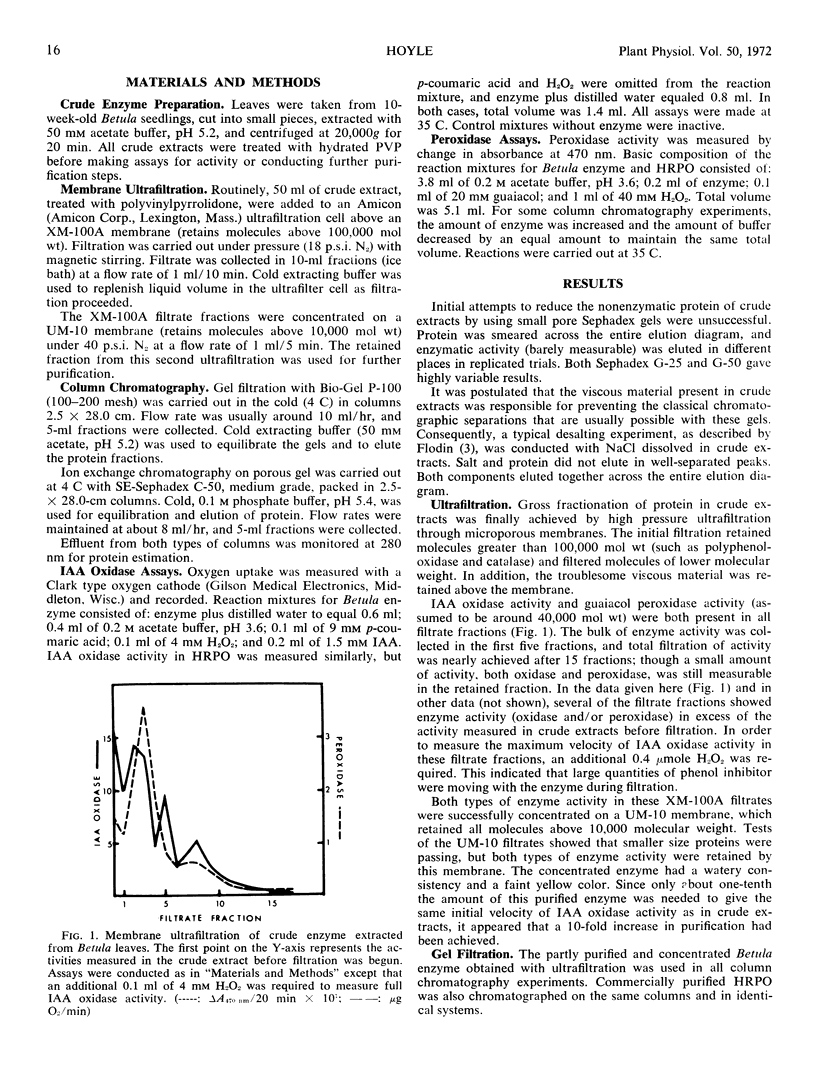
Abstract
The isolation of a unique enzyme capable of oxidizing indoleacetic acid, but devoid of peroxidase activity, has been reported for preparations from tobacco roots and commercial horseradish peroxidase. Experiments were made to verify these results using enzyme obtained from Betula leaves and commercial horseradish peroxidase. Both indoleacetic acid oxidase and guaiacol peroxidase activity appeared at 2.5 elution volumes from sulfoethyl-Sephadex. These results were obtained with both sources of enzyme. In no case was a separate peak of indoleacetic acid oxidase activity obtained at 5.4 elution volumes as reported for the tobacco enzyme using the same chromatographic system. Both types of activity, from both sources of enzyme, also eluted together during gel filtration. Successful column chromatography of Betula enzyme was dependent upon previous purification by membrane ultrafiltration. These results indicate indoleacetic acid oxidase activity and guaiacol peroxidase activity are dual catalytic functions of a single enzyme.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fisher H. F., Gates R. E., Cross D. G. A ligand exclusion theory of allosteric effects. Nature. 1970 Oct 17;228(5268):247–249. doi: 10.1038/228247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku H. S., Yang S. F., Pratt H. K. Inactivity of apoperoxidase in indoleacetic acid oxidation and in ethylene formation. Plant Physiol. 1970 Mar;45(3):358–359. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.3.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnicol P. K. Peroxidases of the Alaska pea (Pisum sativum L.). Enzymic properties and distribution within the plant. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Nov;117(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY P. M. The destruction of indoleacetic acid. III. Relationships between peroxidase action and indoleacetic acid oxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Mar;87:19–30. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sequeira L., Mineo L. Partial purification and kinetics of indoleacetic Acid oxidase from tobacco roots. Plant Physiol. 1966 Sep;41(7):1200–1208. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.7.1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel B. Z., Galston A. W. Indoleacetic acid oxidase activity of apoperoxidase. Science. 1967 Sep 29;157(3796):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3796.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz R. E. The Indole-3-Acetic Acid Oxidase of Lupinus albus L. Plant Physiol. 1957 Jan;32(1):31–39. doi: 10.1104/pp.32.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


