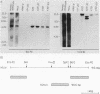
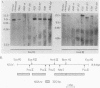
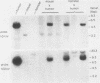
Abstract
The genes and gene products involved in the mammalian DNA repair processes have yet to be identified. Toward this end we made use of a number of DNA repair-proficient transformants that were generated after transfection of DNA from repair-proficient human cells into a mutant hamster line that is defective in the initial incision step of the excision repair process. In this report, biochemical evidence is presented that demonstrates that these transformants are repair proficient. In addition, we describe the molecular identification and cloning of unique DNA sequences closely associated with the transfected human DNA repair gene and demonstrate the presence of homologous DNA sequences in human cells and in the repair-proficient DNA transformants. The chromosomal location of these sequences was determined by using a panel of rodent-human somatic cell hybrids. Both unique DNA sequences were found to be on human chromosome 19.
Full text
PDF

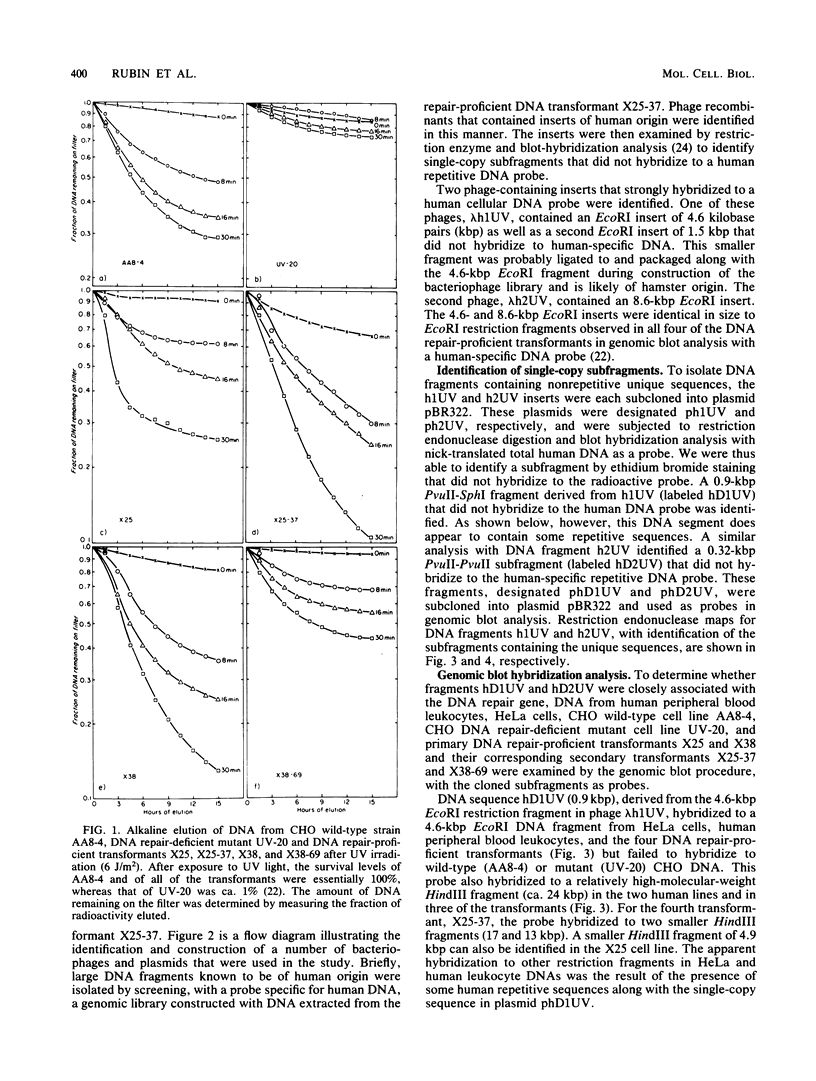
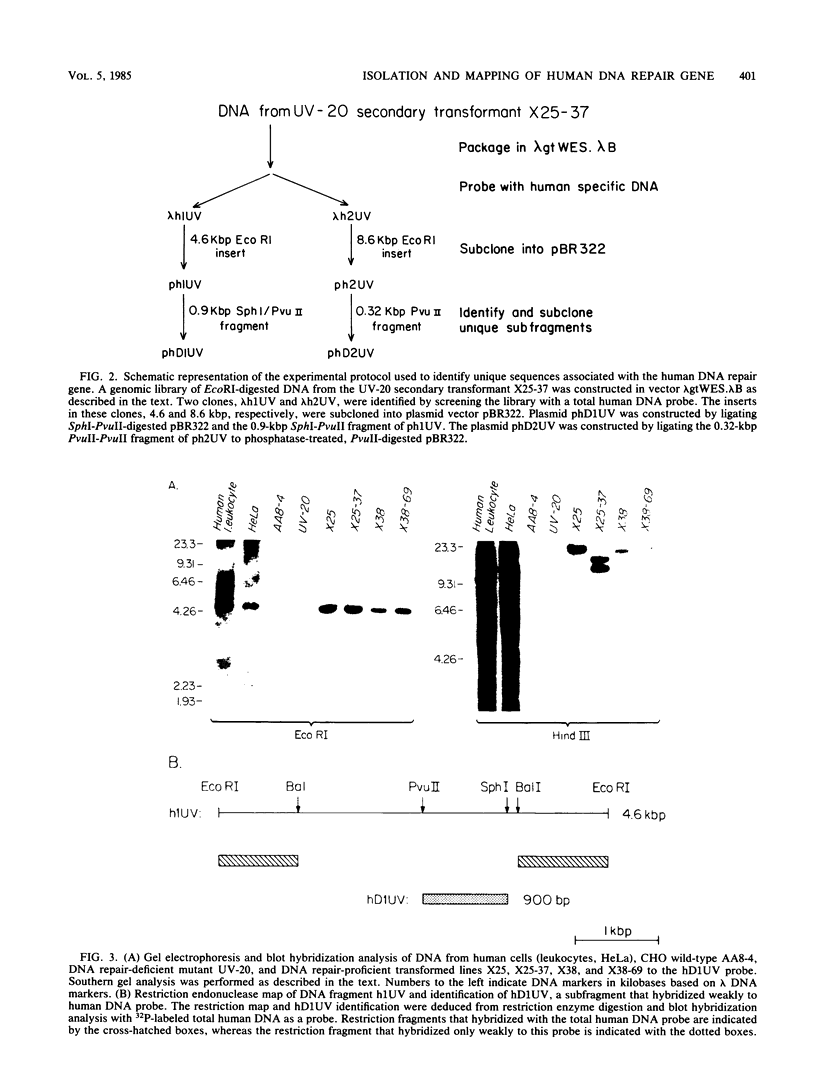
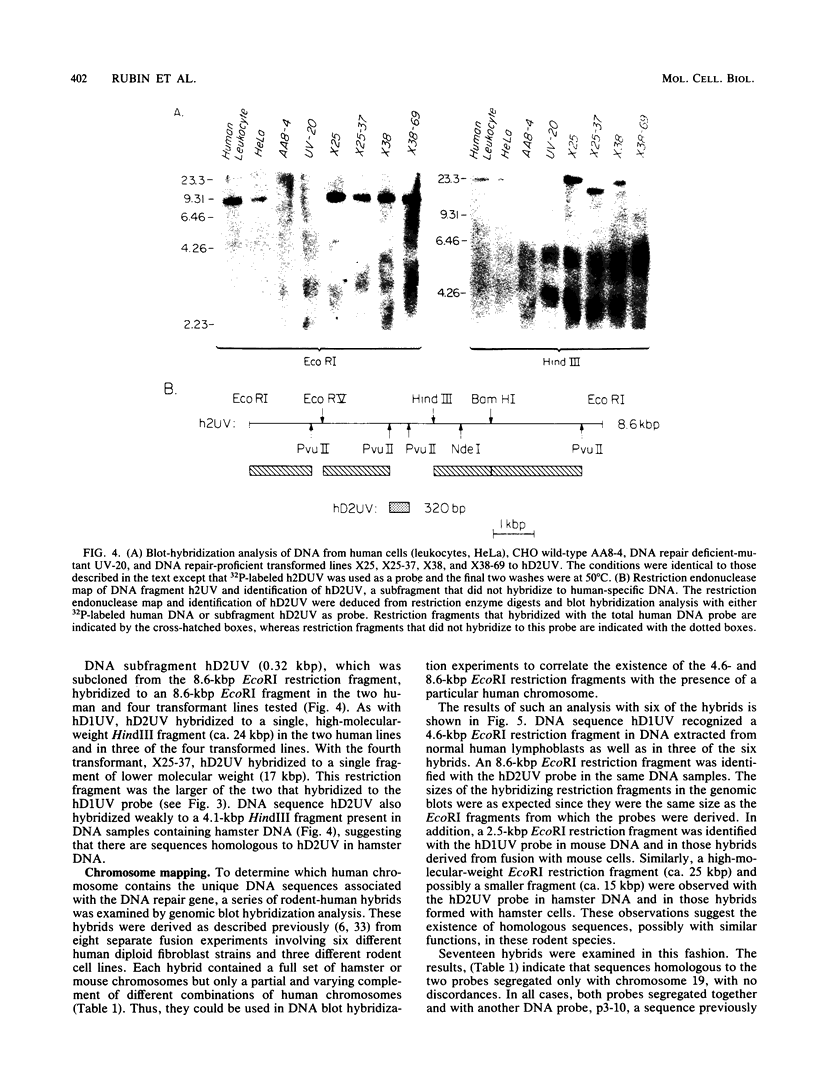
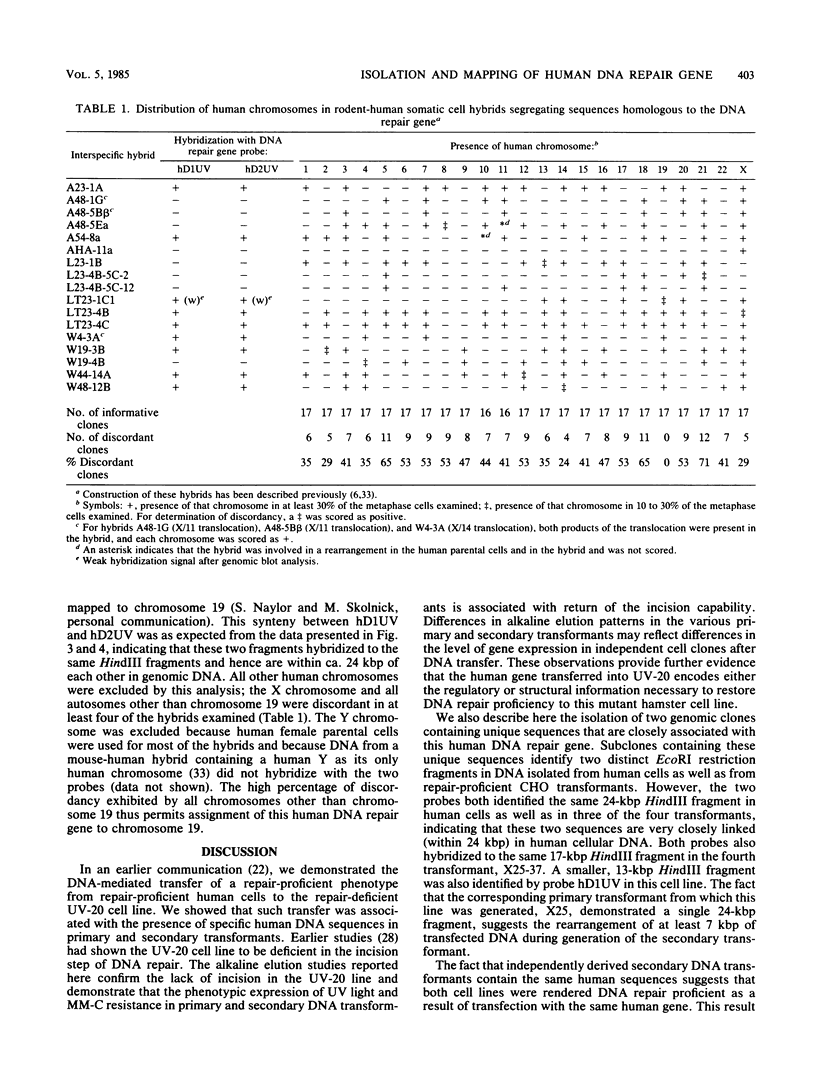


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker A., Gold M. Isolation of the bacteriophage lambda A-gene protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):581–585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch D. B., Cleaver J. E., Glaser D. A. Large-scale isolation of UV-sensitive clones of CHO cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 May;6(3):407–418. doi: 10.1007/BF01542792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccia N., Kronenberg M., Saxe D., Haars R., Bruns G. A., Goverman J., Malissen M., Willard H., Yoshikai Y., Simon M. The T cell receptor beta chain genes are located on chromosome 6 in mice and chromosome 7 in humans. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1091–1099. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90443-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Kohn K. W., Kann H. E., Jr DNA single-strand breaks during repair of UV damage in human fibroblasts and abnormalities of repair in xeroderma pigmentosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):39–43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Oliver N. Quantitative analysis of high-resolution trypsin-giemsa bands on human prometaphase chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1978 Dec 18;45(2):137–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00286957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanawalt P. C., Cooper P. K., Ganesan A. K., Smith C. A. DNA repair in bacteria and mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Murray K. Packaging recombinant DNA molecules into bacteriophage particles in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3259–3263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori T., Shiomi T., Sato K. Human chromosome 13 compensates a DNA repair defect in UV-sensitive mouse cells by mouse--human cell hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5655–5659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murnane J. P., Painter R. B. Complementation of the defects of DNA synthesis in irradiated and unirradiated ataxia-telangiectasia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1960–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. S., Joyner A. L., Bernstein A., Whitmore G. F. Molecular identification of a human DNA repair gene following DNA-mediated gene transfer. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):206–208. doi: 10.1038/306206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Setlow R. B. DNA repair in a UV-sensitive mutant of a mouse cell line. Mutat Res. 1981 Dec;84(2):443–455. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(81)90211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamato T. D., Hinkle L., Collins A. R., Waldren C. A. Chinese hamster ovary mutant UV-1 is hypomutable and defective in a postreplication recovery process. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 May;7(3):307–320. doi: 10.1007/BF01538856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanners C. P., Eliceiri G. L., Green H. Two types of ribosome in mouse-hamster hybrid cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 10;230(10):52–54. doi: 10.1038/newbio230052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini M., Reuser A., Bootsma D. Isolation of Chinese hamster ovary cells with reduced unscheduled DNA synthesis after UV irradiation. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Sep;8(5):635–642. doi: 10.1007/BF01542856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Brookman K. W., Dillehay L. E., Mooney C. L., Carrano A. V. Hypersensitivity to mutation and sister-chromatid-exchange induction in CHO cell mutants defective in incising DNA containing UV lesions. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Nov;8(6):759–773. doi: 10.1007/BF01543017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Busch D. B., Brookman K., Mooney C. L., Glaser D. A. Genetic diversity of UV-sensitive DNA repair mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3734–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Rubin J. S., Cleaver J. E., Whitmore G. F., Brookman K. A screening method for isolating DNA repair-deficient mutants of CHO cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 May;6(3):391–405. doi: 10.1007/BF01542791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiemer D., Enquist L., Leder P. Improved derivative of a phage lambda EK2 vector for cloning recombinant DNA. Nature. 1976 Oct 7;263(5577):526–527. doi: 10.1038/263526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerveld A., Hoeijmakers J. H., van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Pastink A., Wood R. D., Bootsma D. Molecular cloning of a human DNA repair gene. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):425–429. doi: 10.1038/310425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Holmes M. T. A sensitive and dependable assay for distinguishing hamster and human X-linked steroid sulfatase activity in somatic cell hybrids. Hum Genet. 1984;66(2-3):272–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00286615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D., de Veciana M., Presson-Tincknell B. Postirradiation properties of a UV-sensitive variant of CHO. Photochem Photobiol. 1982 Aug;36(2):169–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1982.tb04359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakrzewski S., Sperling K. Genetic heterogeneity of Fanconi's anemia demonstrated by somatic cell hybrids. Hum Genet. 1980;56(1):81–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00281573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelle B., Lohman P. H. Repair of UV-endonuclease-susceptible sites in the 7 complementation groups of xeroderma pigmentosum A through G. Mutat Res. 1979 Sep;62(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(79)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]