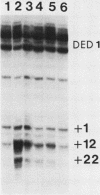
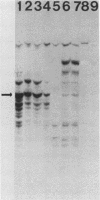
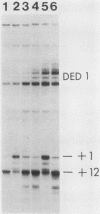
Abstract
his3 and pet56 are adjacent Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes that are transcribed in opposite directions from initiation sites that are separated by 200 base pairs. Under normal growth conditions, in which his3 and pet56 are transcribed at similar basal levels, a poly(dA-dT) sequence located between the genes serves as the upstream promoter element for both. In contrast, his3 but not pet56 transcription is induced during conditions of amino acid starvation, even though the critical regulatory site is located upstream of both respective TATA regions. Moreover, only one of the two normal his3 initiation sites is subject to induction. From genetic and biochemical evidence, I suggest that the his3-pet56 intergenic region contains constitutive and inducible promoters with different properties. In particular, two classes of TATA elements, constitutive (Tc) and regulatory (Tr), can be distinguished by their ability to respond to upstream regulatory elements, by their effects on the selection of initiation sites, and by their physical structure in nuclear chromatin. Constitutive and inducible his3 transcription is mediated by distinct promoters representing each class, whereas pet56 transcription is mediated by a constitutive promoter. Molecular mechanisms for these different kinds of S. cerevisiae promoters are proposed.
Full text
PDF
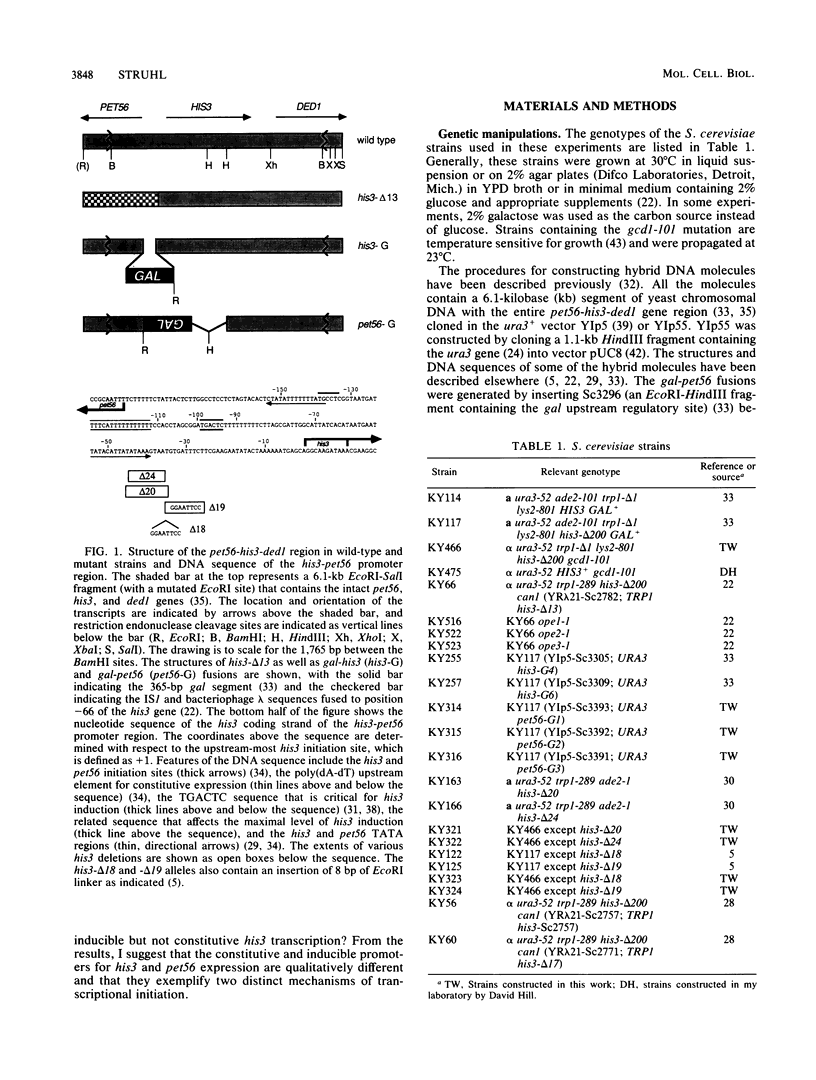





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beier D. R., Young E. T. Characterization of a regulatory region upstream of the ADR2 locus of S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):724–728. doi: 10.1038/300724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A eukaryotic transcriptional activator bearing the DNA specificity of a prokaryotic repressor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Yeast mRNA initiation sites are determined primarily by specific sequences, not by the distance from the TATA element. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3273–3280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Daves R. S., Lucchini G., Fink G. R. A short nucleotide sequence required for regulation of HIS4 by the general control system of yeast. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90499-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Leung D. W., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Smith M. Deletion mapping of sequences essential for in vivo transcription of the iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Hoar E. Upstream activation sites of the CYC1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are active when inverted but not when placed downstream of the "TATA box". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7860–7864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters: positive and negative elements. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Yocum R. R., Gifford P. A GAL10-CYC1 hybrid yeast promoter identifies the GAL4 regulatory region as an upstream site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Evidence for translational regulation of the activator of general amino acid control in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6442–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Lucchini G., Fink G. R. A synthetic HIS4 regulatory element confers general amino acid control on the cytochrome c gene (CYC1) of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4 protein, synthesized in vitro, binds HIS3 regulatory sequences: implications for general control of amino acid biosynthetic genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Herskowitz I. A repressor (MAT alpha 2 Product) and its operator control expression of a set of cell type specific genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):237–247. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil J. B., Smith M. Transcription initiation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Multiple, independent T-A-T-A sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):363–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagawa F., Fink G. R. The relationship between the "TATA" sequence and transcription initiation sites at the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8557–8561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettinger M. A., Struhl K. Suppressors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae his3 promoter mutations lacking the upstream element. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1901–1909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Botstein D. Structure and function of the yeast URA3 gene. Differentially regulated expression of hybrid beta-galactosidase from overlapping coding sequences in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):883–904. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Structure and function of the yeast URA3 gene: expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarokin L., Carlson M. Upstream region required for regulated expression of the glucose-repressible SUC2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2750–2757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Tatchell K. Transcription and regulatory signals at the mating type locus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90431-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Chen W., Hill D. E., Hope I. A., Oettinger M. A. Constitutive and coordinately regulated transcription of yeast genes: promoter elements, positive and negative regulatory sites, and DNA binding proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:489–503. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Davis R. W. Transcription of the his3 gene region in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 5;152(3):535–552. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Deletion mapping a eukaryotic promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4461–4465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Direct selection for gene replacement events in yeast. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Genetic properties and chromatin structure of the yeast gal regulatory element: an enhancer-like sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7865–7869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Naturally occurring poly(dA-dT) sequences are upstream promoter elements for constitutive transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8419–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoter elements, regulatory elements, and chromatin structure of the yeast his3 gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):901–910. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. The yeast his3 promoter contains at least two distinct elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7385–7389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thireos G., Penn M. D., Greer H. 5' untranslated sequences are required for the translational control of a yeast regulatory gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. M., Geever R. F., Case M. E., Giles N. H. Cis-acting and trans-acting regulatory mutations define two types of promoters controlled by the qa-1F gene of Neurospora. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfner M., Yep D., Messenguy F., Fink G. R. Integration of amino acid biosynthesis into the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 5;96(2):273–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]