Abstract
BACKGROUND
Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have a poor prognosis if their tumors are not diagnosed early. The authors investigated factors associated with the receipt of liver transplant among patients with HCC and evaluated the effects of these differences on survival.
METHODS
The authors reviewed records from consecutive patients diagnosed with HCC at Columbia University Medical Center from January 1, 2002 to September 1, 2008. We compared patient clinical and demographic characteristics, developed a multivariable logistic regression model of predictors of transplant, and used a Cox model to analyze predictors of mortality.
RESULTS
Of 462 HCC patients, 175 (38%) received a transplant. Black patients were much less likely than whites to receive a transplant (odds ratio [OR], 0.03; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.0–0.37). Hispanics and Asians were also less likely to undergo transplantation, but the differences were not statistically significant. Patients with private insurance were more likely to receive a transplant than those with Medicaid (odds ratio [OR], 22.07; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.67–182.34). Black and Hispanic patients, and Medicaid recipients, presented with more advanced disease than whites and privately insured patients, and had poorer survival. In a Cox model, those who did not receive a transplant were 3 times as likely as transplant recipients to die, but race and insurance were not independently predictive of mortality.
CONCLUSIONS
Race and insurance status were strongly associated with receipt of transplantation and with more advanced disease at diagnosis, but transplantation was the most important determinant of survival. Improved access to care for non-white and Medicaid patients may allow more patients to benefit from transplant.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, liver transplant, disparities, race, insurance
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive disease with a poor prognosis. In the United States, the overall 5-year relative survival rate for HCC is 11.7%. In 2008, more than 21,000 people were diagnosed with HCC and more than 18,000 died from their cancer.1 In the past 30 years, the incidence and mortality rates for HCC in the United States have more than doubled. This increase has been attributed to the rising rates of hepatitis C (HCV) infection in the United States, and migration from hepatitis B (HBV)-endemic areas.2
Liver transplantation is an effective treatment for some patients with early HCC. Among patients who met the Milan criteria (defined as a single lesion ≤5 cm, up to 3 separate lesions, none larger than 3 cm, no evidence of gross vascular invasion, and no regional nodal or distant metastases), 4-year survival rates were found to be 75%,3 similar to outcomes in patients who received transplants for nonmalignant indications.4 In 2002, the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) developed the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) allocation system which gave priority for liver transplants to HCC patients who met the Milan criteria. Implementation of the MELD system led to a 6-fold increase in the proportion of liver transplantation patients with HCC.5
Unfortunately, only about one-third of all cases of HCC are diagnosed while they are within the Milan criteria.1 Barriers to early diagnosis and receipt of transplant are, therefore, important areas of investigation. The purpose of our study was to identify factors associated with receipt of transplant in patients with HCC and to evaluate how these differences affect survival.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample Selection
By using ICD-9 code 155.0 (malignant neoplasm liver primary) as a search criterion for our medical center’s clinical information system (CIS), we identified all patients diagnosed with HCC at Columbia Presbyterian College of Physicians and Surgeons–New York-Presbyterian Hospital from January 1, 2002 to September 1, 2008. We corroborated these data with a second search for patients with an alpha fetoprotein (AFP) > 200 ng/mL, all of whom were then clinically confirmed to have HCC through review of imaging and clinical characteristics. The protocol was approved by the Columbia University Medical Center Institutional Review Board.
Sociodemographic and Surgical Treatment Variables
We obtained information from our electronic medical records and paper charts on patients’ demographic characteristics, (eg, age, gender, and self-reported race/ethnicity), health history (eg, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, ethanol use, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [NASH]), and HCC-related variables (Child-Pugh score, Milan criteria, American Joint Committee on Cancer [AJCC] stage, AFP, and tumor size). Child-Pugh score was computed according to a formula incorporating measures of total serum bilirubin, albumin, international normalized ratio, presence of ascites and encephalopathy grade taken closest to and preceding the date of surgery. The AFP level was the maximum serum AFP measured before surgery. Tumor size was determined by the maximum tumor diameter by radiologic measurement, either by CT scan or MRI.
We also collected data on some comorbid conditions (hyperlipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, and coronary artery disease) and categorized patients as having one of these conditions if the clinical notes mentioned it or if the patient used medications for it. We categorized patients taking beta blockers as having systemic hypertension only if the clinical notes mentioned an indication other than portal hypertension. NASH was defined clinically as a body mass index (BMI) >30 kg/m2 plus 1 additional component of the metabolic syndrome. Tobacco use was categorized as ever or never, and insurance coverage was categorized as private, Medicare, or Medicaid. We obtained information on median household income of the patient’s zip code of residence from the United States Census Bureau FactFinder database.6 We also collected information on surgical treatment, including liver transplantation. Dates of death were abstracted using our medical records and the social security death index.
Statistical Analysis
Frequency distributions of the above variables were compared between patients who did and did not receive transplant. Continuous variables (age, AFP, tumor size, and median household income) were divided into quartiles for statistical analyses. χ2 tests were used to evaluate the statistical significance of differences in distribution of the variables between groups. We developed logistic regression models to analyze the association of these variables with the receipt of liver transplant. Survival curves for receipt of transplant, ethnicity, and insurance status were generated using Kaplan-Meier analysis. Cox proportional hazards models were used to evaluate predictors of all-cause mortality. All statistical analyses were performed with SAS software (Cary, NC, version 9.1).
RESULTS
From January 1, 2002 to September 1, 2008, 462 consecutive patients with HCC were evaluated at our institution. Their median age at diagnosis was 60 years (range = 23–94), and 79% were men. About 40% of patients were non-Hispanic white (white), 31% Hispanic, 14% non-Hispanic black (black), 10% Asian, and 5% other; 62% had private insurance, 20% Medicare, and 19% Medicaid. Of the total, 175 (38%) received liver transplantation (Table 1).
Table 1.
Patient Characteristics
| Transplant | No Transplant | Total | P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | ||
| 175 | 37.9 | 287 | 62.1 | 462 | |||
| Sex | .957 | ||||||
| Male | 137 | 79.7 | 228 | 79.4 | 365 | 79.5 | |
| Female | 35 | 20.3 | 59 | 20.6 | 94 | 20.5 | |
| Ethnicity | <.0001 | ||||||
| White | 97 | 57.1 | 87 | 30.4 | 184 | 40.4 | |
| Black | 19 | 11.2 | 44 | 15.4 | 63 | 13.8 | |
| Hispanic | 35 | 20.6 | 104 | 36.4 | 139 | 30.5 | |
| Asian | 17 | 10.0 | 30 | 10.5 | 47 | 10.3 | |
| Other | 2 | 1.2 | 21 | 7.3 | 23 | 5.0 | |
| Age, y | <.0001 | ||||||
| ≤52 | 50 | 29.1 | 65 | 22.9 | 115 | 25.2 | |
| 53–60 | 59 | 34.3 | 70 | 24.6 | 129 | 28.3 | |
| 61–67 | 52 | 30.2 | 58 | 20.4 | 110 | 24.1 | |
| ≥68 | 11 | 6.4 | 91 | 32.0 | 102 | 22.4 | |
| Child-Pugh class | <.0001 | ||||||
| A | 77 | 45.6 | 82 | 29.2 | 159 | 35.3 | |
| B | 54 | 32.0 | 83 | 29.5 | 137 | 30.4 | |
| C | 38 | 22.5 | 116 | 41.3 | 154 | 34.2 | |
| Milan criteria | <.0001 | ||||||
| No | 39 | 28.9 | 183 | 76.9 | 222 | 59.5 | |
| Yes | 96 | 71.1 | 55 | 23.1 | 151 | 40.5 | |
| Maximum AFP | <.0001 | ||||||
| ≤49 | 86 | 57.0 | 23 | 8.0 | 109 | 24.9 | |
| 50–774 | 40 | 26.5 | 69 | 24.1 | 109 | 24.9 | |
| 775–6666 | 14 | 9.3 | 96 | 33.6 | 110 | 25.2 | |
| ≥6667 | 11 | 7.3 | 98 | 34.3 | 109 | 24.9 | |
| AJCC stage | <.0001 | ||||||
| 1 | 68 | 44.7 | 45 | 16.1 | 113 | 26.2 | |
| 2 | 62 | 40.8 | 71 | 25.4 | 133 | 30.9 | |
| 3 | 22 | 14.5 | 103 | 36.9 | 125 | 29.0 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0.0 | 60 | 21.5 | 60 | 13.9 | |
| Tumor size | <.0001 | ||||||
| ≤2.6 cm | 58 | 43.9 | 28 | 14.4 | 86 | 26.3 | |
| 2.7–4 cm | 37 | 28.0 | 42 | 21.5 | 79 | 24.2 | |
| 4.1–6.5 cm | 32 | 24.2 | 39 | 20.0 | 71 | 21.7 | |
| ≥6.6 cm | 5 | 3.8 | 86 | 44.1 | 91 | 27.8 | |
| Median household income, $ | .0005 | ||||||
| ≤27,776 | 31 | 18.5 | 81 | 28.9 | 112 | 25.0 | |
| 27,777–40,497 | 34 | 20.2 | 80 | 28.6 | 114 | 25.4 | |
| 40,498–60,075 | 45 | 26.8 | 65 | 23.2 | 110 | 24.6 | |
| ≥60,076 | 58 | 34.5 | 54 | 19.3 | 112 | 25.0 | |
| Insurance | <.0001 | ||||||
| Private | 143 | 83.1 | 127 | 47.9 | 270 | 61.8 | |
| Medicare | 17 | 9.9 | 69 | 26.0 | 86 | 19.7 | |
| Medicaid | 12 | 7.0 | 69 | 26.0 | 81 | 18.5 | |
| HCV | .0002 | ||||||
| No | 48 | 28.1 | 129 | 45.4 | 177 | 38.9 | |
| Yes | 123 | 71.9 | 155 | 54.6 | 278 | 61.1 | |
| HBV | .318 | ||||||
| No | 142 | 83.0 | 225 | 79.2 | 367 | 80.7 | |
| Yes | 29 | 17.0 | 59 | 20.8 | 88 | 19.3 | |
| NASH | .272 | ||||||
| No | 139 | 81.3 | 242 | 85.2 | 381 | 83.7 | |
| Yes | 32 | 18.7 | 42 | 14.8 | 74 | 16.3 | |
| DM | .698 | ||||||
| No | 120 | 70.2 | 193 | 68.7 | 313 | 69.1 | |
| Yes | 51 | 29.8 | 88 | 31.3 | 139 | 30.7 | |
| HTN | .757 | ||||||
| No | 104 | 61.5 | 170 | 60.1 | 274 | 60.6 | |
| Yes | 65 | 38.5 | 113 | 39.9 | 178 | 39.4 | |
| CAD | .469 | ||||||
| No | 160 | 93.0 | 224 | 91.1 | 384 | 91.9 | |
| Yes | 12 | 7.0 | 22 | 8.9 | 34 | 8.1 | |
| Tobacco | .004 | ||||||
| No | 61 | 37.4 | 114 | 52.3 | 175 | 45.9 | |
| Yes | 102 | 62.6 | 104 | 47.7 | 206 | 54.1 | |
AFP indicates alpha fetoprotein; AJCC, American Joint Committee on Cancer; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HBV, hepatitis B virus; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; DM, diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension; CAD, coronary artery disease.
More transplant recipients than nontransplant recipients were white, ≤60 years of age, and privately insured. Transplant recipients also had less advanced disease than those who did not receive a transplant (Table 1). In a multivariable logistic regression model, receiving a transplant was associated with private insurance, smaller tumors, fitting the Milan criteria, being younger, and having a lower AFP. Black patients were much less likely than white patients to receive a liver transplant (OR = 0.03; 95% CI, 0.0–0.37) (Table 2). Hispanics and Asians were also less likely than whites to receive a transplant, but the associations were not statistically significant (OR = 0.42; 95% CI, 0.09–2.08 for Hispanics, and OR = 0.33; 95% CI, 0.02–4.44 for Asians). Patients with private insurance were 22 times more likely to receive transplants than those with Medicaid (OR, 22.07; 95% CI, 2.67–182.34).
Table 2.
Association of Demographic and Clinical Characteristics With Receipt of Transplant
| OR | 95% CI | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | |||
| White | 1.0 | Referent | |
| Black | 0.03 | 0.00–0.37 | .007 |
| Hispanic | 0.42 | 0.09–2.08 | .29 |
| Asian | 0.33 | 0.02–4.44 | .40 |
| Other | 0.005 | 0.00–69.26 | .28 |
| Tumor size | |||
| ≥6.6 cm | 1.0 | Referent | |
| 4.1–6.5 cm | 163.80 | 9.03–999 | .001 |
| 2.7–4 cm | 18.69 | 1.51–231.73 | .02 |
| ≤2.6 cm | 6.98 | 0.46–105.56 | .16 |
| Milan criteria | |||
| No | 1.0 | Referent | |
| Yes | 7.3 | 1.67–32.31 | .008 |
| AFP | |||
| ≥6667 | 1.0 | Referent | |
| 775–6666 | 1.14 | 0.20–6.63 | .89 |
| 50–774 | 18.6 | 2.20–157.15 | .007 |
| ≤49 | 220.10 | 19.34–999 | <.0001 |
| Insurance | |||
| Medicaid | 1.0 | Referent | |
| Medicare | 3.20 | 0.34–30.18 | .31 |
| Private | 22.07 | 2.67–182.34 | .004 |
| Age, y | |||
| ≤52 | 1.0 | Referent | |
| 53–60 | 0.09 | 0.01–0.54 | .009 |
| 61–67 | 0.49 | 0.09–2.69 | .41 |
| ≥68 | 0.01 | 0.00–0.14 | .001 |
CI indicates confidence interval; OR, odds ratio; AFP, alpha fetoprotein. All variables controlled for each other, as well as for the following: gender, Child-Pugh status, stage, median household income, diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and tobacco.
Overall median survival was 1.9 years. The 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year survival percentages were 92.6%, 70.6%, and 57.3% for transplanted patients and 48.2%, 14.0%, and 6.2% for nontransplanted patients. One-year, 3-year, and 5-year survival percentages were more favorable for whites than for those of other groups and for the privately insured than for those on Medicaid or Medicare (Table 3). Kaplan Meier survival curves differed significantly by receipt of transplant (P < .0001; Fig. 1), ethnicity (P = .0008; Fig. 2), and insurance status (P < .0001; Fig. 3) using the log-rank test.
Table 3.
Predictors of Median and 1-Year, 3-Year, and 5-Year Survival
| Median Survival, y | 1-Year Survival | 3-Year Survival | 5-Year Survival | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 1.9 | 66.9 | 38.8 | 28.6 |
| Transplant | 7.9 | 92.6 | 70.6 | 57.3 |
| Nontransplant | 0.9 | 48.2 | 14.0 | 6.2 |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| White | 2.8 | 93.3 | 48.1 | 38.0 |
| Black | 1.5 | 59.3 | 37.1 | 0.0 |
| Hispanic | 1.2 | 58.1 | 31.7 | 16.7 |
| Asian | 2.5 | 83.5 | 37.0 | 15.1 |
| Insurance | ||||
| Private | 3.0 | 77.8 | 48.9 | 38.6 |
| Medicare | 1.0 | 51.5 | 22.3 | 10.8 |
| Medicaid | 1.1 | 50.3 | 17.4 | 0.0 |
Figure 1.
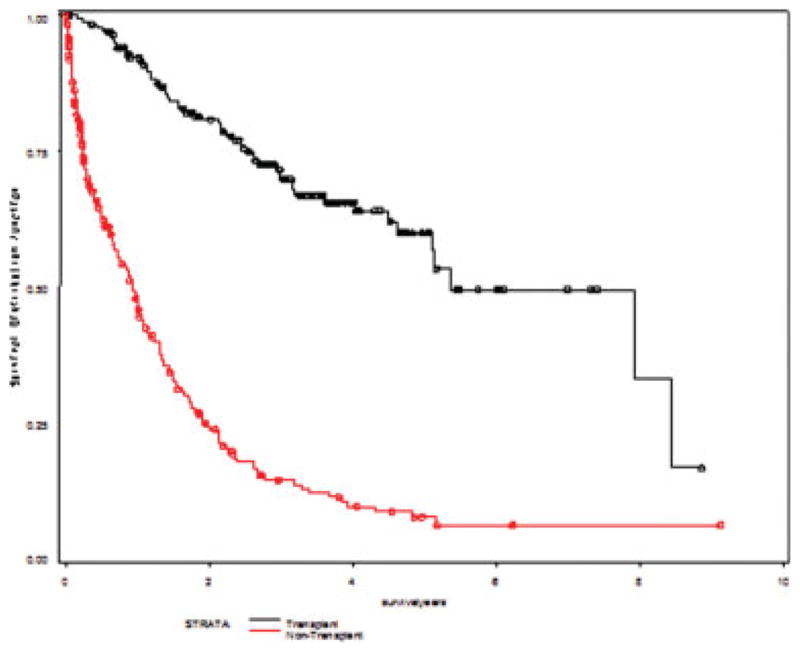
Kaplan-Meier survival curves are shown for transplant versus nontransplant for hepatocellular carcinoma. Log-rank, P < .0001.
Figure 2.
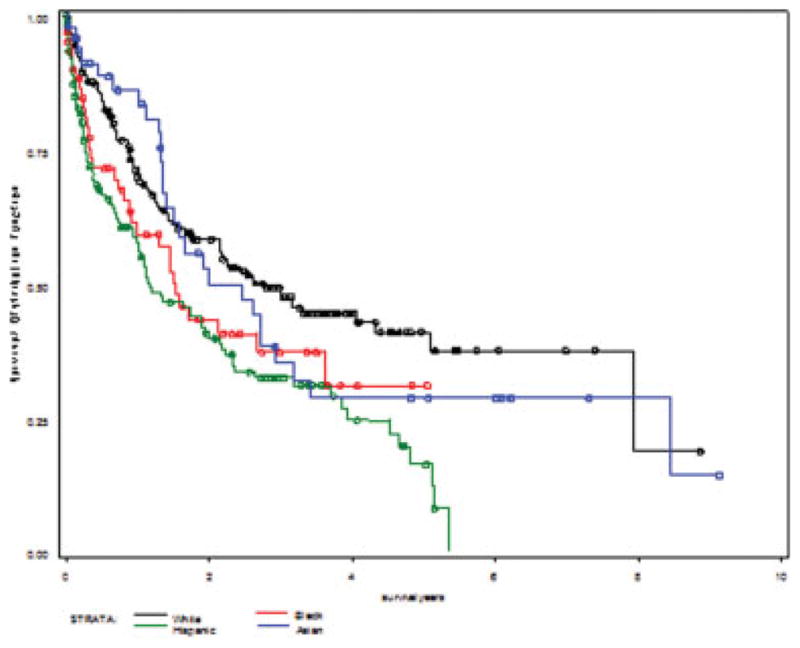
Depicted are Kaplan-Meier survival curves by race and/or ethnicity. Log-rank, P = .0008.
Figure 3.
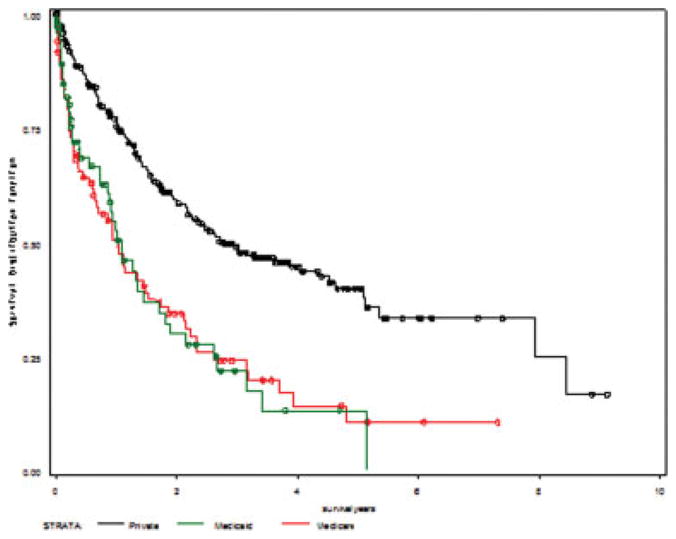
Kaplan-Meier survival curves are shown for insurance status. Log-rank, P<.0001.
We then performed a Cox proportional hazards model to determine predictors of all-cause mortality (Table 4). Mortality was more than 3 times as high among nontransplanted patients as among transplanted patients (hazard ratio [HR], 3.62; 95% CI, 1.81–7.27), even when factors such as Child-Pugh class and AFP were taken into account. In the Cox model, ethnicity and insurance status were not significant independent predictors of all-cause mortality.
Table 4.
Cox Proportional Hazards Mortality Rate Ratios
| HR | 95% CI | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transplant | |||
| Yes | 1.0 | Referent | |
| No | 3.62 | 1.81–7.27 | .0003 |
| Child-Pugh class | |||
| A | 1.0 | Referent | |
| B | 2.45 | 1.37–4.36 | .002 |
| C | 2.20 | 1.21–4.02 | .01 |
| AFP | |||
| ≤49 | 1.0 | Referent | |
| 50–774 | 1.88 | 0.81–4.35 | .14 |
| 775–6666 | 2.20 | 0.96–5.04 | .06 |
| ≥6667 | 3.26 | 1.48–7.17 | .003 |
| Ethnicity | |||
| White | 1.0 | Referent | |
| Black | 1.03 | 0.46–2.29 | .94 |
| Hispanic | 0.99 | 0.54–1.83 | .97 |
| Asian | 0.60 | 0.24–1.48 | .27 |
| Insurance | |||
| Private | 1.0 | Referent | |
| Medicare | 1.7 | 0.80–3.73 | .17 |
| Medicaid | 1.4 | 0.67–2.73 | .39 |
HR indicates hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
All variables controlled for each other, as well as for the following: age, gender, etiology, stage, tumor size, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, tobacco, and income.
In an analysis of patient characteristics evaluating race/ethnicity, we found that blacks and Hispanics were more likely than whites to be diagnosed with late-stage disease, tumors outside of the Milan criteria, high Child-Pugh scores, high AFP levels and lower median household incomes. They were also less likely than whites to have private insurance and more likely to have comorbid conditions, such as hypertension (Table 5).
Table 5.
Patient Characteristics by Ethnicity
| White | Black | Hispanic | Asian | Total | P | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | No. | No. | No. | No. | |||||||
| 184 | 39.8 | 63 | 13.6 | 139 | 30.1 | 4 | 10.2 | 462 | |||
| Sex | .243 | ||||||||||
| Male | 156 | 84.8 | 45 | 71.4 | 108 | 77.7 | 37 | 78.7 | 365 | 79.5 | |
| Female | 28 | 15.2 | 18 | 28.6 | 31 | 22.3 | 10 | 21.3 | 94 | 20.5 | |
| Age, y | .023 | ||||||||||
| ≤52 | 34 | 18.7 | 19 | 30.2 | 37 | 26.6 | 19 | 40.4 | 114 | 25.2 | |
| 53–60 | 65 | 35.7 | 18 | 28.6 | 37 | 26.6 | 7 | 14.9 | 129 | 28.5 | |
| 61–67 | 46 | 25.3 | 16 | 25.4 | 31 | 22.3 | 8 | 17.0 | 109 | 24.1 | |
| ≥68 | 37 | 20.3 | 10 | 15.9 | 34 | 24.5 | 13 | 27.7 | 101 | 22.3 | |
| Child-Pugh class | <.0001 | ||||||||||
| A | 75 | 40.8 | 20 | 31.7 | 31 | 22.3 | 28 | 59.6 | 159 | 34.6 | |
| B | 58 | 31.5 | 21 | 33.3 | 42 | 30.2 | 11 | 23.4 | 137 | 29.8 | |
| C | 46 | 25.0 | 22 | 34.9 | 64 | 46.0 | 8 | 17.0 | 154 | 33.6 | |
| Milan criteria | .014 | ||||||||||
| No | 85 | 46.2 | 40 | 64.5 | 89 | 64.0 | 21 | 44.7 | 251 | 54.7 | |
| Yes | 76 | 41.3 | 15 | 23.8 | 40 | 28.8 | 21 | 44.7 | 160 | 34.9 | |
| Maximum AFP | .001 | ||||||||||
| ≤49 | 61 | 35.3 | 15 | 25.4 | 19 | 14.2 | 12 | 25.5 | 108 | 24.8 | |
| 50–774 | 41 | 23.7 | 15 | 25.4 | 33 | 24.6 | 13 | 27.7 | 108 | 24.8 | |
| 775–6666 | 44 | 25.4 | 13 | 22.0 | 41 | 30.6 | 6 | 12.8 | 110 | 24.3 | |
| ≥6667 | 27 | 15.6 | 16 | 27.1 | 41 | 30.6 | 16 | 34.0 | 109 | 24.1 | |
| AJCC stage | .015 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 54 | 29.3 | 20 | 31.7 | 21 | 15.1 | 11 | 23.4 | 113 | 24.6 | |
| 2 | 58 | 31.5 | 12 | 19.0 | 42 | 30.2 | 14 | 29.8 | 133 | 29.0 | |
| 3 | 44 | 23.9 | 13 | 20.6 | 44 | 31.7 | 14 | 29.8 | 125 | 27.2 | |
| 4 | 14 | 7.6 | 13 | 20.6 | 27 | 19.4 | 4 | 8.5 | 60 | 13.1 | |
| Tumor size | .003 | ||||||||||
| ≤2.6 cm | 34 | 24.5 | 10 | 20.8 | 26 | 26.8 | 14 | 46.7 | 86 | 26.2 | |
| 2.7–4 cm | 36 | 25.9 | 7 | 14.6 | 25 | 25.8 | 6 | 20.0 | 78 | 23.8 | |
| 4.1–6.5 cm | 42 | 30.2 | 9 | 18.8 | 18 | 18.6 | 0 | 0.0 | 72 | 22.0 | |
| 6.6 cm | 27 | 19.4 | 22 | 45.8 | 28 | 28.9 | 10 | 33.3 | 92 | 28.1 | |
| Median household income, $ | <.0001 | ||||||||||
| ≤27,776 | 9 | 5.1 | 28 | 45.2 | 64 | 47.1 | 3 | 6.4 | 112 | 25.2 | |
| 27,777–40,497 | 33 | 18.6 | 19 | 30.7 | 43 | 31.6 | 13 | 27.7 | 114 | 25.6 | |
| 40,498–60,075 | 54 | 30.5 | 13 | 21.0 | 16 | 11.8 | 20 | 42.6 | 108 | 24.3 | |
| ≥60,076 | 81 | 45.8 | 2 | 3.2 | 13 | 9.6 | 11 | 23.4 | 111 | 24.9 | |
| Insurance | <.0001 | ||||||||||
| Private | 156 | 84.8 | 30 | 47.6 | 44 | 31.7 | 36 | 76.6 | 282 | 61.4 | |
| Medicare | 14 | 7.6 | 11 | 17.5 | 53 | 38.1 | 8 | 17.0 | 93 | 20.3 | |
| Medicaid | 14 | 7.6 | 22 | 34.9 | 41 | 29.5 | 3 | 6.4 | 83 | 18.9 | |
| HCV | <.0001 | ||||||||||
| No | 69 | 37.5 | 18 | 28.6 | 43 | 30.9 | 37 | 78.7 | 177 | 38.6 | |
| Yes | 112 | 60.9 | 45 | 71.4 | 96 | 69.1 | 10 | 21.3 | 279 | 60.8 | |
| HBV | <.0001 | ||||||||||
| No | 163 | 88.6 | 52 | 82.5 | 119 | 85.6 | 15 | 31.9 | 368 | 80.7 | |
| Yes | 18 | 9.8 | 11 | 17.5 | 21 | 15.1 | 32 | 68.1 | 88 | 19.2 | |
| ETOH | .004 | ||||||||||
| No | 137 | 74.5 | 48 | 76.2 | 92 | 66.2 | 46 | 97.9 | 345 | 75.2 | |
| Yes | 44 | 23.9 | 15 | 23.8 | 47 | 33.8 | 1 | 2.1 | 111 | 16.1 | |
| NASH | .064 | ||||||||||
| No | 138 | 75.0 | 56 | 88.9 | 122 | 87.8 | 42 | 89.4 | 382 | 83.2 | |
| Yes | 43 | 23.4 | 7 | 11.1 | 17 | 12.2 | 5 | 10.6 | 74 | 16.1 | |
| DM | <.0001 | ||||||||||
| No | 119 | 64.7 | 47 | 74.6 | 89 | 64.0 | 37 | 78.7 | 313 | 68.2 | |
| Yes | 61 | 33.2 | 15 | 23.8 | 49 | 35.3 | 10 | 21.3 | 139 | 30.3 | |
| HTN | <.0001 | ||||||||||
| No | 110 | 59.8 | 32 | 50.8 | 82 | 59.0 | 34 | 72.3 | 274 | 59.7 | |
| Yes | 71 | 38.6 | 31 | 49.2 | 56 | 40.3 | 13 | 27.7 | 180 | 39.2 | |
| CAD | .028 | ||||||||||
| No | 154 | 83.7 | 60 | 95.2 | 127 | 91.4 | 41 | 87.2 | 402 | 87.9 | |
| Yes | 22 | 12.0 | 2 | 3.2 | 5 | 3.6 | 4 | 8.5 | 35 | 7.6 | |
| Tobacco | .014 | ||||||||||
| No | 64 | 34.8 | 27 | 42.9 | 54 | 38.8 | 22 | 46.8 | 175 | 38.1 | |
| Yes | 95 | 51.6 | 29 | 46.0 | 61 | 43.9 | 12 | 25.5 | 206 | 44.9 | |
| Macrovascular invasion | .079 | ||||||||||
| No | 136 | 73.9 | 41 | 65.1 | 84 | 60.4 | 39 | 83.0 | 320 | 69.8 | |
| Yes | 34 | 18.5 | 14 | 22.2 | 44 | 31.7 | 5 | 10.6 | 102 | 22.2 | |
AFP indicates alpha fetoprotein; AJCC, American Joint Committee on Cancer; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HBV, hepatitis B virus; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; DM, diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension; CAD, coronary artery disease.
DISCUSSION
If not diagnosed at an early stage, HCC has a dismal prognosis. In our multivariate model, receipt of transplant was the strongest predictor of survival. Among transplant recipients, patients who fit the Milan criteria have better survival than those who do not.3 However, our data indicate that patients who meet those criteria are not randomly distributed in the population. In our study, race/ethnicity and insurance status were associated with both meeting the Milan criteria and receiving a transplant.
We found that black patients with HCC were 30 times less likely than whites to receive liver transplantation. Racial disparities in liver transplantation have been reported in the past. In a national study using data from 1998–2003, blacks with end-stage liver disease were less likely than whites to be listed for transplantation, and once listed, less likely to receive a transplant. The overall rate of liver transplantation was 3 times as high among whites as among blacks.7 In a pre-MELD cohort, black patients were less likely than white patients to receive a liver transplant and more likely to die or become too sick for liver transplantation within 3 years of registering on the waiting list. After the introduction of the MELD score, black race was no longer associated with receipt of transplant or increased likelihood of death on the waiting list.8
Racial disparities in liver transplantation for patients with HCC have been less well described. By using the 1998–2002 SEER database, we found that blacks and Asians with HCC were about half as likely as whites to receive a transplant. Hispanics also were less likely to receive a transplant, but the difference was not statistically significant.9 A similar study using the SEER database also found that blacks were 58% less likely to be transplanted for small solitary HCC than whites.10
In addition to several studies showing lower rates of nononcologic surgical procedures in black patients, many studies have shown similar racial disparities in the receipt of cancer-related surgeries and procedures. Bach et al found that among patients with resectable nonsmall-cell lung cancer, the rate of surgery for black patients was only 64% compared with 76.7% for white patients.11 In patients with locoregional esophageal cancer, the rate of surgery for black patients was found to be half that of white patients (25% vs 46%, respectively).12
Many explanations have been proposed for these racial disparities. One explanation is that black patients present with more advanced disease. In this study, we found that blacks presented with larger tumors, were more likely to exceed the Milan criteria, and had higher Child-Pugh scores compared with whites. An analysis of the UNOS database from 2002–2006 found that liver transplant candidates who were black and Hispanic presented with higher MELD scores than whites.13 In a single institution study, blacks were more likely than whites to present with HCC that exceeded the Milan criteria.14
Other explanations for these disparities in access to transplant may be patient-related barriers or healthcare-related barriers. A meta-analysis of 11 articles studying barriers in access to renal transplantation among African Americans found that patient-related barriers included personal and cultural beliefs about transplantation and lower socioeconomic status and levels of education. Healthcare-related barriers included physician perceptions, inadequate transplant workup, referral delays and immunologic mismatching based on human leukocyte antigen (HLA) status.15 A study by Ayanian et al in patients with end-stage renal disease found that black patients were less likely than white patients to want a kidney transplant. However, even after adjustment for patients’ preferences, blacks were still significantly less likely than whites to have been referred for evaluation and placed on a waiting list for a transplant or to have received a transplant within 18 months after the start of dialysis therapy.16 A subsequent study also found that physicians were less likely to believe that renal transplantation improves survival for blacks compared with whites (69% vs 81%; P = .001). Physicians believed that reasons why blacks were less likely to be evaluated for transplant included patients’ preferences, availability of donors, failure to complete evaluations, comorbid illnesses and, less commonly, patient-physician mistrust or physician bias.17 Another study in end-stage liver disease patients found that disproportionately fewer black patients were referred for liver transplantation than white patients.18 The authors speculated that limited access to healthcare, distrust of the medical community and patient misconception about transplantation may have contributed to these differences.
In our study, HCC patients with private insurance were 22 times more likely to receive transplant than those with Medicaid. Few studies have examined the role of insurance in liver transplantation for patients with HCC. One explanation is that Medicaid recipients present with more advanced disease than privately insured patients. We found that Medicaid recipients were more likely to have higher Child-Pugh scores, tumors that exceeded the Milan criteria, and higher AJCC stage. An analysis of the UNOS database from 2002–2006 also found that patients with Medicaid were more likely than privately insured patients to have a high MELD score at initial testing. The percentage of Medicaid patients who presented with a MELD score >20 was 46.3% compared with 36.5% of private patients.13 Medicaid patients in general have also been shown to have less access to subspecialists and sub-specialists are less likely to accept new Medicaid patients, especially those in managed care programs.19
Medicaid insurance is also an indicator of socioeconomic status. In our study, Medicaid patients had a lower median household income than privately insured patients. Medicaid patients may lack access to a full-time caregiver and a stable support network, which are deterrents to transplantation. If patients are not well-educated or have language barriers, then health literacy may play a part in these disparities. Unfortunately, the role of these factors in liver transplantation has not been formally studied.
In our univariate analysis, black and Hispanic patients and patients with Medicaid or Medicare had significantly poorer survival than white or privately insured patients. However, in a multivariate model that included receipt of transplant, other demographic and clinical factors, including race/ethnicity and insurance status, were not independently associated with survival. Wong et al found that black females with localized HCC were 56% less likely to survive 3 years than non-Hispanic white males using the SEER database.20 In a single institution study, African American and Hispanic patients with HCC had a 5-year survival rate of 12%, which was significantly lower than that of white patients.21 In a post-MELD cohort, blacks transplanted for HCC had a significantly lower overall survival and graft survival at 2 years than whites.22 An additional study in HCC patients found that the association of race with mortality risk became statistically non-significant after adjustment for receipt of therapy, disease stage, and other demographic variables.23 An analysis of the UNOS database from 1987–2001 found that neighborhood income did not influence the outcome of liver transplantation, and education had minimal influence, but patients with Medicare and Medicaid had lower survival post-transplant than those with private insurance.24
An advantage of our study is that we had access to demographic and clinical variables not available in many population-based databases, allowing us to analyze associations that have not been well characterized in the past. However, our study is limited because it is based on data from a single institution, which is a large tertiary referral transplant center with an ethnically diverse patient population. Our transplant rate for patients with HCC overall was 38%, compared with 21% in the 1998–2002 SEER database.9 Of our 86 patients with Medicare, about 20% received a transplant, compared with 0.9% among Medicare recipients nationwide.25 Therefore, our results may not necessarily be generalizable to other populations.
Our findings may reflect patient factors, such as differences in patient preferences, social and cultural beliefs, support networks, socioeconomic status, and education. However, they may also reflect delays in diagnosis, referral to transplant, and physician biases. These are shortcomings of the healthcare system that we need to correct to eliminate these disparities. We must improve access to care for black and Hispanic patients and for those receiving Medicaid insurance. Educational interventions targeting both patients and healthcare professionals will foster more effective patient-physician interactions and improve quality of care. Our study suggests that if we can overcome these barriers and provide these groups with transplantation, then we may succeed in improving survival overall.
Footnotes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURES
Supported by NIH/Columbia CTSA K12 Mentored Career Development Award (K12 RR024157-03), NIH CALME pilot grant (P30 AG135294-10), a Pardes Scholarship, and the Steven J. Levinson Medical Research Foundation (to ABS).
References
- 1.Ries LAG, Melbert D, Krapcho M, et al. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975–2005. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: [Accessed February 20, 2009.]. Available at: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2005/ [Google Scholar]
- 2.El-Serag HB, Davila JA, Petersen NJ, McGlynn KA. The continuing increase in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: An update. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:817–823. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-139-10-200311180-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mazzaferro V, Regalia E, Doci R, et al. Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:693–699. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199603143341104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Figueras J, Jaurrieta E, Valls C, et al. Survival after liver transplantation in cirrhotic patients with and without hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparative study. Hepatology. 1997;25:1485–1489. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ioannou GN, Perkins JD, Carithers RL. Jr Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: impact of the MELD allocation system and predictors of survival. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1342–1351. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.US Census Bureau. [Accessed February 20, 2009.];Census 2000 demographic profile highlights, American factfinder zip code tabulation. Available at: http://factfinder.census.gov.
- 7.Nguyen GC, Segev DL, Thuluvath PJ. Racial disparities in the management of hospitalized patients with cirrhosis and complications of portal hypertension: a national study. Hepatology. 2007;45:1282–1289. doi: 10.1002/hep.21580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Moylan CA, Brady CW, Johnson JL, Smith AD, Tuttle-Newhall JE, Muir AJ. Disparities in liver transplantation before and after introduction of the MELD score. JAMA. 2008;300:2371–2378. doi: 10.1001/jama.2008.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Siegel AB, McBride RB, El-Serag HB, et al. Racial disparities in utilization of liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States, 1998–2002. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:120–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sonnenday CJ, Dimick JB, Schulick RD, Choti MA. Racial and geographic disparities in the utilization of surgical therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007;11:1636–1646. doi: 10.1007/s11605-007-0315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bach PB, Cramer LD, Warren JL, Begg CB. Racial differences in the treatment of early-stage lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1198–1205. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199910143411606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Steyerberg EW, Earle CC, Neville BA, Weeks JC. Racial differences in surgical evaluation, treatment, and outcome of locoregional esophageal cancer: a population-based analysis of elderly patients. JCO. 2005;23:510–517. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kemmer N, Zacharias V, Kaiser TE, Neff GW. Access to liver transplantation in the MELD era: role of ethnicity and insurance. [Accessed February 21, 2009.];Dig Dis Sci [serial online] 2008 doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0567-5. Available at: http://www.springerlink.com/content/v7x686382063563l/ [DOI] [PubMed]
- 14.Kemmer N, Neff G, Secic M, Zacharias V, Kaiser T, Buell J. Ethnic differences in hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for liver transplantation. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:551–555. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-9872-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Navaneethan SD, Singh S. A systematic review of barriers in access to renal transplantation among African Americans in the United States. Clin Transplant. 2006;20:769–775. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2006.00568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ayanian JZ, Cleary PD, Weissman JS, Epstein AM. The effect of patients” preferences on racial differences in access to renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1661–169. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199911253412206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ayanian JZ, Cleary PD, Keogh JH, Noonan SJ, David-Kasdan JA, Epstein AM. Physicians” beliefs about racial differences in referral for renal transplantation. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43:350–357. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2003.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Eckhoff DE, McGuire BM, Young CJ, et al. Race: a critical factor in organ donation, patient referral and selection, and orthotopic liver transplantation? Liver Transpl Surg. 1998;4:499–505. doi: 10.1002/lt.500040606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Backus L, Osmond D, Grumbach K, Vranizan K, Phuong L, Bindman AB. Specialists” and primary care physicians” participation in medicaid managed care. J Gen Intern Med. 2001;16:815–821. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2001.01239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wong RJ, Corley DA. Survival differences by race/ethnicity and treatment for localized hepatocellular carcinoma within the United States. [Accessed February 21, 2009.];Dig Dis Sci [serial online] 2009 doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0661-8. Available at: http://www.springerlink.com/content/539488v15600441j/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Harrison LE, Reichman T, Koneru B, et al. Racial discrepancies in the outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2004;139:992–996. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.139.9.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ananthakrishnan A, Saeian K. Racial differences in liver transplantation outcomes in the MELD era. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:901–910. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Davila JA, El-Serag HB. Racial differences in survival of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: a population-based study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:104–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yoo HY, Thuluvath PJ. Outcome of liver transplantation in adult recipients: influence of neighborhood income, education and insurance. Liver Transpl. 2004;10:235–243. doi: 10.1002/lt.20069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.El-Serag HB, Siegel AB, Davila JA, et al. Treatment and outcomes of treating of hepatocellular carcinoma among Medicare recipients in the United States: A population-based study. J Hepatol. 2006;44:158–166. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


