Abstract
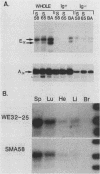
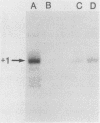
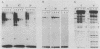
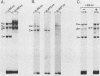
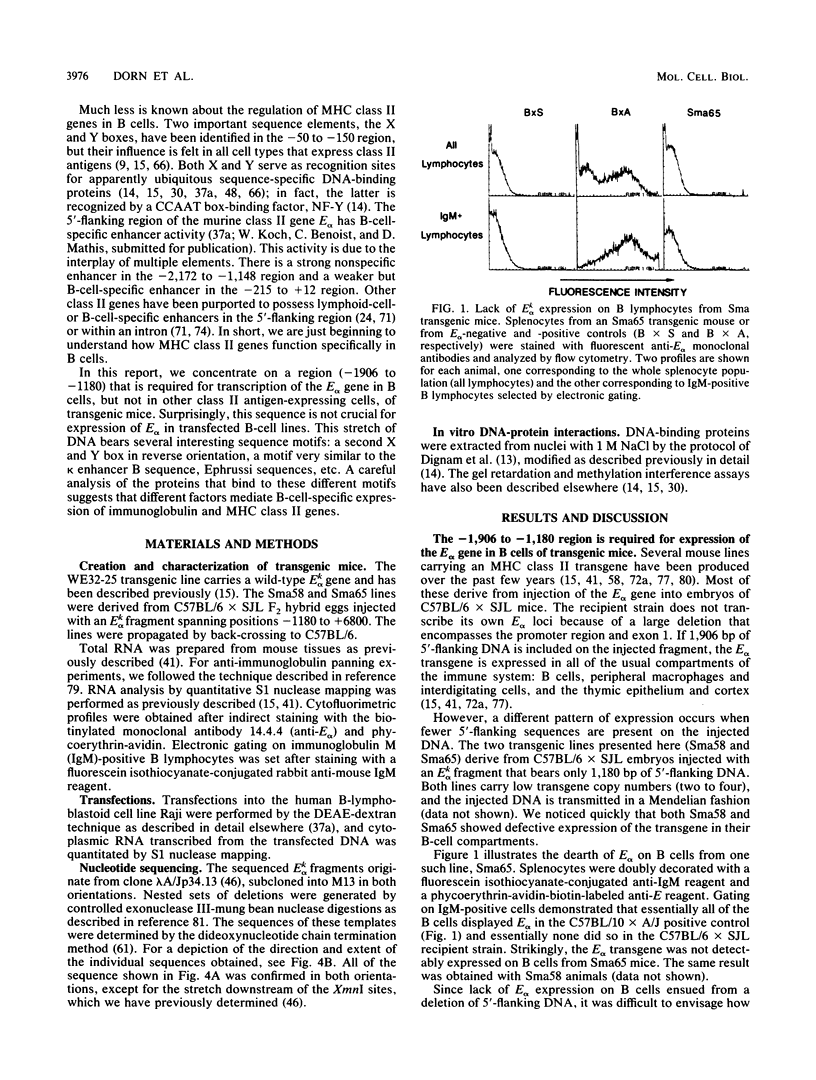
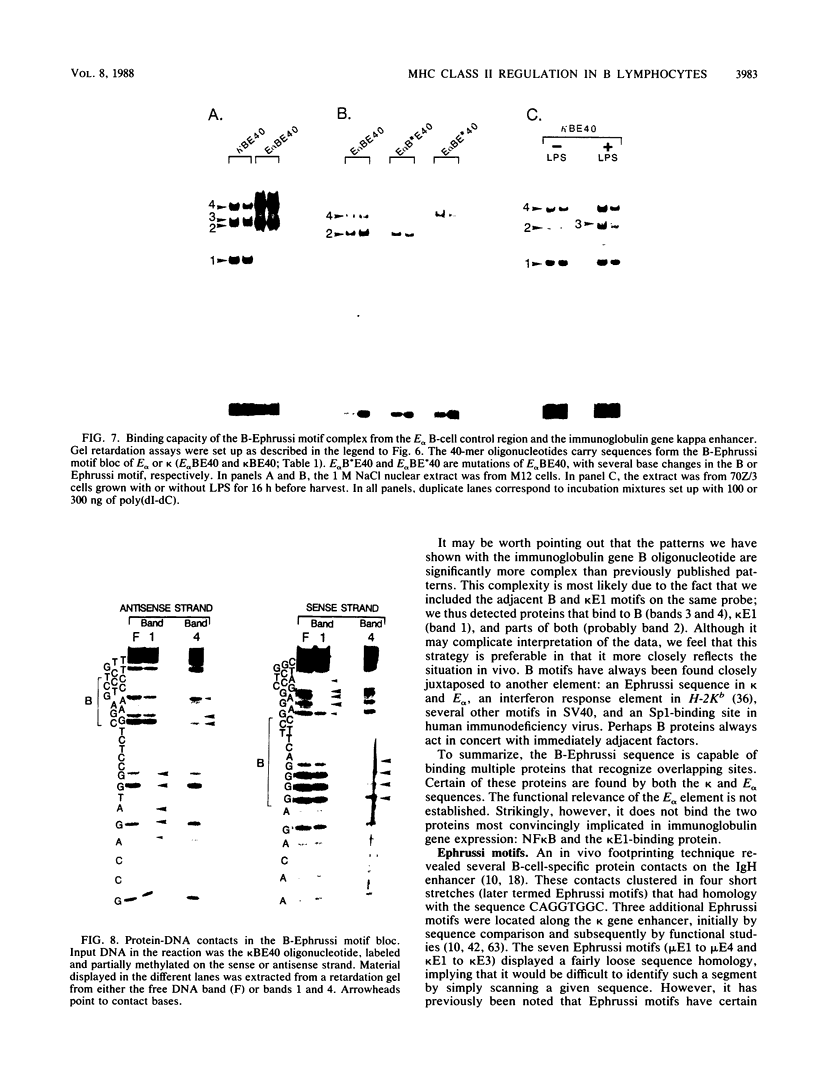
Transcription of major histocompatibility complex class II genes is elaborately regulated. Mouse class II genes are transcribed primarily in B cells, peripheral macrophages and interdigitating cells, and thymic cortical and medullary cells. In this study, we began to identify the DNA sequences and protein factors that control expression of a class II gene in B cells, addressing in particular how closely they resemble those that regulate immunoglobulin gene expression. We describe a region upstream of the E alpha gene that is crucial for its transcription in the B cells of transgenic mice but is less important in cultured B-cell lines. The sequence of this region reveals several familiar motifs, including a second X-Y pair reminiscent of that residing in the promoter-proximal region of all class II genes, a B motif strikingly homologous to that associated with the immunoglobulin kappa gene enhancer, several Ephrussi motifs, and a Pu box-like sequence very similar to that implicated in simian virus 40 and lymphotrophic papovavirus expression in B cells. Careful study of the proteins that bind specifically to these different motifs prompts us to suggest that major histocompatibility complex class II and immunoglobulin genes rely on quite different factors to achieve B-cell-specific expression.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The role of the kappa enhancer and its binding factor NF-kappa B in the developmental regulation of kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augereau P., Chambon P. The mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer: effect on transcription in vitro and binding of proteins present in HeLa and lymphoid B cell extracts. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1791–1797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Two transcription factors, NF-kappa B and H2TF1, interact with a single regulatory sequence in the class I major histocompatibility complex promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Bothwell A. Mutational analysis of the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9626–9630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Keller W., Dale T., Schöler H. R., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. A transcription factor which binds to the enhancers of SV40, immunoglobulin heavy chain and U2 snRNA genes. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):268–272. doi: 10.1038/325268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Strominger J. L. Regulation of a transfected human class II major histocompatibility complex gene in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Fromental C., Augereau P., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Cell-type specific protein binding to the enhancer of simian virus 40 in nuclear extracts. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):544–548. doi: 10.1038/323544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Rüther U., Tripodi M., Wagner E. F., Cortese R. Expression of human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein genes in cultured cells and in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):259–266. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Durand B., Marfing C., Le Meur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Conserved major histocompatibility complex class II boxes--X and Y--are transcriptional control elements and specifically bind nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6249–6253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M., Doyen N., Rougeon F. The conserved decanucleotide from the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter induces a very high transcriptional activity in B-cells when introduced into an heterologous promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1685–1690. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell R. A., Allen H., Huber B., Wake C., Widera G. Organization and expression of the MHC of the C57 black/10 mouse. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;84:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J., Stafford J., Queen C. An immunoglobulin promoter displays cell-type specificity independently of the enhancer. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):423–425. doi: 10.1038/315423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Hung M. C., Wensink P. C. Independent control elements that determine yolk protein gene expression in alternative Drosophila tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Folsom V., Tonegawa S. Cell type-specific enhancer element associated with a mouse MHC gene, E beta. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):594–597. doi: 10.1038/310594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal T. V., Shimada T., Baur A. W., Nienhuis A. W. Contribution of promoter to tissue-specific expression of the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1102–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.2994213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Krumlauf R., Camper S. A., Brinster R. L., Tilghman S. M. Diversity of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in mice is generated by a combination of separate enhancer elements. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2432657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Gehring W. J. Regulation and function of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. A., Bollekens J., Dorn A., Benoist C., Mathis D. Properties of a CCAAT box-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7265–7282. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hromas R., Van Ness B. Nuclear factors bind to regulatory regions of the mouse kappa immunoglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4837–4848. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Lemaire C., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Negative regulation contributes to tissue specificity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2558–2567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara T., Kudo A., Watanabe T. Induction of immunoglobulin gene expression in mouse fibroblasts by cycloheximide treatment. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1937–1942. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Kimura A., Kieran M., Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. A common positive trans-acting factor binds to enhancer sequences in the promoters of mouse H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Pollok B. A., Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The coupling between enhancer activity and hypomethylation of kappa immunoglobulin genes is developmentally regulated. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):930–937. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Israël A., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. Detailed analysis of the mouse H-2Kb promoter: enhancer-like sequences and their role in the regulation of class I gene expression. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura D., Maeda H., Araki K., Kudo A., Watanabe T. Regulation of immunoglobulin gene transcription by labile repressor factor(s). Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1249–1256. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Candeias S., Guardiola J., Accolla R., Benoist C., Mathis D. An enhancer factor defect in a mutant Burkitt lymphoma cell line. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1781–1790. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Protein-nucleotide contacts in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3851–3855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Hammerling U., Denaro M., Lund T., Flavell R. A., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Structure of the murine immune response I-A beta locus: sequence of the I-A beta gene and an adjacent beta-chain second domain exon. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Meur M., Gerlinger P., Benoist C., Mathis D. Correcting an immune-response deficiency by creating E alpha gene transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):38–42. doi: 10.1038/316038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Araki K., Kitamura D., Wang J., Watanabe T. Nuclear factors binding to the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2851–2869. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. O., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. Transcription cell type specificity is conferred by an immunoglobulin VH gene promoter that includes a functional consensus sequence. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C. O., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M. R., McDevitt H. O. The murine E alpha immune response gene. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):745–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Wang X. F., Olsen J., Calame K. Transcriptional enhancer elements in the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.6306772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa K., Doyle C., Strominger J. L. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with conserved sequences of human class II major histocompatibility complex genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocikat R., Falkner F. G., Mertz R., Zachau H. G. Upstream regulatory sequences of immunoglobulin genes are recognized by nuclear proteins which also bind to other gene regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8829–8844. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S. Expression and regulation of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene transfected into lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1373–1378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petterson M., Schaffner W. A purine-rich DNA sequence motif present in SV40 and lymphotropic papovavirus binds a lymphoid-specific factor and contributes to enhancer activity in lymphoid cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):962–972. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. Cell-type preference of immunoglobulin kappa and lambda gene promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2831–2838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Oligonucleotide that binds nuclear factor NF-kappa B acts as a lymphoid-specific and inducible enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1482–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Ornitz D. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. An albumin enhancer located 10 kb upstream functions along with its promoter to direct efficient, liver-specific expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):268–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Widera G., Cowing C., Heber-Katz E., Palmiter R. D., Flavell R. A., Brinster R. L. Tissue-specific, inducible and functional expression of the E alpha d MHC class II gene in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2225–2230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03918.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. In vitro binding of cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the octamer motif of the SV40 enhancer and related motifs present in other promoters and enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3015–3025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlokat U., Bohmann D., Schöler H., Gruss P. Nuclear factors binding specific sequences within the immunoglobulin enhancer interact differentially with other enhancer elements. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3251–3258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelley C. S., Baralle F. E. Dual tissue-specific expression of apo-AII is directed by an upstream enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3801–3821. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Ting J. P. Upstream DNA sequences required for tissue-specific expression of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4254–4258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a common factor with conserved promoter and enhancer sequences in histone H2B, immunoglobulin, and U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6382–6386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. E., Peterlin B. M. Transcriptional enhancers in the HLA-DQ subregion. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3315–3319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theisen M., Stief A., Sippel A. E. The lysozyme enhancer: cell-specific activation of the chicken lysozyme gene by a far-upstream DNA element. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):719–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R., Briskin M., Carter C., Govan H., Taylor A., Kincade P. A labile inhibitor blocks immunoglobulin kappa-light-chain-gene transcription in a pre-B leukemic cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):295–298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Larsen A. S., Peterlin B. M. A tissue-specific transcriptional enhancer is found in the body of the HLA-DR alpha gene. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):625–636. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Jat P. S., Sharp P. A. Localization of a repressive sequence contributing to B-cell specificity in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):988–992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widera G., Burkly L. C., Pinkert C. A., Böttger E. C., Cowing C., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Flavell R. A. Transgenic mice selectively lacking MHC class II (I-E) antigen expression on B cells: an in vivo approach to investigate Ia gene function. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Staudt L., Baltimore D. An octamer oligonucleotide upstream of a TATA motif is sufficient for lymphoid-specific promoter activity. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):174–178. doi: 10.1038/329174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura K., Kikutani H., Folsom V., Clayton L. K., Kimoto M., Akira S., Kashiwamura S., Tonegawa S., Kishimoto T. Functional expression of a microinjected Ed alpha gene in C57BL/6 transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):67–69. doi: 10.1038/316067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ewijk W., Ron Y., Monaco J., Kappler J., Marrack P., Le Meur M., Gerlinger P., Durand B., Benoist C., Mathis D. Compartmentalization of MHC class II gene expression in transgenic mice. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):357–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]