Abstract
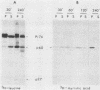
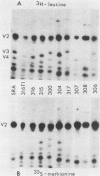
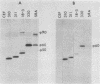
p60src of wild-type Rous sarcoma virus is myristylated at its N-terminal glycine residue. We have shown previously that this myristylation is necessary for p60src membrane association and for cell transformation by using src mutants with alterations within the N-terminal 30 kilodaltons of p60src. In this study we analyzed the process of p60src myristylation in wild type- and mutant-infected cells. All myristylated src proteins examined lack the initiator methionine, but two mutant src proteins lacking the initiator methionine are not myristylated, indicating that removal of the initiator methionine and myristylation are not obligatorily coupled. Analysis of the kinetics of myristylation and the association of p60src with cellular proteins p50 and p90 indicated that myristylation occurs before p60src becomes membrane associated and that transient association with p50 and p90 occurs regardless of myristylation. Myristylation is required for stable association of p60src with the plasma membrane but is not sufficient for membrane association. A mutant with an src deletion of amino acids 169 through 264 has an src protein that is myristylated but not membrane bound, remaining stably associated with p50 and p90. This mutant is transformation defective. Several N-terminal deletion mutants possessing tyrosine kinase activity have myristylated and membrane-bound src proteins but are not fully active in cell transformation, suggesting that additional N-terminal functional domains exist.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Cohen P., Santikarn S., Williams D. H., Calder A. G., Smith A., Klee C. B. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Darrow D. Analysis of the catalytic domain of phosphotransferase activity of two avian sarcoma virus-transforming proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4550–4557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. The specific interaction of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, pp60src, with two cellular proteins. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J., Yonemoto W., Darrow D. Interaction between the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein and two cellular phosphoproteins: analysis of the turnover and distribution of this complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):9–19. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D., Parsons J. T. Site-directed mutagenesis of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus: construction and characterization of a deletion mutant temperature sensitive for transformation. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):683–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.683-691.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid is attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus during or immediately after synthesis and is present in both soluble and membrane-bound forms of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2697–2704. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid, a rare fatty acid, is the lipid attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus and its cellular homolog. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.7-12.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Transit of pp60v-src to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7117–7121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus (pp60src) and a homologous protein in normal cells (pp60proto-src) are associated with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3783–3787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. N-terminal deletions in Rous sarcoma virus p60src: effects on tyrosine kinase and biological activities and on recombination in tissue culture with the cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2789–2795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Local mutagenesis of Rous sarcoma virus: the major sites of tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of pp60src are dispensable for transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita D. J., Bechberger J., Nedic I. Four Rous sarcoma virus mutants which affect transformed cell morphology exhibit altered src gene products. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Only membrane-associated RSV src proteins have amino-terminally bound lipid. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):161–163. doi: 10.1038/302161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Low level of cellular protein phosphorylation by nontransforming overproduced p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1058–1066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Takeya T., Cross F. R., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Rous sarcoma virus variants that carry the cellular src gene instead of the viral src gene cannot transform chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4424–4428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R., Hunter T. Role of methionine in the initiation of haemoglobin synthesis. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):672–676. doi: 10.1038/227672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Hanafusa H. Viral and cellular src genes contribute to the structure of recovered avian sarcoma virus transforming protein. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90511-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Chin S. S., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Size-variant pp60src proteins of recovered avian sarcoma viruses interact with adhesion plaques as peripheral membrane proteins: effects on cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):454–467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R., Hanafusa H. Changes in amino-terminal sequences of pp60src lead to decreased membrane association and decreased in vivo tumorigenicity. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):889–896. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R. Subcellular localization of pp60src in RSV-transformed cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:51–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific messenger RNAs in permissive cells infected by avian sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):8015–8022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The purified product of the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11973–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Cutt J. R., Brugge J. S. Association of the transforming proteins of Rous, Fujinami, and Y73 avian sarcoma viruses with the same two cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):875–880. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchildon G. A., Casnellie J. E., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G. Covalently bound myristate in a lymphoma tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7679–7682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozols J., Carr S. A., Strittmatter P. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase as myristic acid and the complete amino acid sequence of the membrane-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13349–13354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. An N-terminal peptide from p60src can direct myristylation and plasma membrane localization when fused to heterologous proteins. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):374–377. doi: 10.1038/314374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Fine structural mapping of a critical NH2-terminal region of p60src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1623–1627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Jovanovich S., Erikson R. L. Sites of synthesis of viral proteins in avian sarcoma virus-infected chicken cells. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):629–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.629-636.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Amino terminal myristylation of the protein kinase p60src, a retroviral transforming protein. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):427–429. doi: 10.1126/science.3917576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. In vivo modification of retroviral gag gene-encoded polyproteins by myristic acid. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):355–361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.355-361.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A., Oroszlan S. Myristylation of gag-onc fusion proteins in mammalian transforming retroviruses. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Walter G. Antiserum specific for the carboxy terminus of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):467–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.467-474.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Enrietto P. J., Wyke J. A. Functional domains of the pp60v-src protein as revealed by analysis of temperature-sensitive Rous sarcoma virus mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1508–1514. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Feldman R. A., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the viral and cellular src gene of chickens. 1. Complete nucleotide sequence of an EcoRI fragment of recovered avian sarcoma virus which codes for gp37 and pp60src. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.1-11.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A. F., Buss J. E., Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Characterization of the protein apparently responsible for the elevated tyrosine protein kinase activity in LSTRA cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2705–2713. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells S. K., Collett M. S. Specific proteolytic fragmentation of p60v-src in transformed cell lysates. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):253–258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.253-258.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Dintzis H. M. Protein chain initiation in rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1282–1289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Watanabe S., Morris J. Initiation of rabbit hemoglobin synthesis: methionine and formylmethionine at the N-terminal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1600–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]