Abstract
Partially purified aminoacyl synthetase preparations from pea roots (Pisum sativum L. var. Alaska) contain a heat-labile factor which can degrade leucyl-tRNA6leu to a new species. The singular electrophoretic and chromatographic mobilities, the isoprenoid nucleoside content, and the charging characteristics of the new species (designated leucyl-tRNALleu), suggest that it is a fragment of tRNA6leu containing at least that portion of the original molecule extending from the 3′ terminus to the anticodon. Conversion appears to be highly specific since neither bulk tRNA, the other leucine tRNA subspecies, nor tyrosine, phenylalanine, or tryptophan tRNAs are susceptible to degradation during incubation with the synthetase preparation.
Full text
PDF

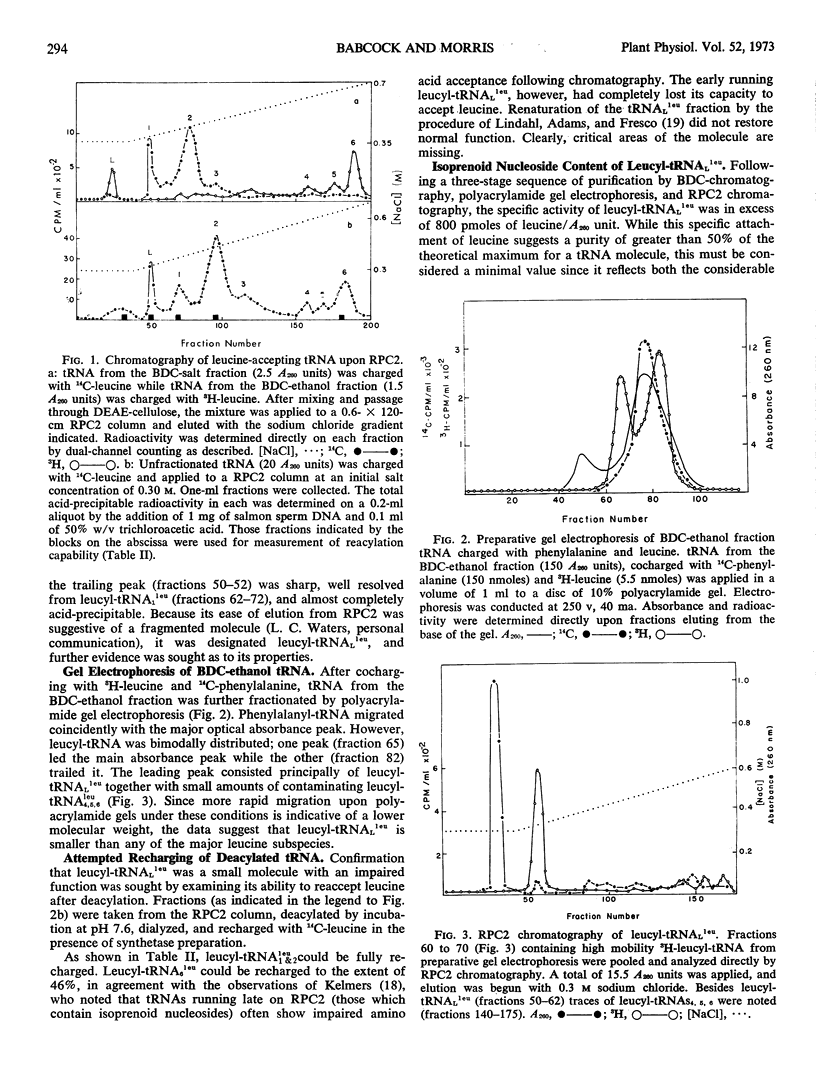
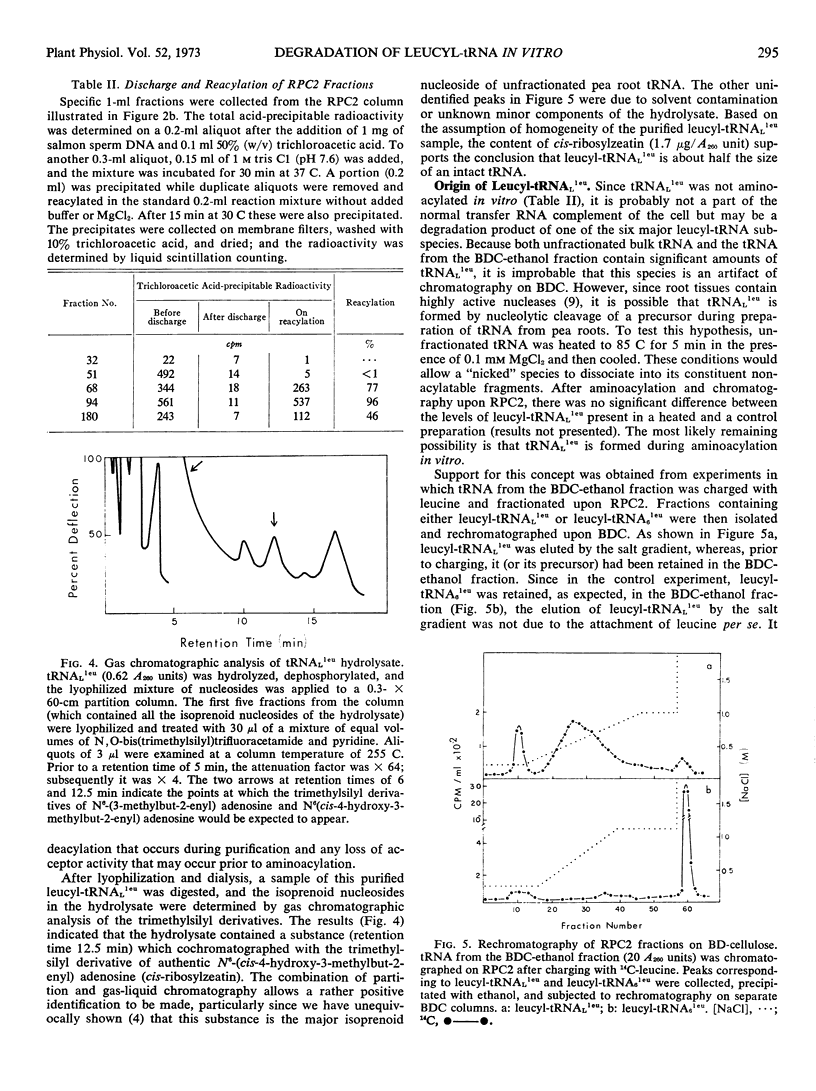
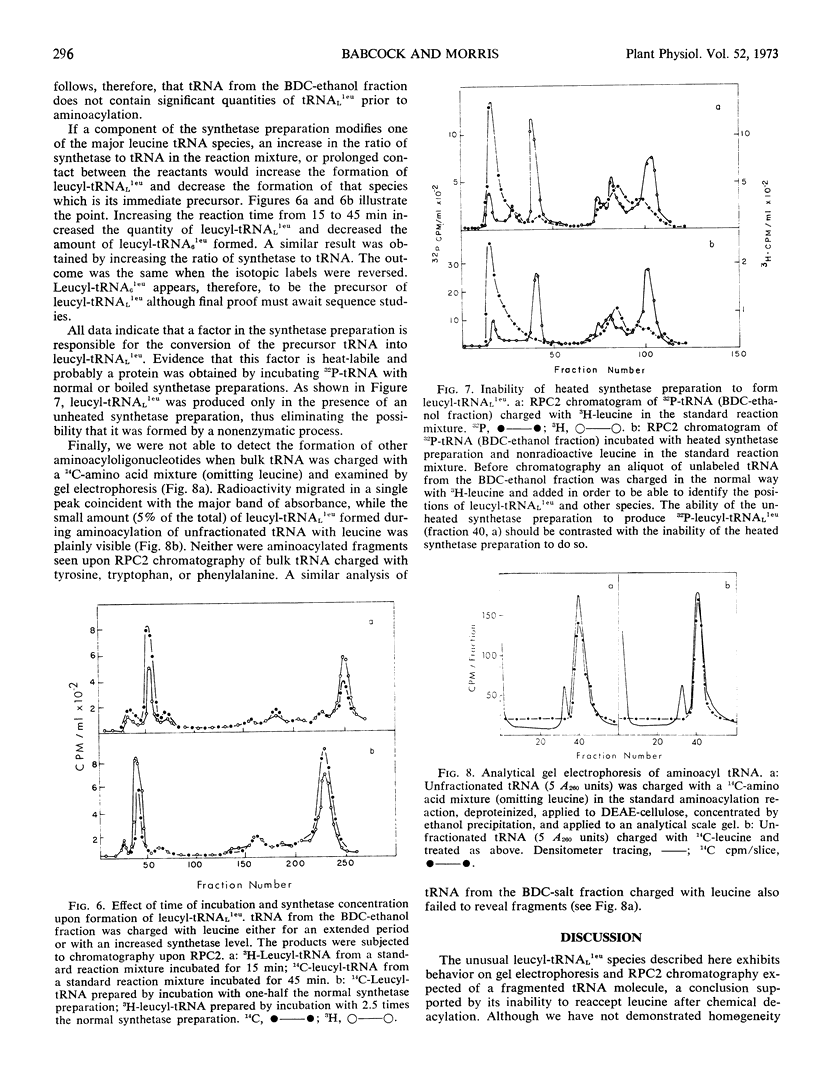

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman S., Smith J. D. Tyrosine tRNA precursor molecule polynucleotide sequence. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):35–39. doi: 10.1038/newbio233035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. B., Cherry J. H. Differences in leucyl-transfer rna's and synthetase in soybean seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):202–209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D. J., Burrows W. J., Skoog F., Roy K. L., Söll D. Cytokinins: distribution in transfer RNA species of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):834–841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babcock D. F., Morris R. O. Quantitative measurement of isoprenoid nuceosides in transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1970 Sep 15;9(19):3701–3705. doi: 10.1021/bi00821a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bick M. D., Liebke H., Cherry J. H., Strehler B. L. Changes in leucyl- and tyrosyl-tRNA of soybean cotyledons during plant growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 19;204(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows W. J., Skoog F., Leonard N. J. Isolation and identification of cytokinins located in the transfer ribonucleic acid of tobacco callus grown in the presence of 6-benzylaminopurine. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 8;10(12):2189–2194. doi: 10.1021/bi00788a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. H., Osborne D. J. Specificity of leucyl-tRNA and synthetase in plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 24;40(4):763–769. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90968-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIERS W., VANDENDRIESSCHE L. The ribonuclease-activity of barley. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1961 May;69:339–363. doi: 10.3109/13813456109092802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Chen C. Characterization of labeled ribonucleic acid from tissue grown on 14C-containing cytokinins. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4490–4494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Pestka S. Transfer RNA species in normal and leukemic human lymphoblasts. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 14;52(2):195–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam I., Millward S., Blew D., von Tigerstrom M., Wimmer E., Tener G. M. The separation of soluble ribonucleic acids on benzoylated diethylaminoethylcellulose. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3043–3056. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield G. W., Burns R. O. Specific binding of leucyl transfer RNA to an immature form of L-threonine deaminase: its implications in repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1027–1035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K. B. Role of an isoacceptor transfer ribonucleic acid as an enzyme inhibitor: effect on tryptophan pyrrolase of Drosophila. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 5;231(18):17–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano-Sueoka T., Nirenberg M., Sueoka N. Effect of bacteriophage infection upon the specificity of leucine transfer RNA for RNA codewords. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;35(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano-Sueoka T., Sueoka N. Characterization of a modified leucyl-tRNA of Escherichia coli after bacteriophage T2 infection. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):475–491. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano-Sueoka T., Sueoka N. Leucine tRNA and cessation of Escherichia coli protein synthesis upon phage T2 infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1229–1236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelmers A. D. Effect of divalent metal ions on the reversed-phase chromatographic separation of transfer ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4401–4404. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Adams A., Fresco J. R. Renaturation of transfer ribonucleic acids through site binding of magnesium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):941–948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäenpä P. H., Bernfield M. R. A specific hepatic transfer RNA for phosphoserine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):688–695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON M. S., GREENE R. C. MEASUREMENT OF LOW ENERGY BETA-EMITTERS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF EMULSIONS. Anal Chem. 1965 Jun;37:854–857. doi: 10.1021/ac60226a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Altman S., Smith J. D. Purification and properties of a specific Escherichia coli ribonuclease which cleaves a tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid presursor. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5243–5251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy K. L., Söll D. Fractionation of Escherichia coli transfer RNA on benzoylated DEAE-cellulose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jul 23;161(2):572–574. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90137-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. C., Morris R. O. Preparation of aminoacyl synthetases from higher plants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;185(2):474–477. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardzik D. R., Grell E. H., Jacobson K. B. Mechanism of suppression in Drosophila: a change in tyrosine transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):231–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Novelli G. D. A new change in leucine transfer RNA observed in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):979–985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. F., Kelmers A. D. A new chromatographic system for increased resolution of transfer ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2507–2513. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W. K., Novelli G. D. Isoaccepting +RNA's in mouse plasma cell tumors that synthesize different myeloma protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 May 23;31(4):534–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudelevich A. Specific cleavage of an Escherichia coli leucine transfer RNA following bacteriophage T4 infection. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90444-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


