Abstract
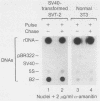
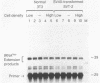
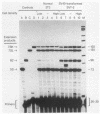
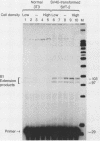
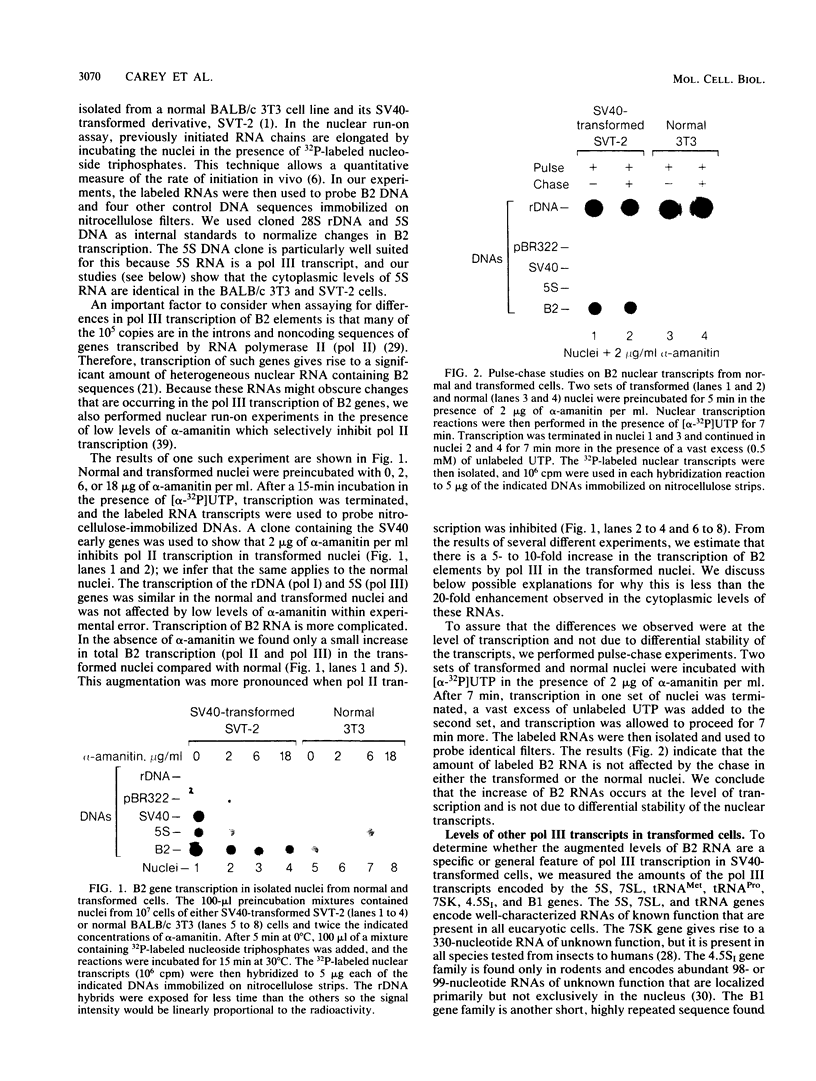
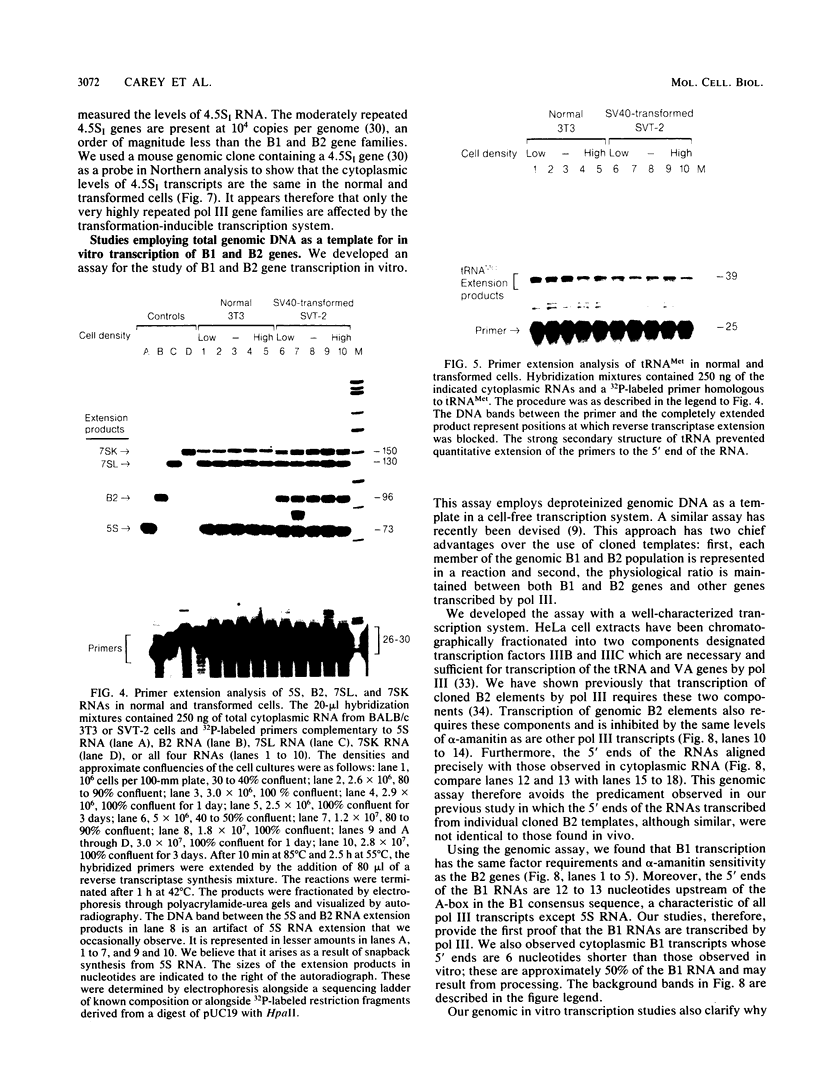
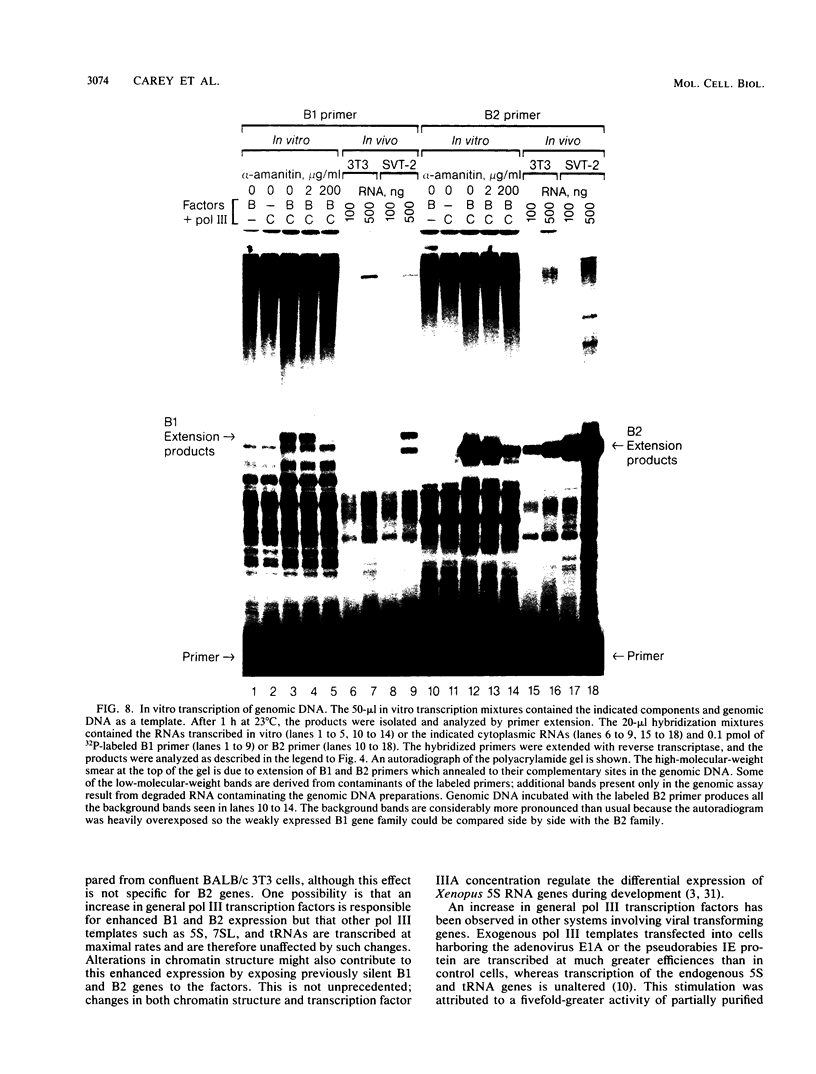
RNA polymerase III (pol III) transcripts of the highly repeated mouse B2 gene family are increased in many oncogenically transformed murine cell lines. In cells transformed by simian virus 40, the small, cytoplasmic B2 RNAs are present at 20-fold-higher levels than in normal cells (M. R. D. Scott, K. Westphal, and P. W. J. Rigby, Cell 34:557-567, 1983; K. Singh, M. Carey, S. Saragosti, and M. Botchan, Nature [London] 314:553-556). We found that transcripts of the highly repeated B1 gene family are also increased 20-fold upon simian virus 40 transformation and showed that these RNAs result from pol III transcription. In contrast, transcripts from less highly repeated pol III templates such as the 5S, 7SL, 7SK, 4.5SI, tRNAMet, and tRNAPro genes are unaffected. The expression of the B2 RNAs in isolated nuclei shows that the augmentation is due mainly to an increased rate of transcription by pol III. There is thus specific transformation-inducible pol III transcription. We developed an in vitro transcription assay which utilizes genomic DNA as a template to study the transcription of all members of a repetitive gene family in their native context. This assay reproduces the low cytoplasmic levels of B1 compared with B2 RNAs suggesting that this ratio is dictated by intrinsic signals in the DNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Development of 3T3-like lines from Balb-c mouse embryo cultures: transformation susceptibility to SV40. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2):141–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett K. L., Hill R. E., Pietras D. F., Woodworth-Gutai M., Kane-Haas C., Houston J. M., Heath J. K., Hastie N. D. Most highly repeated dispersed DNA families in the mouse genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1561–1571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Schlissel M. S. A positive transcription factor controls the differential expression of two 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. F., Gerrard S. P., Cozzarelli N. R. Analysis of RNA polymerase III transcription complexes by gel filtration. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4309–4317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Castagnoli L., Cortese R. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:59–88. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60579-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. R., Parfett C. L., Denhardt D. T. Transcriptional regulation of two serum-induced RNAs in mouse fibroblasts: equivalence of one species to B2 repetitive elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3280–3288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Roeder R. G. DNA sequences and transcription factor interactions of active and inactive forms of mammalian 5 S RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7926–7935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh H., Okada N. Total DNA transcription in vitro: a procedure to detect highly repetitive and transcribable sequences with tRNA-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):251–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Feldman L. T., Berk A. J. Transcription of class III genes activated by viral immediate early proteins. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):447–450. doi: 10.1126/science.2996135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoryan M. S., Kramerov D. A., Tulchinsky E. M., Revasova E. S., Lukanidin E. M. Activation of putative transposition intermediate formation in tumor cells. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2209–2215. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03916.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J. H., Rooney R. J., Harding J. D. Structure and evolution of mammalian tRNA genes: sequence of a mouse tRNAiMet gene, the 5'-flanking region of which is homologous to a human gene. Gene. 1984 May;28(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler W. K., Roeder R. G. Enhancement of RNA polymerase III transcription by the E1A gene product of adenovirus. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):955–963. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. C., Cote B. D., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. Isolation and characterization of genomic mouse DNA clones containing sequences homologous to tRNAs and 5S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4809–4821. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Glasser S., King D., Lingrel J. B. A cluster of repetitive elements within a 700 base pair region in the mouse genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2177–2184. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramerov D. A., Grigoryan A. A., Ryskov A. P., Georgiev G. P. Long double-stranded sequences (dsRNA-B) of nuclear pre-mRNA consist of a few highly abundant classes of sequences: evidence from DNA cloning experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):697–713. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramerov D. A., Tillib S. V., Lekakh I. V., Ryskov A. P., Georgiev G. P. Biosynthesis and cytoplasmic distribution of small poly(A)-containing B2 RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 20;824(2):85–98. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Kramerov D. A., Skryabin K. G., Ryskov A. P., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. The nucleotide sequence of the ubiquitous repetitive DNA sequence B1 complementary to the most abundant class of mouse fold-back RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1201–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Markusheva T. V., Kramerov D. A., Ryskov A. P., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. Ubiquitous transposon-like repeats B1 and B2 of the mouse genome: B2 sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7461–7475. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. Y., Reddy R., Henning D., Epstein P., Busch H. Nucleotide sequence of 7 S RNA. Homology to Alu DNA and La 4.5 S RNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5136–5142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., La Mantia G., Simeone A., Boncinelli E., Lania L. Activation of major histocompatibility complex class I mRNA containing an Alu-like repeat in polyoma virus-transformed rat cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):457–459. doi: 10.1038/314457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D., Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Transcripts regulated during normal embryonic development and oncogenic transformation share a repetitive element. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):865–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Subrahmanyam C. S., Busch H. Primary and secondary structure of 7-3 (K) RNA of Novikoff hepatoma. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12265–12270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba J. A., Busch H., Reddy R. A new moderately repetitive rat DNA sequence detected by a cloned 4.5 SI DNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1354–1357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Brown D. D. The transcriptional regulation of Xenopus 5s RNA genes in chromatin: the roles of active stable transcription complexes and histone H1. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. R., Westphal K. H., Rigby P. W. Activation of mouse genes in transformed cells. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Carey M., Saragosti S., Botchan M. Expression of enhanced levels of small RNA polymerase III transcripts encoded by the B2 repeats in simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):553–556. doi: 10.1038/314553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Saragosti S., Botchan M. Isolation of cellular genes differentially expressed in mouse NIH 3T3 cells and a simian virus 40-transformed derivative: growth-specific expression of VL30 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2590–2598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Tschudi C. Alu sequences are processed 7SL RNA genes. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):171–172. doi: 10.1038/312171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannice J. L., Taylor J. M., Ringold G. M. Glucocorticoid-mediated induction of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein: evidence for hormone-regulated RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4241–4245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Role of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase 3 in the transcription of the tRNA and 5S RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]