Abstract
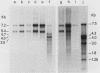
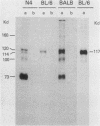
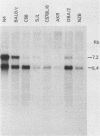
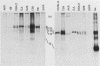
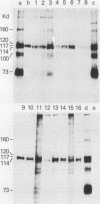
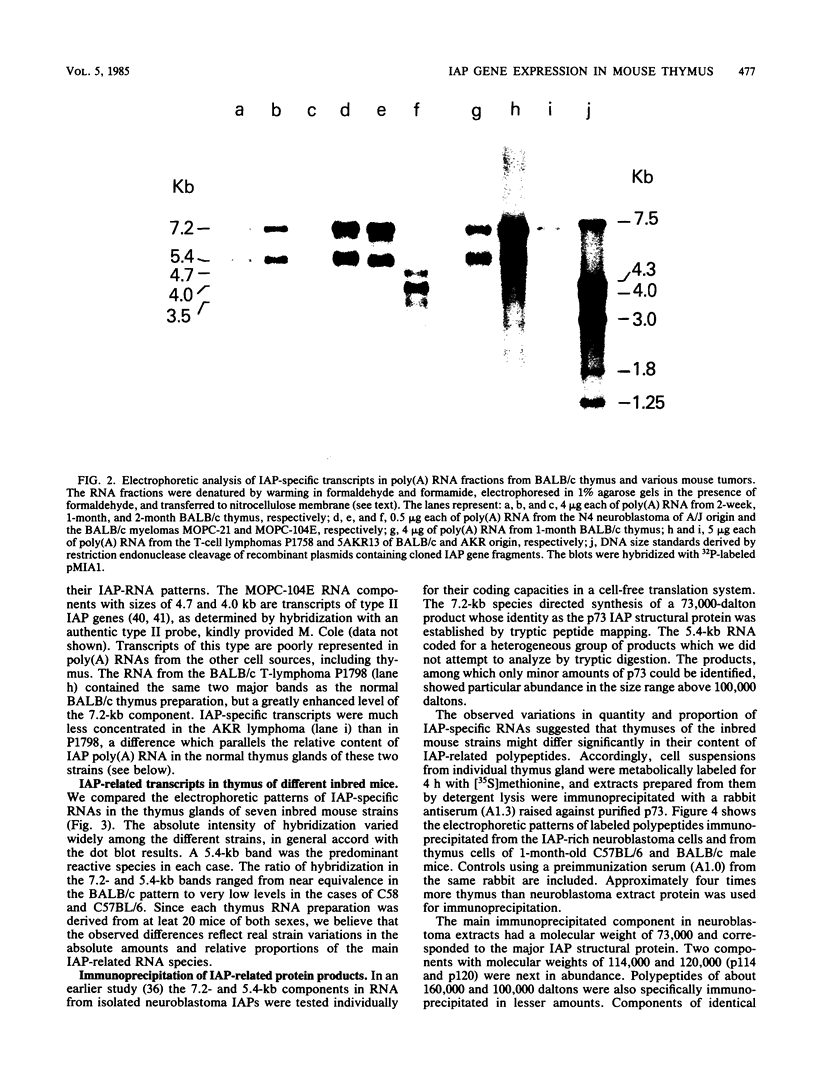
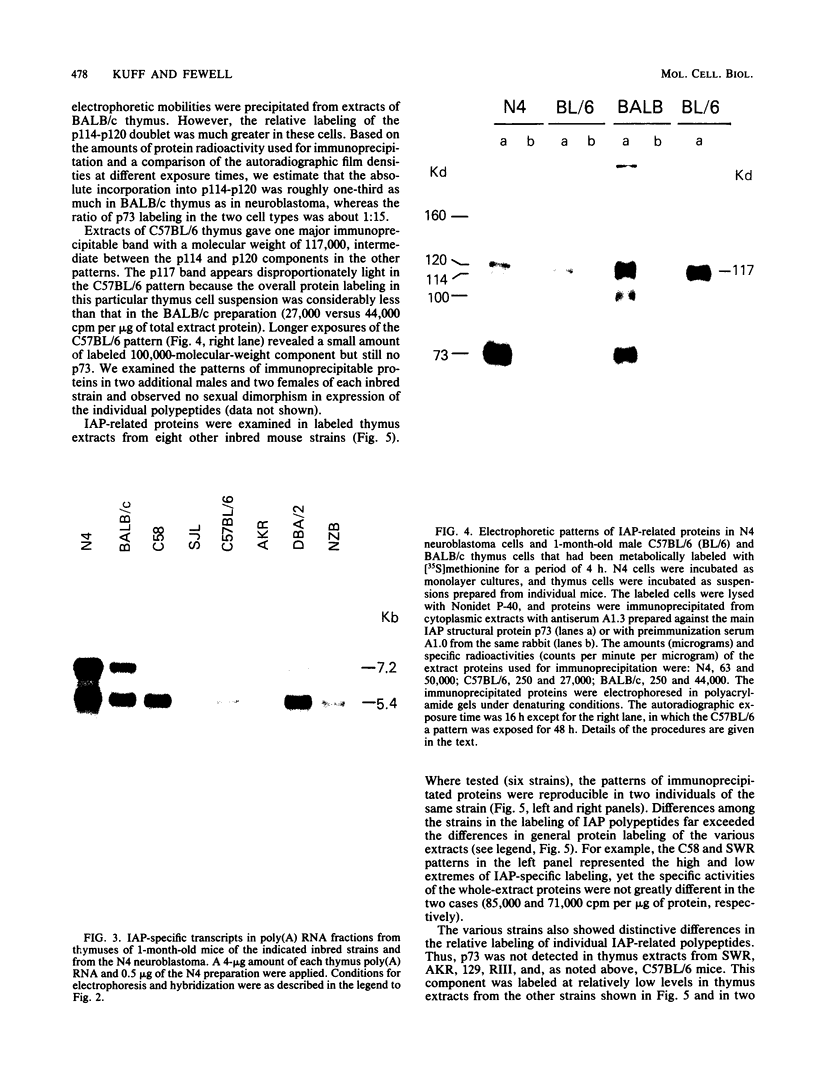
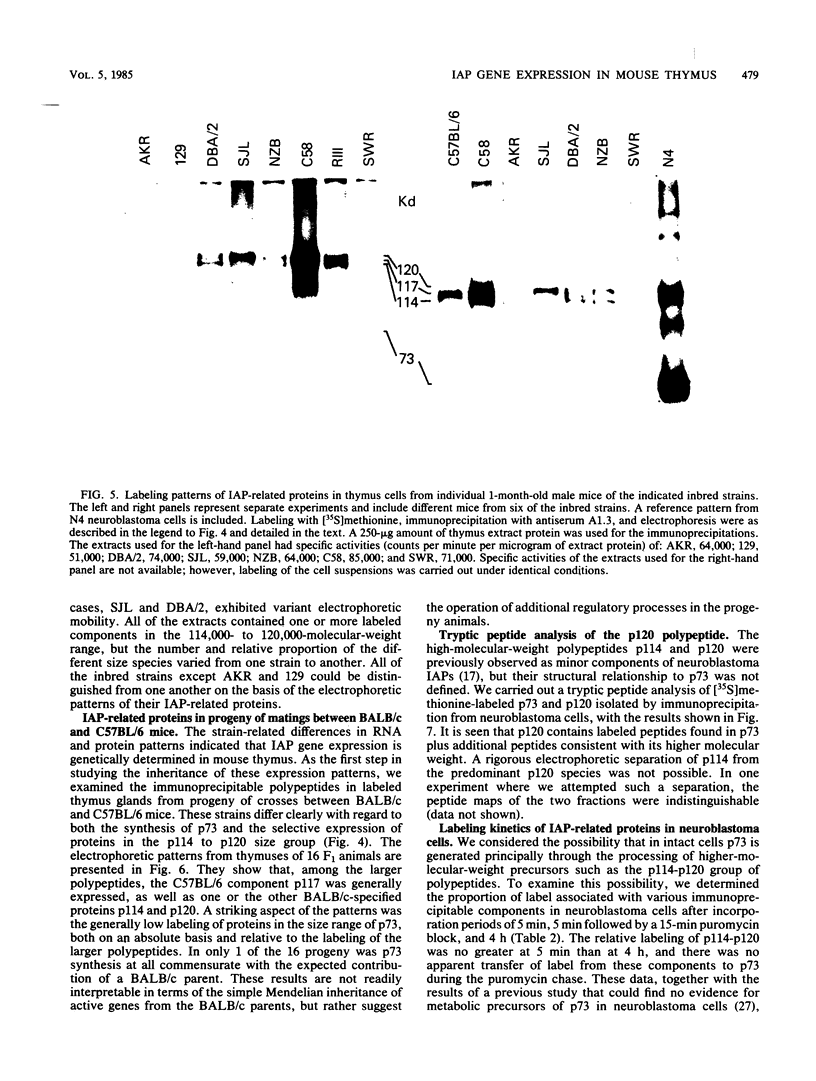
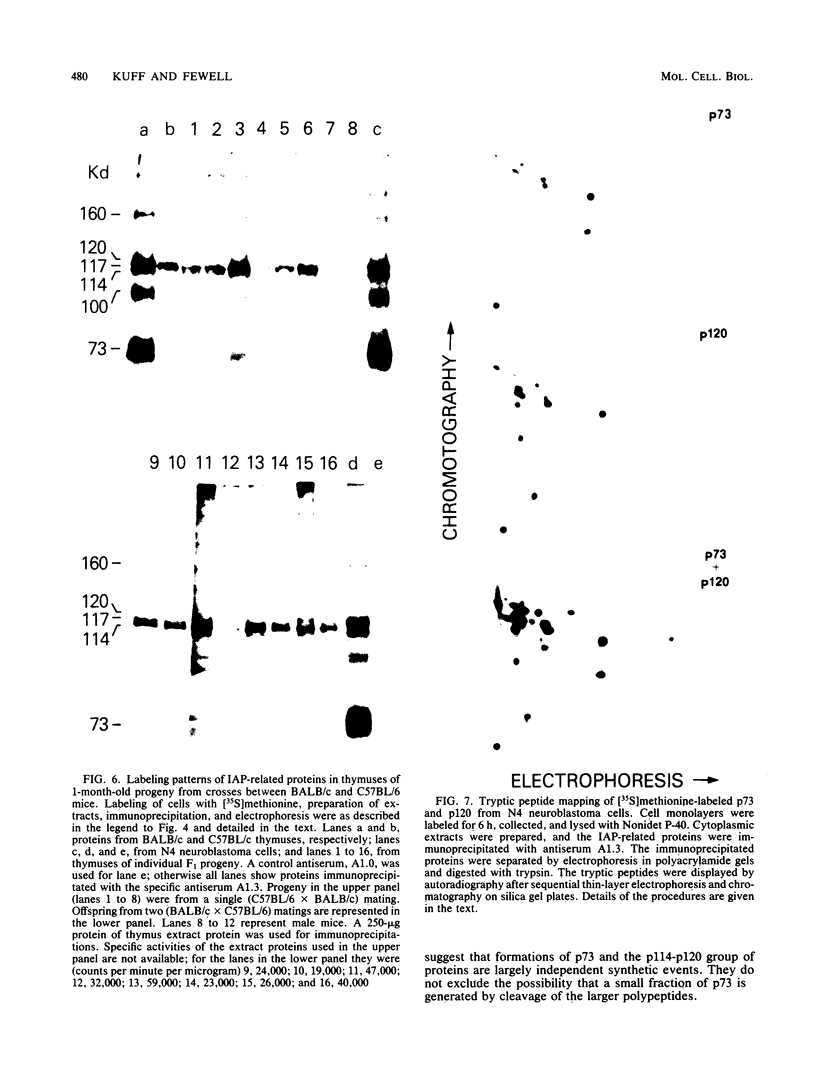
Intracisternal A-particle (IAP)-specific sequences were 5- to 10-fold enriched in polyadenylated RNA from BALB/cJ thymus as compared with RNAs from liver, spleen, and kidney. The major transcripts of 7.2 and 5.4 kilobases were the same size as those found in an IAP-rich neuroblastoma cell line. The absolute levels and proportions of these transcripts varied in thymuses from mice of different inbred strains. With antiserum prepared against p73, the main IAP structural protein, several size classes of IAP-related proteins were immunoprecipitated from extracts of thymus cells incubated with [35S]methionine; these included p73 itself and a group of polypeptides in the size range of 114 to 120 kilodaltons (p114-p120). The inbred strains showed marked characteristic differences in the electrophoretic patterns of their IAP-related proteins. Earlier studies showed that the 7.2-kilobase RNA from neuroblastoma IAPs coded for p73 in a cell-free translation system. Correlations between the RNA and protein patterns in thymuses of the different inbred strains indicated that 5.4-kilobase RNA gives rise to the p114-p120 polypeptides. Metabolically labeled p120 was found to include methionine-containing tryptic peptides of p73 plus additional peptides consistent with its larger size. In vivo labeling kinetics showed that the p114-p120 polypeptides were not major precursors of p73 in intact neuroblastoma cells. This study shows that IAP gene expression in mouse thymus is genetically determined and that a novel class of IAP-related polypeptides can be expressed independently of the major particle structural protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano T., Richelson E., Nirenberg M. Neurotransmitter synthesis by neuroblastoma clones (neuroblast differentiation-cell culture-choline acetyltransferase-acetylcholinesterase-tyrosine hydroxylase-axons-dendrites). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):258–263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R., Kuff E. L., Lueders K. K., Birkenmeier E. Genetic relationship between the Mus cervicolor M432 retrovirus and the Mus Musculus intracisternal type A particle. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):901–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.901-911.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Dreazen O., Klar A., Rechavi G., Ram D., Cohen J. B., Givol D. Activation of the c-mos oncogene in a mouse plasmacytoma by insertion of an endogenous intracisternal A-particle genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7118–7122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase D. G., Pikó L. Expression of A- and C-type particles in early mouse embryos. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Dec;51(6):1971–1975. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.6.1971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Unger T., Rechavi G., Canaani E., Givol D. Rearrangement of the oncogene c-mos in mouse myeloma NSI and hybridomas. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):797–799. doi: 10.1038/306797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan D. J. Transposable elements in eukaryotes. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:281–326. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni-Celli S., Hsiao W. L., Weinstein I. B. Rearranged c-mos locus in a MOPC 21 murine myeloma cell line and its persistence in hybridomas. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):795–796. doi: 10.1038/306795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Shulman M. J., Murialdo H., Gibson D. M., Hozumi N. Mutant immunoglobulin genes have repetitive DNA elements inserted into their intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7425–7429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. T., Jr, Calarco P. G. Evidence for the cell surface expression of intracisternal A particle-associated antigens during early mouse development. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):388–392. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90462-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. T., Jr, Calarco P. G. Immunologic relatedness of intracisternal A-particles in mouse embryos and neoplastic cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Apr;68(4):643–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. T., Jr, Calarco P. G. Immunoprecipitation of intracisternal A-particle-associated antigens from preimplantation mouse embryos. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Nov;67(5):1129–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly F., Condamine H. Tumor viruses and early mouse embryos. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 29;651(2-3):105–141. doi: 10.1016/0304-419X(82)90009-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Callahan R., Howk R. S. Immunological relationship between the structural proteins of intracisternal A-particles of Mus musculus and the M432 retrovirus of Mus cervicolor. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1211–1214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1211-1214.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Feenstra A., Lueders K., Rechavi G., Givol D., Canaani E. Homology between an endogenous viral LTR and sequences inserted in an activated cellular oncogene. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):547–548. doi: 10.1038/302547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Feenstra A., Lueders K., Smith L., Hawley R., Hozumi N., Shulman M. Intracisternal A-particle genes as movable elements in the mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1992–1996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Leuders K. K., Ozer H. L., Wivel N. A. Some structural and antigenic properties of intracisternal A particles occurring in mouse tumors (complement fixation-immunodiffusion-neuroblastoma-plasma-cell tumor). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):218–222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Smith L. A., Lueders K. K. Intracisternal A-particle genes in Mus musculus: a conserved family of retrovirus-like elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):216–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Kuff E. L. Intracisternal Type A particles in murine pancreatic B cells. Immunocytochemical demonstration of increased antigen (p73) in genetically diabetic mice. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jan;114(1):46–55. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Fewell J. W., Kuff E. L., Koch T. The long terminal repeat of an endogenous intracisternal A-particle gene functions as a promoter when introduced into eucaryotic cells by transfection. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2128–2135. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Intracisternal A-particle genes: identification in the genome of Mus musculus and comparison of multiple isolates from a mouse gene library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3571–3575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Sequences associated with intracisternal A particles are reiterated in the mouse genome. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):963–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Synthesis and turnover of intracisternal A-particle structural protein in cultured neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5192–5199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Segal S., Kuff E. L. RNA sequences specifically associated with mouse intracisternal A particles. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):83–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90319-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciani D. J., Kuff E. L. Isolation and partial characterization of the internal structural proteins from murine intracisternal A particles. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5075–5083. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire K. R., Asofsky R. M., Potter M., Kuff E. L. Macroglobulin-producing plasma-cell tumor in mice: identification of a new light chain. Science. 1965 Oct 15;150(3694):360–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Cole M. D., White A. T., Huang R. C. Sequence organization of cloned intracisternal A particle genes. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Bishop J. O. Changes in the mRNA population of chick myoblasts during myogenesis in vitro. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):751–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Segal S., Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. RNA associated with murine intracisternal type A particles codes for the main particle protein. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):118–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.118-126.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikó L., Hammons M. D., Taylor K. D. Amounts, synthesis, and some properties of intracisternal A particle-related RNA in early mouse embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechavi G., Givol D., Canaani E. Activation of a cellular oncogene by DNA rearrangement: possible involvement of an IS-like element. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):607–611. doi: 10.1038/300607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Cole M. D. Amplification of a specific set of intracisternal A-particle genes in a mouse plasmacytoma. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):171–177. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.171-177.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Cole M. D. Differing populations of intracisternal A-particle genes in myeloma tumors and mouse subspecies. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):411–421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.411-421.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. H., Bohn E. W., Matsukage A., Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Studies on the relationship between deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase activity and intracisternal A-type particles in mouse myeloma. Biochemistry. 1974 Mar 12;13(6):1087–1094. doi: 10.1021/bi00703a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. H., Kuff E. L. A novel DNA polymerase activity found in association with intracisternal A-type particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1531–1536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wivel N. A., Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Structural organization of murine intracisternal A particles. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):329–334. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.329-334.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wivel N. A., Smith G. H. Distribution of intracisternal A-particles in a variety of normal and neoplastic mouse tissues. Int J Cancer. 1971 Jan 15;7(1):167–175. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910070119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotsuyanagi Y., Szöllösi D. Early mouse embryo intracisternal particle: Fourth type of retrovirus-like particle associated with the mouse. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Sep;67(3):677–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]