Abstract
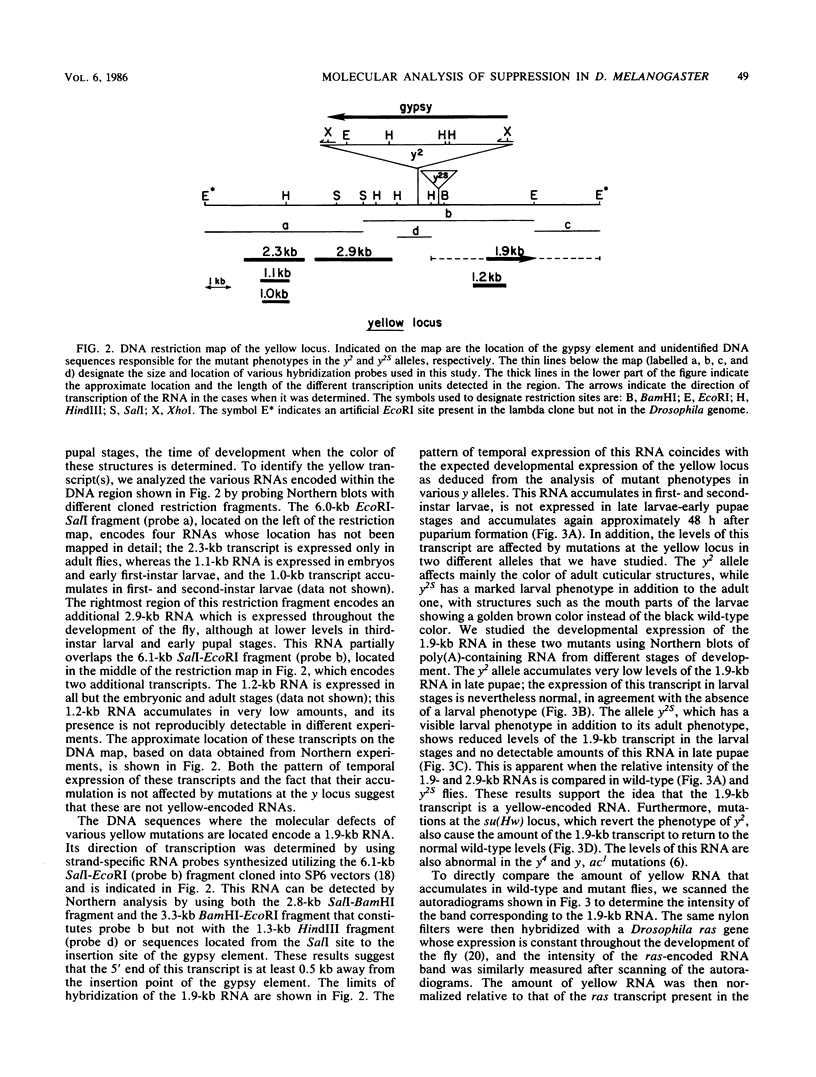
We cloned and characterized the yellow locus of Drosophila melanogaster. We also studied its transcription pattern in the suppressible allele y2, which is caused by the insertion of the transposable element gypsy, and the effect of mutations at the unlinked suppressor of Hairy-wing locus on the transcription of yellow RNAs. The gypsy element is transcribed in a temporal fashion that correlates with the pattern of expression of the yellow locus. We propose that the mutational effect of the gypsy element is due to developmentally specific transcriptional interference on yellow transcription. Mutations at the su(Hw) locus reverse this effect by altering the quantitative expression of gypsy.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender W., Akam M., Karch F., Beachy P. A., Peifer M., Spierer P., Lewis E. B., Hogness D. S. Molecular Genetics of the Bithorax Complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):23–29. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4605.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Zachar Z. Evidence that two mutations, wDZL and z1, affecting synapsis-dependent genetic behavior of white are transcriptional regulatory mutations. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):819–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnet B., Wilson R. Pattern mosaicism for behavior controlled by the yellow locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1980 Dec;36(3):235–247. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300019868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano S., Carramolino L., Cabrera C. V., Ruíz-Gómez M., Villares R., Boronat A., Modolell J. Molecular genetics of the achaete-scute gene complex of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Hutchison K. W., Jenkins N. A. Excision of the DBA ecotropic provirus in dilute coat-color revertants of mice occurs by homologous recombination involving the viral LTRs. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V., Pellicer A., Axel R., Meselson M. Integration, transcription, and control of a Drosophila heat shock gene in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7038–7042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Lomedico P. T., Ju G. Transcriptional interference in avian retroviruses--implications for the promoter insertion model of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):241–245. doi: 10.1038/307241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. Genes with promoters in retrovirus vectors can be independently suppressed by an epigenetic mechanism. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):449–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R., Meselson M. Long terminal repeat nucleotide sequence and specific insertion of the gypsy transposon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4462–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L. New bacteriophage lambda vectors with positive selection for cloned inserts. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:3–19. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Effects of transposable element insertions on RNA encoded by the white gene of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Bender W., Meselson M. Drosophila melanogaster mutations suppressible by the suppressor of Hairy-wing are insertions of a 7.3-kilobase mobile element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1678–1682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozer B., Marlor R., Parkhurst S., Corces V. Characterization and developmental expression of a Drosophila ras oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):885–889. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash W. G. Patterns of pigmentation color states regulated by the y locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1976 Feb;48(2):336–343. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash W. G., Yarkin R. J. Genetic regulation and pattern formation: a study of the yellow locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1974 Aug;24(1):19–26. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300015044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Nucleic acid hybridization to the DNA of cytological preparations. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;10:1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60727-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst S. M., Corces V. G. Forked, gypsys, and suppressors in Drosophila. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):429–437. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Durbin K. J., Fink G. R. The SPT3 gene is required for normal transcription of Ty elements in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90474-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]