Abstract
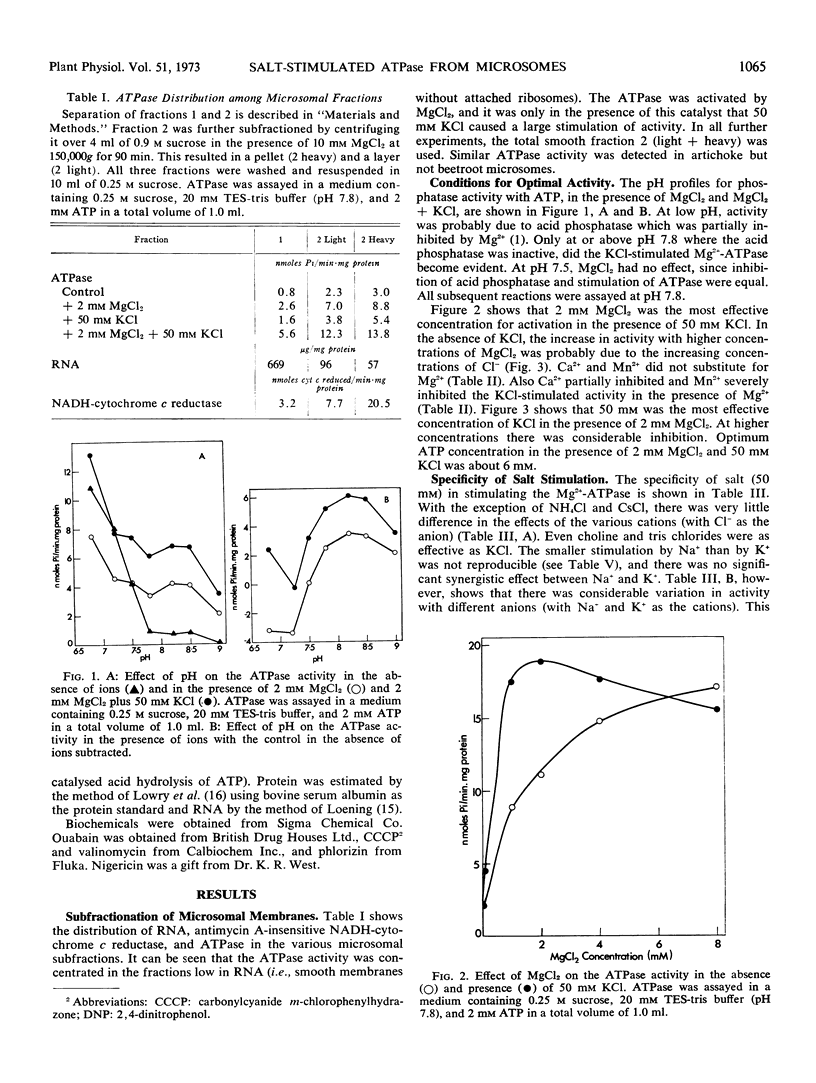
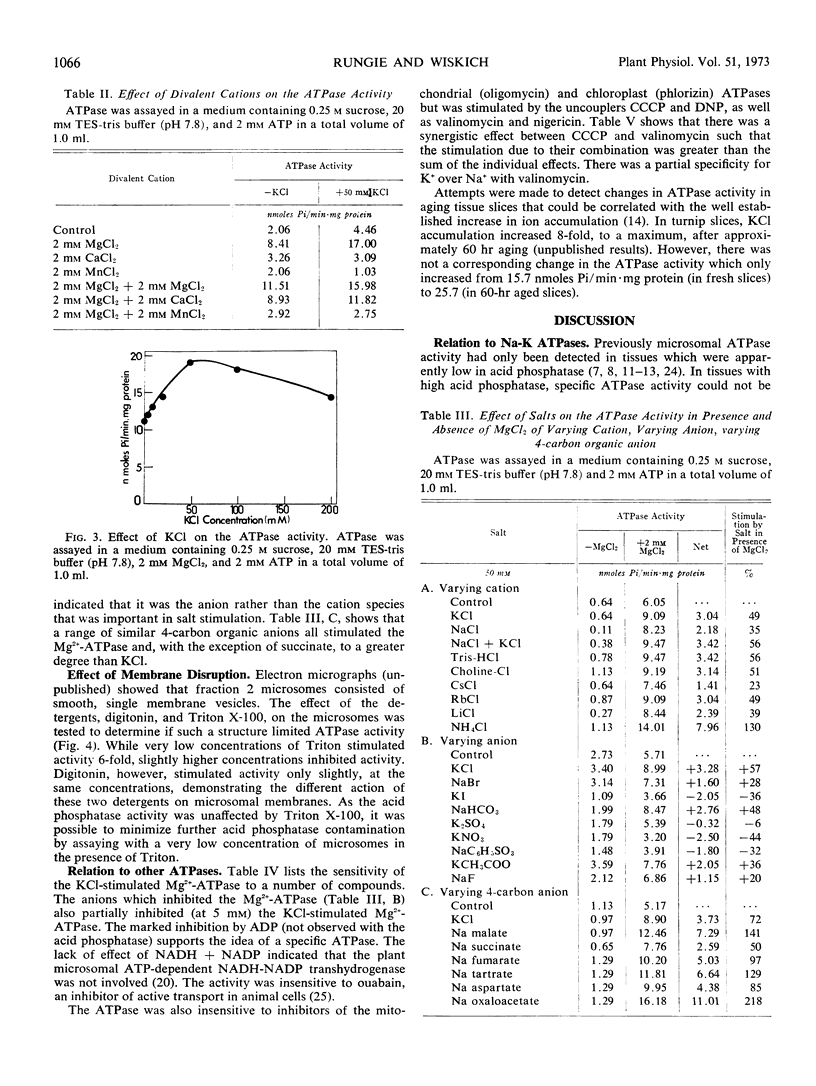
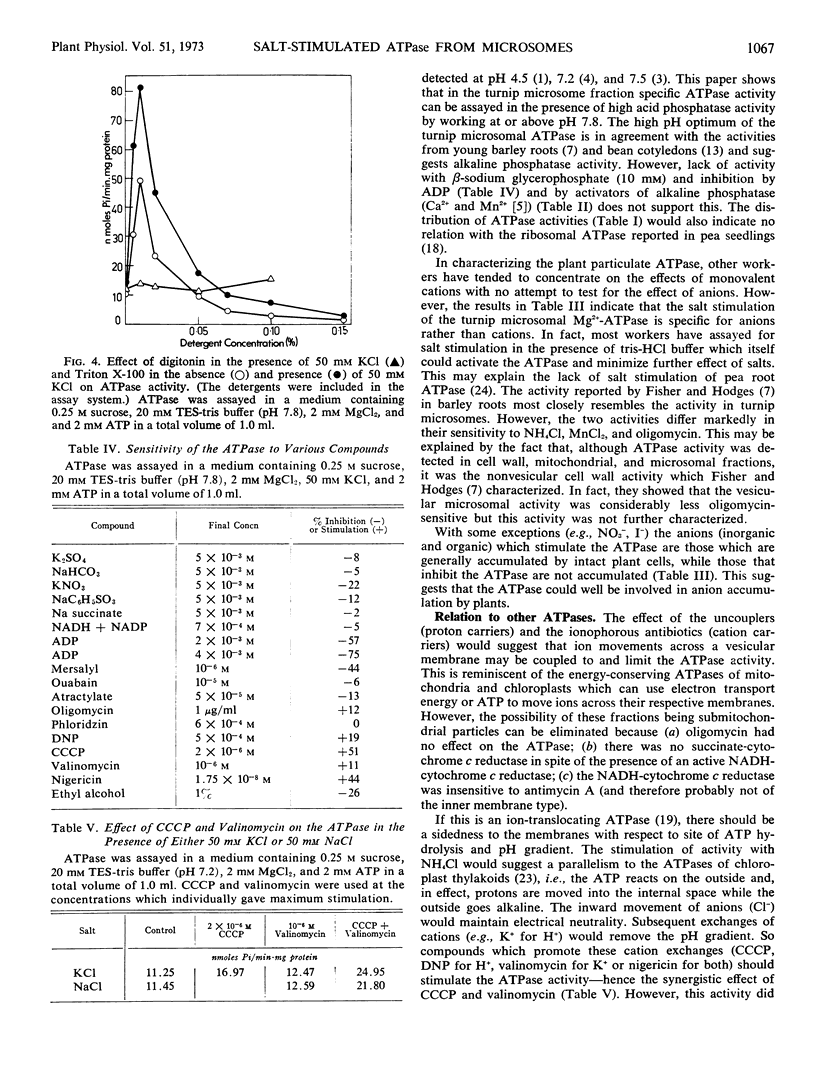
The turnip (Brassica rapa L.) microsome fraction contains both a Mg2+-inhibited acid phosphatase and a salt-stimulated Mg2+-activated ATPase. However, as the pH optimum of the ATPase was 8.0 to 8.5, the acid phosphatase activity could be eliminated by assaying at or above pH 7.8. The ATPase was concentrated in a fraction equivalent to the smooth microsomal membranes and was not due to fragments of mitochondria. The salt-stimulated activity showed specificity for anions rather than cations. The activity was further stimulated by carbonyl cyanide m-chloro-phenylhydrazone (CCCP), 2,4-dinitrophenol, valinomycin, nigericin, and NH4Cl. There was a synergistic effect between CCCP and valinomycin. Activity was insensitive to oligomycin phlorizin, ouabain, and atractylate. Based on similarity to the chloroplast ATPase, it was proposed that this ATPase was situated on the outside of the vesicle.
It is suggested that the ATPase is involved in the movement of ions, particularly anions, and may be related to the anion accumulation mechanism, which is known to occur across the tonoplast of such tissues.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown H. D., Altschul A. M. Glycoside-sensitive ATPase from Arachis hypogaea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Apr 22;15(5):479–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. D., Hansen D., Hodges T. K. Correlation between ion fluxes and ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase activity of plant roots. Plant Physiol. 1970 Dec;46(6):812–814. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.6.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J., Hodges T. K. Monovalent ion stimulated adenosine triphosphatase from oat roots. Plant Physiol. 1969 Mar;44(3):385–395. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.3.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaumann H., Dallner G. Subfractionation of smooth microsomes from rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1970 Oct;47(1):34–48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kylin A., Gee R. Adenosine Triphosphatase Activities in Leaves of the Mangrove Avicennia nitida Jacq: Influence of Sodium to Potassium Ratios and Salt Concentrations. Plant Physiol. 1970 Feb;45(2):169–172. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOENING U. E. Changes in microsomal components accompanying cell differentiation of pea-seedling roots. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:254–260. doi: 10.1042/bj0810254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Y. F., Thompson J. E. The preparation and properties of an isolated plant membrane fraction enriched in (Na plus-K plus)-stimulated ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):84–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90360-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita S., Raacke I. D. Purification of nucleoside triphosphatases from pea seedling ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 29;166(3):707–710. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. J. Effect of sodium on potassium fluxes at the cell membrane and vacuole membrane of red beet. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jun;47(6):731–734. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.6.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid H. B., Gentile A. C., Klein R. M. Adenosine Triphosphatase Activity of Cauliflower Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1964 Nov;39(6):1020–1023. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


