2598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield M. D., Scrace G. T., Whittle N., Stroobant P., Johnsson A., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor is structurally related to the putative transforming protein p28sis of simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):35–39. doi: 10.1038/304035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]