Abstract
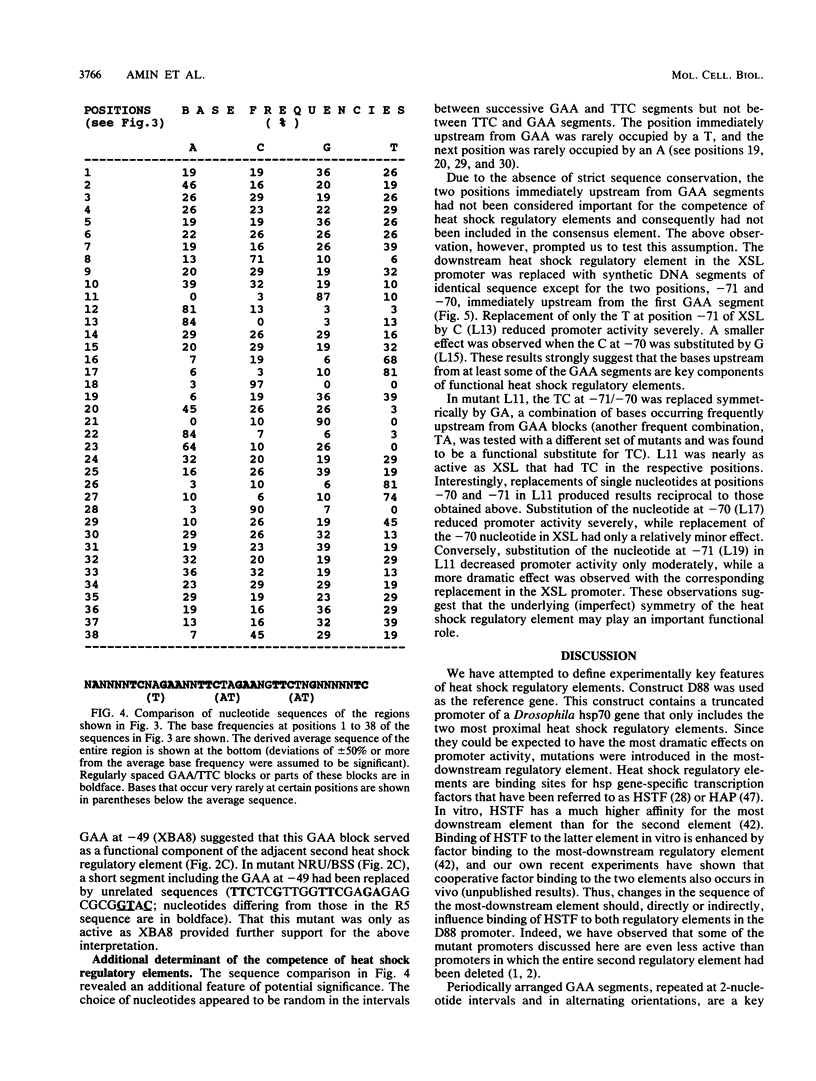
The promoters of heat shock protein genes are among the best-studied inducible eucaryotic promoters. Regions responsible for heat regulation have been identified previously by deletion experiments with several different heat shock genes. In this paper the critical importance of two novel features of heat shock regulatory elements was investigated. First, the elements were modular and, as a consequence, displayed a characteristic 5-nucleotide periodicity produced by multiple GAA blocks that were arranged in alternating orientations and at 2-nucleotide intervals. Functional heat shock regulatory elements appeared to include three or more of these blocks. Second, the nucleotides at the two positions immediately upstream from GAA segments played an important role in defining the competence of regulatory elements.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin J., Mestril R., Lawson R., Klapper H., Voellmy R. The heat shock consensus sequence is not sufficient for hsp70 gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin J., Mestril R., Schiller P., Dreano M., Voellmy R. Organization of the Drosophila melanogaster hsp70 heat shock regulation unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Expression of a Drosophila heat-shock protein in Xenopus oocytes: conserved and divergent regulatory signals. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1583–1588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Heat shock regulatory elements function as an inducible enhancer in the Xenopus hsp70 gene and when linked to a heterologous promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90789-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond U., Schlesinger M. J. The chicken ubiquitin gene contains a heat shock promoter and expresses an unstable mRNA in heat-shocked cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4602–4610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J., Parks C., Parker-Thornburg J., Mortin M. A., Pelham H. R. The use of promoter fusions in Drosophila genetics: isolation of mutations affecting the heat shock response. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):979–991. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90432-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Meselson M. Inducible transcription and puffing in Drosophila melanogaster transformed with hsp70-phage lambda hybrid heat shock genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5509–5513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Meselson M. Separate regulatory elements for the heat-inducible and ovarian expression of the Drosophila hsp26 gene. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):737–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V., Pellicer A., Axel R., Meselson M. Integration, transcription, and control of a Drosophila heat shock gene in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7038–7042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Dawid I. B. Transient expression of genes introduced into cultured cells of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7095–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudler R., Travers A. A. Upstream elements necessary for optimal function of the hsp 70 promoter in transformed flies. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M. Two genes for the major heat-shock protein of Drosophila melanogaster arranged as an inverted repeat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):235–252. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren R., Corces V., Morimoto R., Blackman R., Meselson M. Sequence homologies in the 5' regions of four Drosophila heat-shock genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3775–3778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C., Morimoto R. I. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch F., Török I., Tissières A. Extensive regions of homology in front of the two hsp70 heat shock variant genes in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. J., Boissy R. J., Russnak R. H., Candido E. P. Efficient transcription of a Caenorhabditis elegans heat shock gene pair in mouse fibroblasts is dependent on multiple promoter elements which can function bidirectionally. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3134–3143. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Schuetz T. J., Larin Z. Heat-inducible human factor that binds to a human hsp70 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1530–1534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Sequence requirement for expression of the Drosophila melanogaster heat shock protein hsp22 gene during heat shock and normal development. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2011–2019. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson R., Mestril R., Luo Y., Voellmy R. Ecdysterone selectively stimulates the expression of a 23000-Da heat-shock protein-beta-galactosidase hybrid gene in cultured Drosophila cells. Dev Biol. 1985 Aug;110(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T., Simon J. A., Sutton C. A. New heat shock puffs and beta-galactosidase activity resulting from transformation of Drosophila with an hsp70-lacZ hybrid gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestril R., Rungger D., Schiller P., Voellmy R. Identification of a sequence element in the promoter of the Drosophila melanogaster hsp23 gene that is required for its heat activation. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2971–2976. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestril R., Schiller P., Amin J., Klapper H., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Heat shock and ecdysterone activation of the Drosophila melanogaster hsp23 gene; a sequence element implied in developmental regulation. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1667–1673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Southgate R., Delwart E. Regulation of heat-shock genes: a DNA sequence upstream of Drosophila hsp70 genes is essential for their induction in monkey cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1279–1285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto R. I., Hunt C., Huang S. Y., Berg K. L., Banerji S. S. Organization, nucleotide sequence, and transcription of the chicken HSP70 gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12692–12699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao R. T., Czarnecka E., Gurley W. B., Schöffl F., Key J. L. Genes for low-molecular-weight heat shock proteins of soybeans: sequence analysis of a multigene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3417–3428. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli D., Spierer A., Tissières A. Several hundred base pairs upstream of Drosophila hsp23 and 26 genes are required for their heat induction in transformed flies. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):755–761. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. An underlying repeat in some transcriptional control sequences corresponding to half a double helical turn of DNA. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90866-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. Activation of the Drosophila hsp27 promoter by heat shock and by ecdysone involves independent and remote regulatory sequences. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1653–1658. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russnak R. H., Candido E. P. Locus encoding a family of small heat shock genes in Caenorhabditis elegans: two genes duplicated to form a 3.8-kilobase inverted repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1268–1278. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuey D. J., Parker C. S. Bending of promoter DNA on binding of heat shock transcription factor. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):459–461. doi: 10.1038/323459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuey D. J., Parker C. S. Binding of Drosophila heat-shock gene transcription factor to the hsp 70 promoter. Evidence for symmetric and dynamic interactions. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7934–7940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. A., Sutton C. A., Lobell R. B., Glaser R. L., Lis J. T. Determinants of heat shock-induced chromosome puffing. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):805–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90340-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M. R., Craig E. A. Transcriptional regulation of an hsp70 heat shock gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1906–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate R., Ayme A., Voellmy R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the Drosophila small heat shock gene cluster at locus 67B. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 25;165(1):35–57. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topol J., Ruden D. M., Parker C. S. Sequences required for in vitro transcriptional activation of a Drosophila hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy R., Ahmed A., Schiller P., Bromley P., Rungger D. Isolation and functional analysis of a human 70,000-dalton heat shock protein gene segment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4949–4953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy R., Rungger D. Transcription of a Drosophila heat shock gene is heat-induced in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1776–1780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Shuey D. J., Kibbe W. A., Parker C. S. The Saccharomyces and Drosophila heat shock transcription factors are identical in size and DNA binding properties. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Kingston R. E., Morimoto R. I. Human HSP70 promoter contains at least two distinct regulatory domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):629–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. Germline transformation used to define key features of heat-shock response elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.3125608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


