Abstract
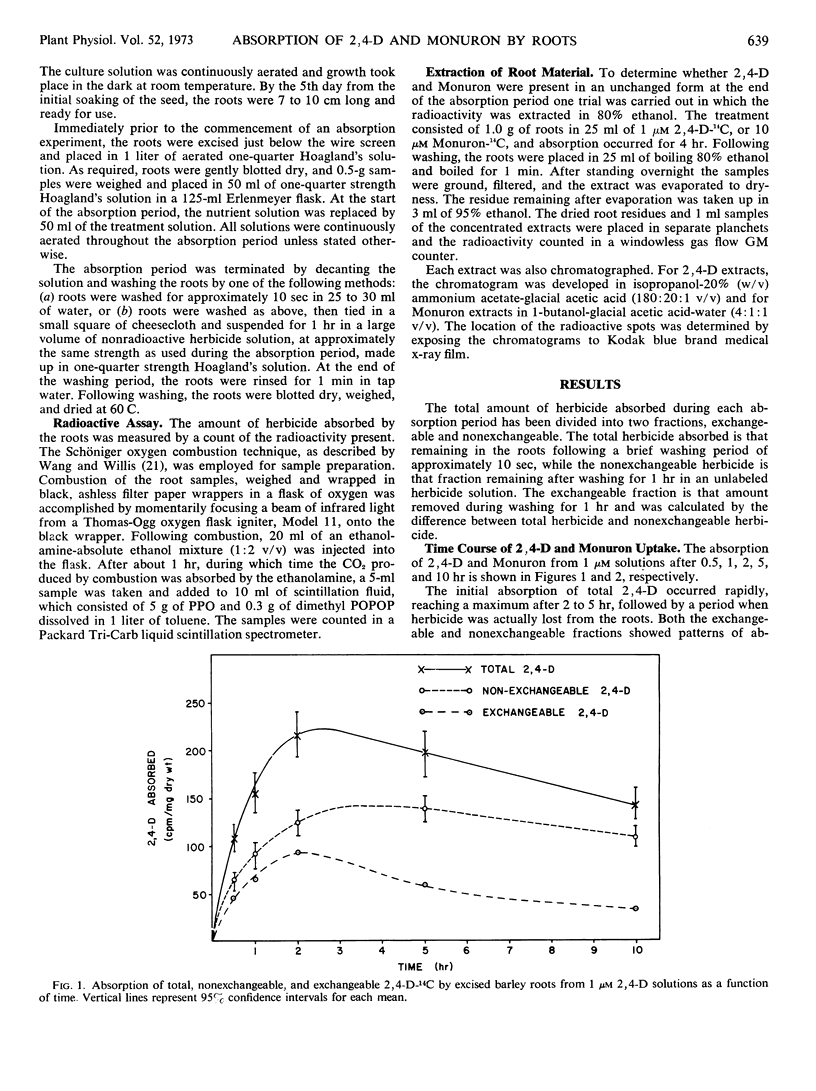
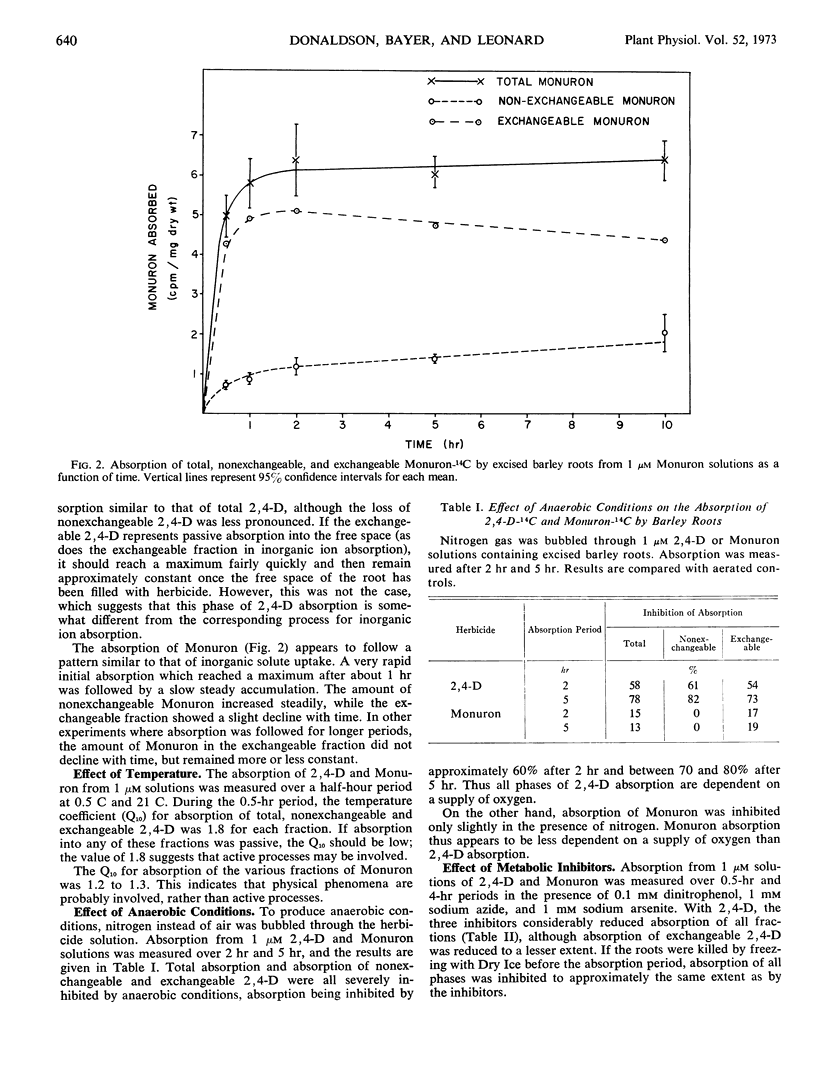
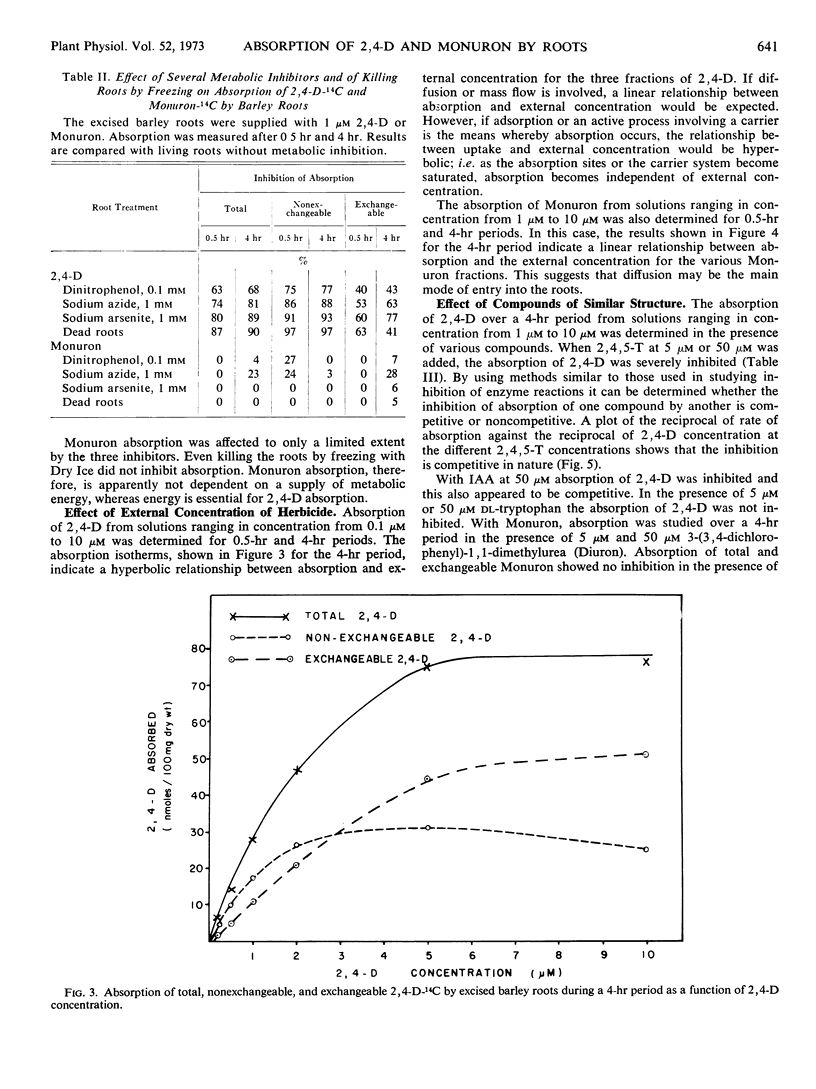
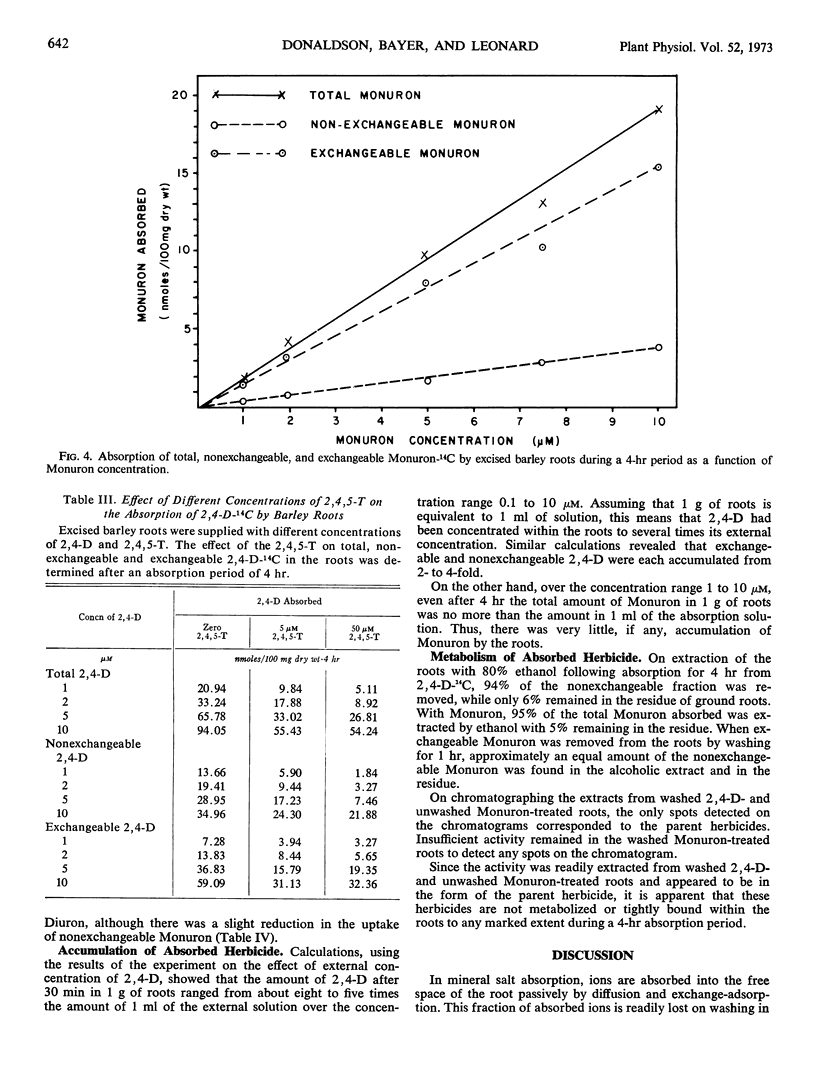
Absorption from culture solution of the herbicides 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4-D) and 3-(p-chlorophenyl)-1, 1-dimethylurea (Monuron) by excised barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) roots was studied to determine whether absorption was due to an active or a passive mechanism. Herbicide absorption was followed at low temperature, under anaerobic conditions, and in the presence of metabolic inhibitors and compounds of structure similar to that of the herbicide. Total absorption was divided into two phases, exchangeable and nonexchangeable herbicide, by washing the roots for 1 hour following absorption. Absorption of both exchangeable and non-exchangeable 2, 4-D appeared to depend on a supply of metabolic energy which suggests that an active mechanism may be involved. A possible conclusion is that 2, 4-D is absorbed by roots by an adsorption mechanism and that energy is required to maintain the integrity of the absorbing surfaces of the cell. In contrast, absorption of Monuron was independent of an energy supply. It is concluded that the bulk of the Monuron absorbed was taken up passively by diffusion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Epstein E. The essential role of calcium in selective cation transport by plant cells. Plant Physiol. 1961 Jul;36(4):437–444. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. G. Uptake of 3-o-Methylglucose by Healthy and Hypomyces-infected Squash Hypocotyls. Plant Physiol. 1969 Sep;44(9):1267–1272. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.9.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen P., Benson A. A. Active Transport of Choline Sulfate by Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1964 Jul;39(4):586–589. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.4.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. J., Thimann K. V. Uptake of Indole-3-acetic Acid and Indole-3-acetonitrile by Avena Coleoptile Sections. Plant Physiol. 1964 Jan;39(1):98–103. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao A. V., Fallin E., Fang S. C. Comparative study of uptake and cellular distribution of Hg203-labeled phenyl-mercuric acetate and mercuric acetate by pea roots. Plant Physiol. 1966 Mar;41(3):443–446. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


