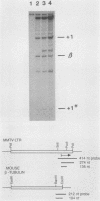
Abstract
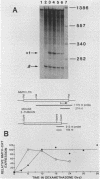
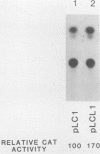
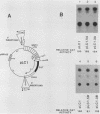
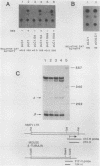
Sets of genes under a common regulatory control in a given cell type are often differentially transcribed. The possibility that this differential transcription can be modulated by the number or strength of cis-acting regulatory sequences associated with a given gene was tested by using the glucocorticoid-responsive enhancer element associated with the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Results indicate that differential levels of hormone-inducible gene expression can be modulated in an additive way by the number of glucocorticoid-responsive enhancers associated with this promoter. Realization of these effects shows little preference for position of the additional elements with respect to the promoter. When sequences that bind the glucocorticoid receptor in vitro with somewhat lower affinity than the enhancer were tested, these additive effects were not detected. The results support that differential transcription of genes subject to a common regulatory control can be mediated, at least in part, by the number or strength of their associated cis-acting regulatory sequences.
Full text
PDF
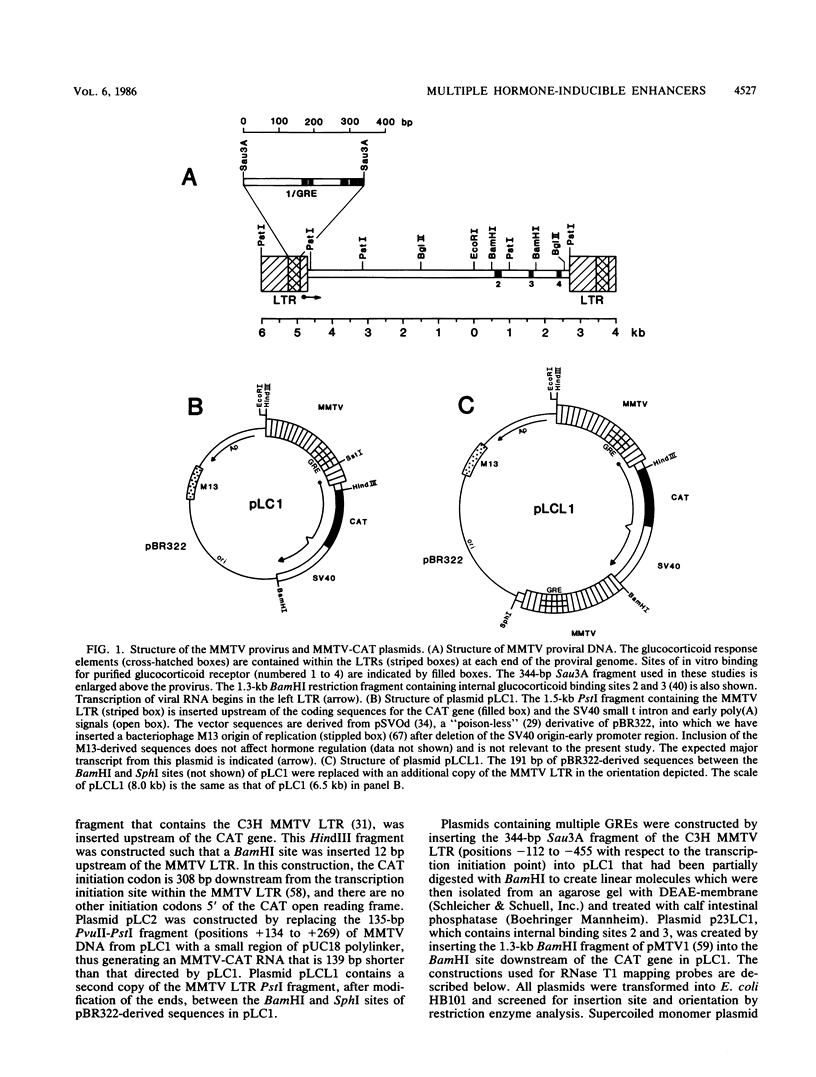

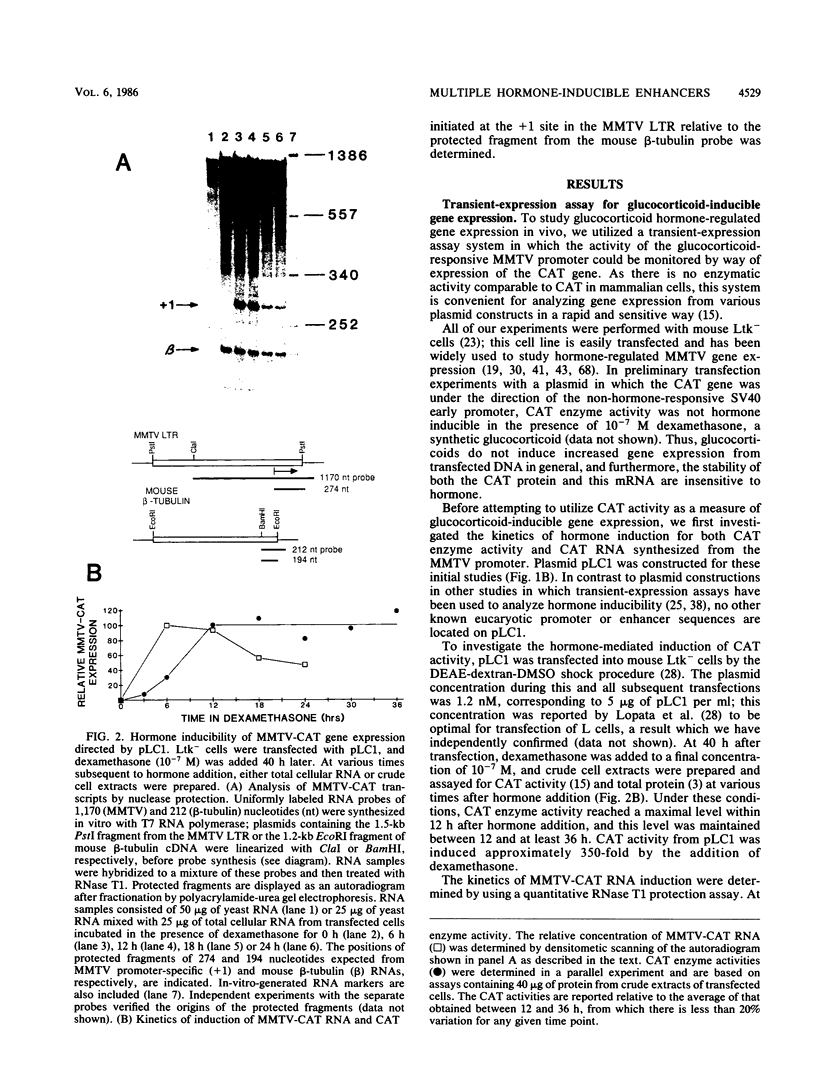

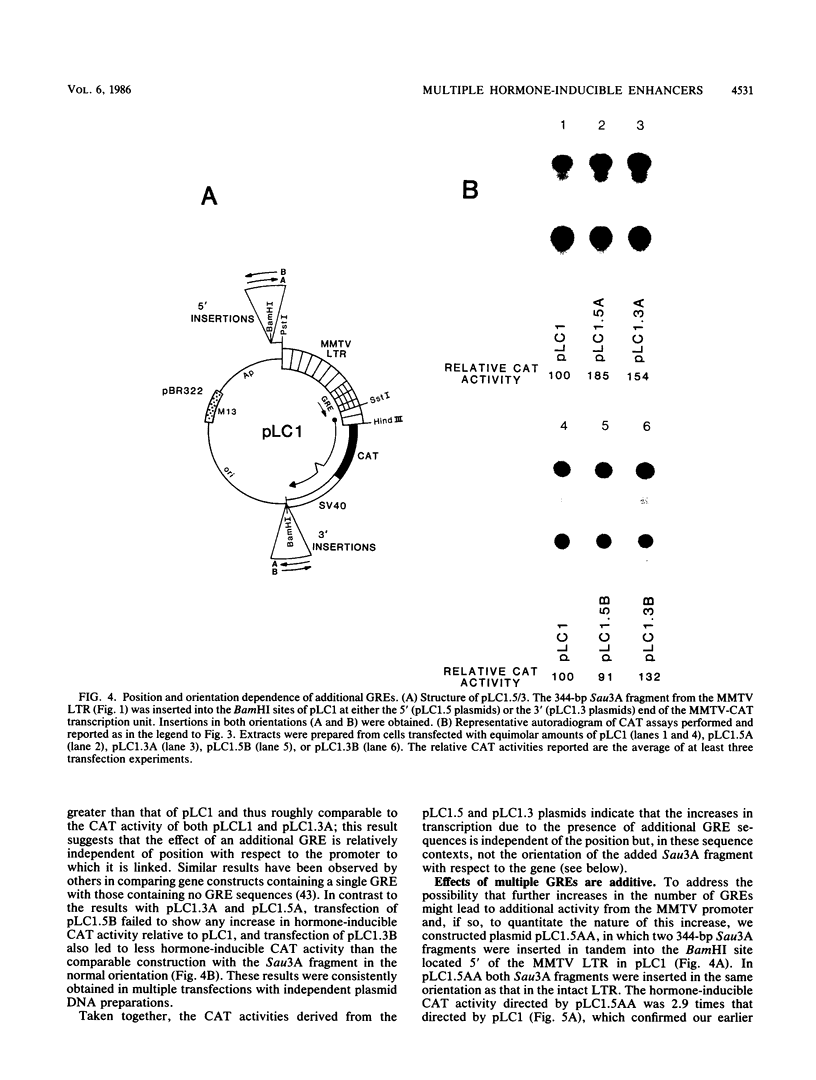




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock M. L., Shapiro D. J. Estrogen stabilizes vitellogenin mRNA against cytoplasmic degradation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D., Haseltine W. A. Tissue-specific transcription preference as a determinant of cell tropism and leukaemogenic potential of murine retroviruses. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):159–162. doi: 10.1038/312159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Simian virus 40 early- and late-region promoter functions are enhanced by the 72-base-pair repeat inserted at distant locations and inverted orientations. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):991–999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisse S., Scheidereit C., Westphal H. M., Hynes N. E., Groner B., Beato M. Glucocorticoid receptors recognize DNA sequences in and around murine mammary tumour virus DNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1613–1619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Human beta-interferon gene expression is regulated by an inducible enhancer element. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindan M. V., Spiess E., Majors J. Purified glucocorticoid receptor-hormone complex from rat liver cytosol binds specifically to cloned mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeats in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5157–5161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. L., Ostrowski M. C., Berard D., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of the Ha-MuSV p21 gene conferred by sequences from mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N., van Ooyen A. J., Kennedy N., Herrlich P., Ponta H., Groner B. Subfragments of the large terminal repeat cause glucocorticoid-responsive expression of mouse mammary tumor virus and of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Hall C. V., Ringold G. M., Dobson D. E., Luh J., Jacob P. E. Functional analysis of the steroid hormone control region of mouse mammary tumor virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4191–4206. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Lee M. G., Cowan N. J. Five mouse tubulin isotypes and their regulated expression during development. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):852–861. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequences at host-proviral junctions for mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):253–258. doi: 10.1038/289253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J., Varmus H. E. A small region of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat confers glucocorticoid hormone regulation on a linked heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5866–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. C., Spence A., Smith M. The distal transcription signals of the herpesvirus tk gene share a common hexanucleotide control sequence. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishoe H., Brady J. N., Radonovich M., Salzman N. P. Simian virus 40 guanine-cytosine-rich sequences function as independent transcriptional control elements in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2911–2920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. W., Florini J. R. A rapid method for desalting small volumes of solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):328–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
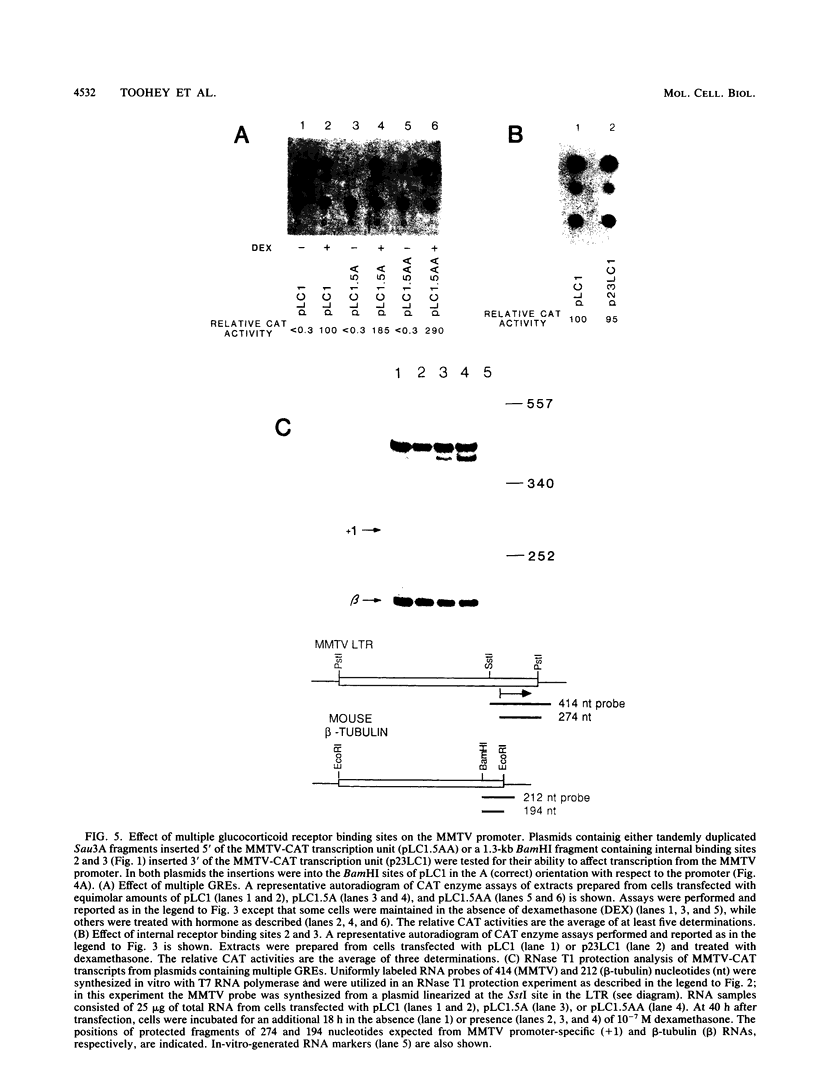
- Ostrowski M. C., Huang A. L., Kessel M., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Modulation of enhancer activity by the hormone responsive regulatory element from mouse mammary tumor virus. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1891–1899. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., DeFranco D., Firestone G. L., Edgar B., Wrange O., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Firestone G. L., Ross S. R., Chandler V. L., Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Multiple specific binding sites for purified glucocorticoid receptors on mammary tumor virus DNA. J Cell Biochem. 1982;19(3):241–247. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240190305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Purified glucocorticoid receptors bind selectively in vitro to a cloned DNA fragment whose transcription is regulated by glucocorticoids in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6628–6632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
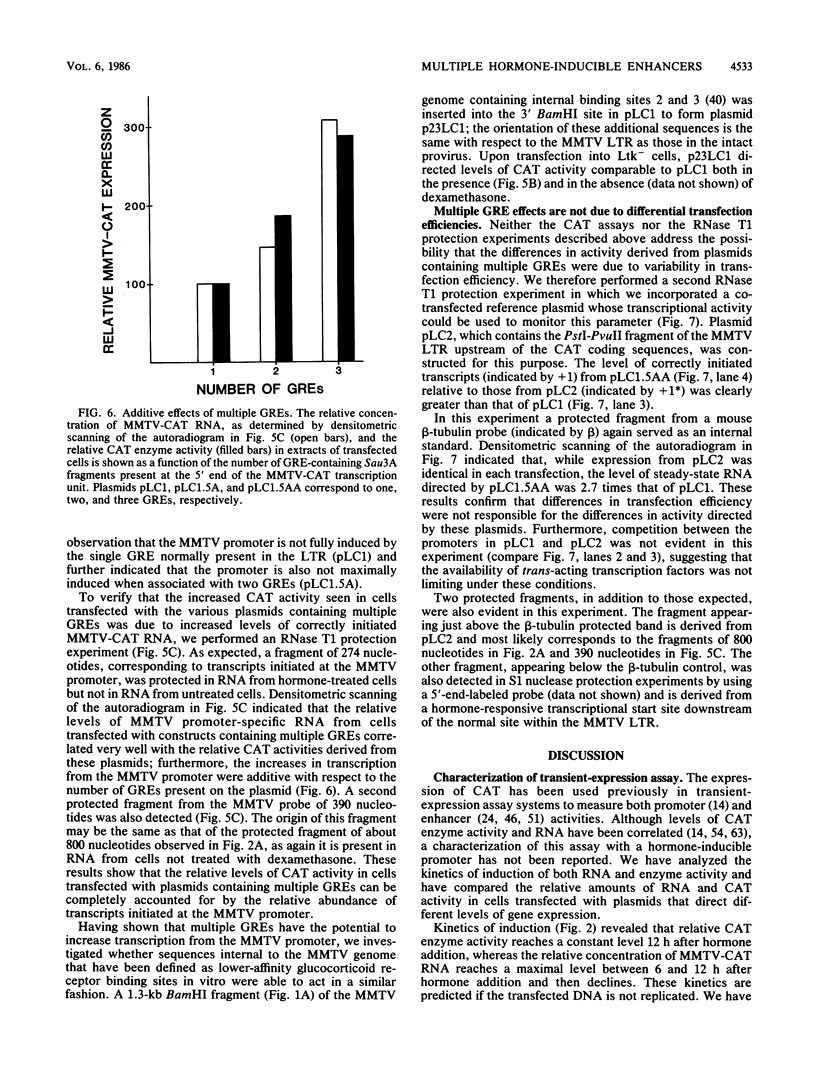
- Ponta H., Kennedy N., Skroch P., Hynes N. E., Groner B. Hormonal response region in the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat can be dissociated from the proviral promoter and has enhancer properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1020–1024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Schütz G., von der Ahe D., Beato M. Sequences in the promoter region of the chicken lysozyme gene required for steroid regulation and receptor binding. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Paek I., Seeburg P. H., Axel R. Regulated expression of human growth hormone genes in mouse cells. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):623–631. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
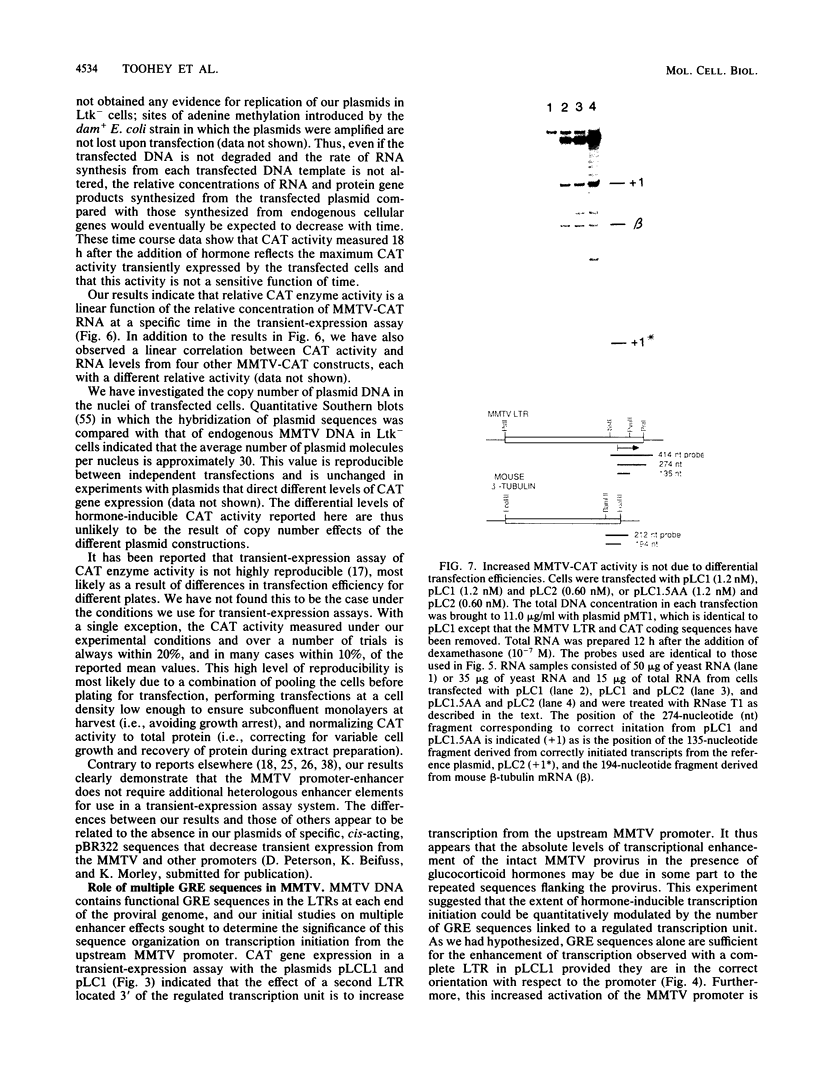
- Sassone-Corsi P., Wildeman A., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor is responsible for the simian virus 40 enhancer activity in vitro. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):458–463. doi: 10.1038/313458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Beato M. Contacts between hormone receptor and DNA double helix within a glucocorticoid regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3029–3033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Geisse S., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to defined nucleotide sequences near the promoter of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):749–752. doi: 10.1038/304749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenborn E. T., Mierendorf R. C., Jr A novel transcription property of SP6 and T7 RNA polymerases: dependence on template structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6223–6236. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Stuart G. W., Palmiter R. D. Building a metal-responsive promoter with synthetic regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1480–1489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. P., Rabenau O., Karin M., Baxter J. D., Beato M. Glucocorticoid receptor binding and activation of a heterologous promoter by dexamethasone by the first intron of the human growth hormone gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2984–2992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of human T lymphotropic viruses in infected cells. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):381–385. doi: 10.1126/science.6330891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Palmiter R. D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):828–831. doi: 10.1038/317828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Maniatis T. Simian virus 40 enhancer increases number of RNA polymerase II molecules on linked DNA. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):73–75. doi: 10.1038/315072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Firestone G. L., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoids and chromosomal position modulate murine mammary tumor virus transcription by affecting efficiency of promoter utilization. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):551–561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Ross S. R., Yamamoto K. R. Mammary tumor virus DNA contains sequences required for its hormone-regulated transcription. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Yamamoto K. R. Early events in the stimulation of mammary tumor virus RNA synthesis by glucocorticoids. Novel assays of transcription rates. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7416–7420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Chambon P. Short and long range activation by the SV40 enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5589–5608. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., Schaffner W. Simian virus 40 enhancer increases RNA polymerase density within the linked gene. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):75–77. doi: 10.1038/315075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagursky R. J., Berman M. L. Cloning vectors that yield high levels of single-stranded DNA for rapid DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Yamamoto K. R. Reversible and persistent changes in chromatin structure accompany activation of a glucocorticoid-dependent enhancer element. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Ahe D., Janich S., Scheidereit C., Renkawitz R., Schütz G., Beato M. Glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors bind to the same sites in two hormonally regulated promoters. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):706–709. doi: 10.1038/313706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]