Abstract
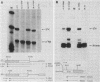
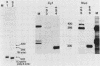
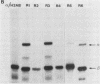
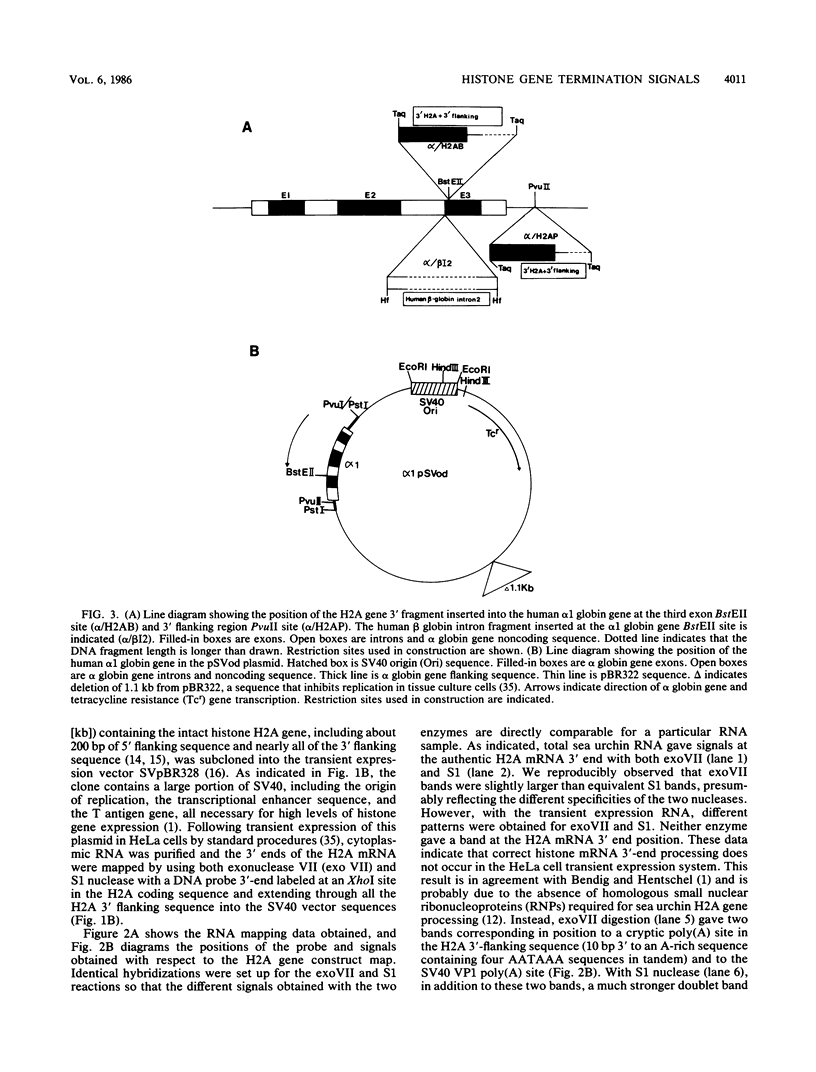
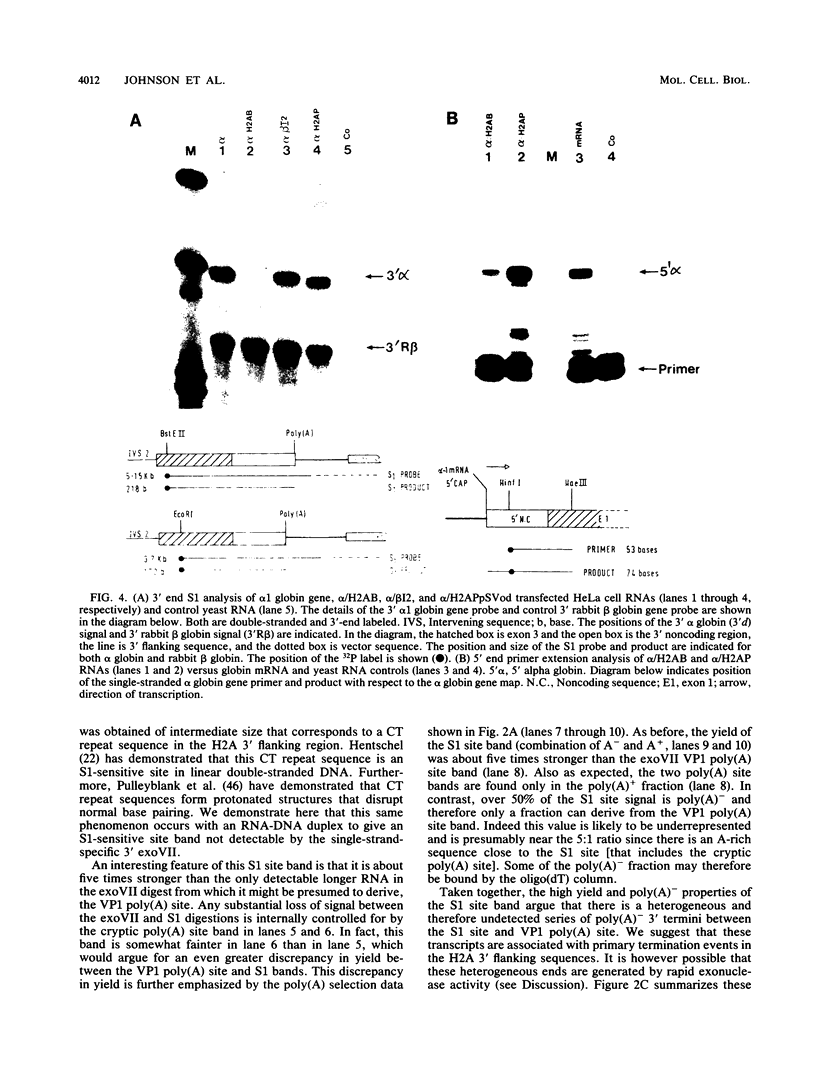
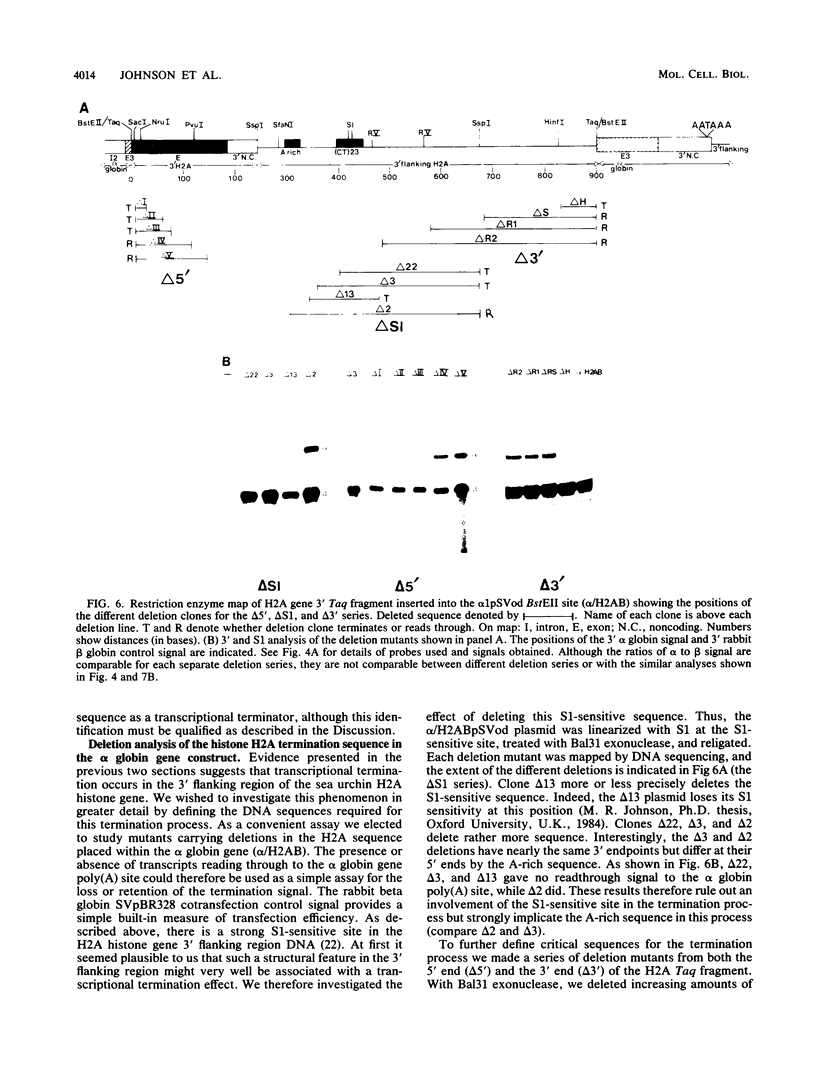
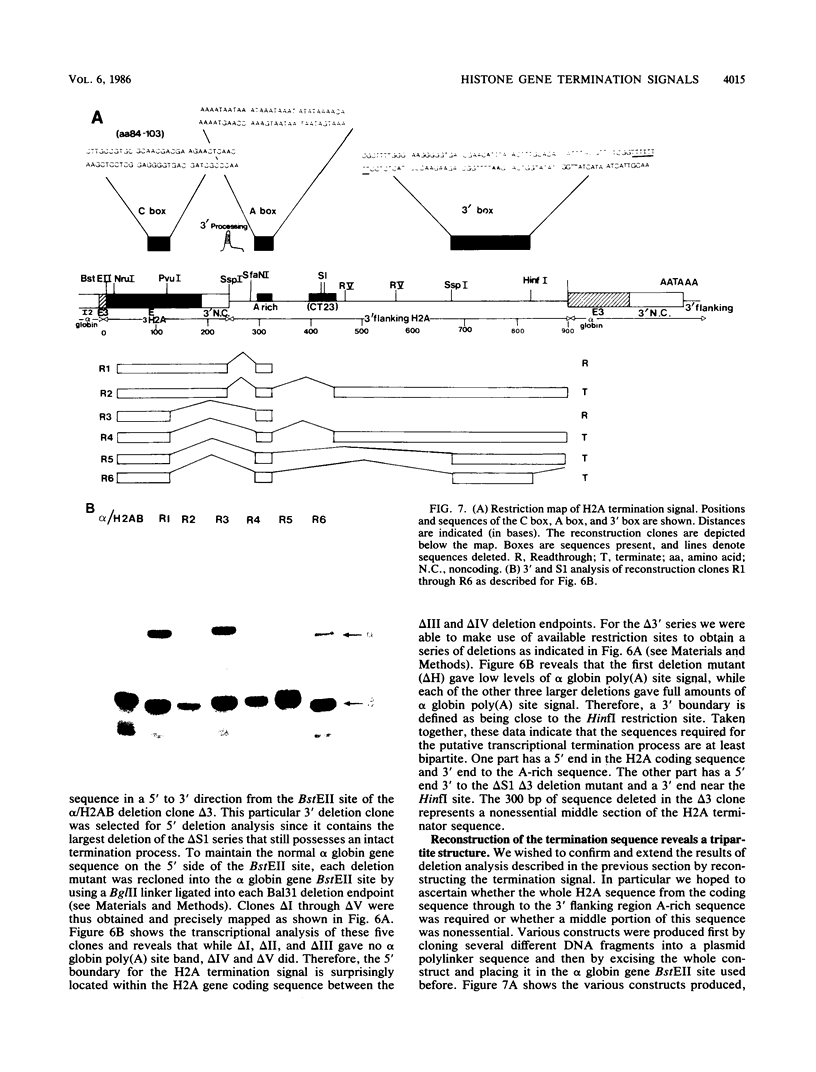
We have defined a DNA sequence that behaves as an RNA polymerase II termination signal by using the human HeLa cell transient expression system. Surprisingly, this sequence is tripartite, including part of the coding region of the sea urchin H2A histone gene together with two separate sequences in the 3' flanking region of the gene. We demonstrate that this signal functions both in its normal gene environment and also when placed within the human alpha-globin gene. However, we have failed to detect a discrete 3' terminus. Rather, our data indicate the presence of an extremely heterogeneous series of nonpolyadenylated RNAs. These heterogeneous nonpolyadenylated RNAs are stable when transcribed from the intact histone gene but are highly unstable within the human alpha-globin gene. This provides evidence for the role of poly(A) in the stability of mRNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendig M. M., Hentschel C. C. Transcription of sea urchin histone genes in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2337–2346. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Folk W., Birnstiel M. L. The terminal RNA stem-loop structure and 80 bp of spacer DNA are required for the formation of 3' termini of sea urchin H2A mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Generation of authentic 3' termini of an H2A mRNA in vivo is dependent on a short inverted DNA repeat and on spacer sequences. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Schümperli D., Sconzo G., Birnstiel M. L. 3' editing of mRNAs: sequence requirements and involvement of a 60-nucleotide RNA in maturation of histone mRNA precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1057–1061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron B., Falck-Pedersen E., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription termination occurs within a 1000 base pair region downstream from the poly(A) site of the mouse beta-globin (major) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8723–8731. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway L., Wickens M. A sequence downstream of A-A-U-A-A-A is required for formation of simian virus 40 late mRNA 3' termini in frog oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3949–3953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck-Pedersen E., Logan J., Shenk T., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription termination within the E1A gene of adenovirus induced by insertion of the mouse beta-major globin terminator element. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):897–905. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford J. P., Hsu M. T. Transcription pattern of in vivo-labeled late simian virus 40 RNA: equimolar transcription beyond the mRNA 3' terminus. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):795–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.795-801.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. W., Nevins J. R., Ziff E., Darnell J. E., Jr The major late adenovirus type-2 transcription unit: termination is downstream from the last poly(A) site. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 25;129(4):643–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90474-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Biochemical complementation with RNA in the Xenopus oocyte: a small RNA is required for the generation of 3' histone mRNA termini. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):823–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Spacer DNA sequences upstream of the T-A-T-A-A-A-T-A sequence are essential for promotion of H2A histone gene transcription in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7102–7106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Cribbs D. L., Schibler U. Termination of transcription in the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-2a occurs at multiple sites downstream of the polyadenylation site. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):737–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site cleavage in a HeLa nuclear extract is dependent on downstream sequences. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Kelly J. D., Cohen E. H. Transcription terminates in yeast distal to a control sequence. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C. Homocopolymer sequences in the spacer of a sea urchin histone gene repeat are sensitive to S1 nuclease. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):714–716. doi: 10.1038/295714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer E., Hofer-Warbinek R., Darnell J. E., Jr Globin RNA transcription: a possible termination site and demonstration of transcriptional control correlated with altered chromatin structure. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):887–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Formation of the 3' end of histone mRNA by post-transcriptional processing. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):203–206. doi: 10.1038/308203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W., Appel B., Lührmann R. The 5' terminus of the RNA moiety of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles is required for the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMeur M. A., Galliot B., Gerlinger P. Termination of the ovalbumin gene transcription. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2779–2786. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Accurate and specific polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in a soluble whole-cell lysate. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90440-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Mode of regulation of immunoglobulin mu- and delta-chain expression varies during B-lymphocyte maturation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Blanchard J. M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription units of adenovirus type 2. Termination of transcription beyond the poly(A) addition site in early regions 2 and 4. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 15;144(3):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom J. L., Hall S. L., Kessler M. M. Polyadenylylation of sea urchin histone RNA sequences in transfected COS cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1094–1098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Mount S. M., Steitz J. A., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors is inhibited by antisera to small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. H., Parker C. S. The 3' end of drosophila histone H3 mRNA is produced by a processing activity in vitro. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90497-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Rutherford T. R., Partington G. A. Transcriptional analysis of human zeta globin genes. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1533–1540. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02007.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. The end of the message and beyond. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):412–413. doi: 10.1038/307412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrbaugh M. L., Johnson J. E., 3rd, James M. D., Hardison R. C. Transcription unit of the rabbit beta 1 globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):147–160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Ito R., Baek K. H., Agarwal K. A specific DNA sequence controls termination of transcription in the gastrin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1032–1043. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffery M., Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Gene expression in murine erythroleukemia cells. Transcriptional control and chromatin structure of the alpha 1-globin gene. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):417–436. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Galli G., Busslinger M., Birnstiel M. L. The cDNA sequences of the sea urchin U7 small nuclear RNA suggest specific contacts between histone mRNA precursor and U7 RNA during RNA processing. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2801–2807. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. Alpha-Globin-gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]