Abstract
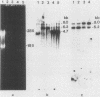
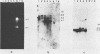
RNA from immature mouse testes was shown to lack a low-molecular-weight c-abl transcript previously noted to be the predominant species in adult testes. The developmental pattern of appearance of this c-abl variant was determined by analyzing RNA obtained from purified populations of testicular cells in different stages of spermatogenesis. The appearance of the c-abl testicular variant was coincident with the entry of the germ cells into their haploid state and suggested that the regulated expression of this proto-oncogene may be important in the normal differentiation of the male germ line.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R., Cavicchia J. C., Millette C. F., O'Brien D. A., Bhatnagar Y. M., Dym M. Spermatogenic cells of the prepuberal mouse. Isolation and morphological characterization. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):68–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Kleene K. C., Hecht N. B. Haploid expression of a mouse testis alpha-tubulin gene. Science. 1984 Apr 6;224(4644):68–70. doi: 10.1126/science.6701535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley K., Potter J., Lyon M. F., Willison K. R. Analysis of male sterile mutations in the mouse using haploid stage expressed cDNA probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4281–4293. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. P. t-Alleles and the possibility of post-meiotic gene expression during mammalian spermatogenesis. Fed Proc. 1978 Sep;37(11):2517–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Gilboa E., Witte O. N., Baltimore D. Structure of the Abelson murine leukemia virus genome and the homologous cellular gene: studies with cloned viral DNA. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyette M., Petropoulos C. J., Shank P. R., Fausto N. Regulated transcription of c-Ki-ras and c-myc during compensatory growth of rat liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1493–1498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene K. C., Distel R. J., Hecht N. B. cDNA clones encoding cytoplasmic poly(A)+ RNAs which first appear at detectable levels in haploid phases of spermatogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1983 Aug;98(2):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90375-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev Z., Leibovitz N., Segev O., Shilo B. Z. Expression of the src and abl cellular oncogenes during development of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):982–984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino R., Hayashi K., Sugimura T. C-myc transcript is induced in rat liver at a very early stage of regeneration or by cycloheximide treatment. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):697–698. doi: 10.1038/310697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Bruce W. R., Clermont Y. Cellular composition of fractions of mouse testis cells following velocity sedimentation separation. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Apr;79(1):213–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Slamon D. J., Tremblay J. M., Cline M. J., Verma I. M. Differential expression of cellular oncogenes during pre- and postnatal development of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):640–644. doi: 10.1038/299640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Verma I. M., Adamson E. D. Expression of c-onc genes: c-fos transcripts accumulate to high levels during development of mouse placenta, yolk sac and amnion. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):679–684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M., Ogata K. Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing results in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):333–338. doi: 10.1038/308333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OAKBERG E. F. A description of spermiogenesis in the mouse and its use in analysis of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium and germ cell renewal. Am J Anat. 1956 Nov;99(3):391–413. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000990303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H. The development of the mouse ovary from birth to maturity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1969 Sep;62(1):98–116. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0620098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey A. J., Evans M. J. A gene sequence expressed only in undifferentiated EC, EK cells and testes. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2279–2285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Quiroga M., Zaldivar J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W., Cleveland D. W. Nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequences encoded by alpha and beta tubulin mRNAs. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):650–655. doi: 10.1038/289650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Baltimore D. Cellular RNA homologous to the Abelson murine leukemia virus transforming gene: expression and relationship to the viral sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):773–779. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock R., Sweet R., Weiss M., Cedar H., Axel R. Intragenic DNA spacers interrupt the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]