Abstract
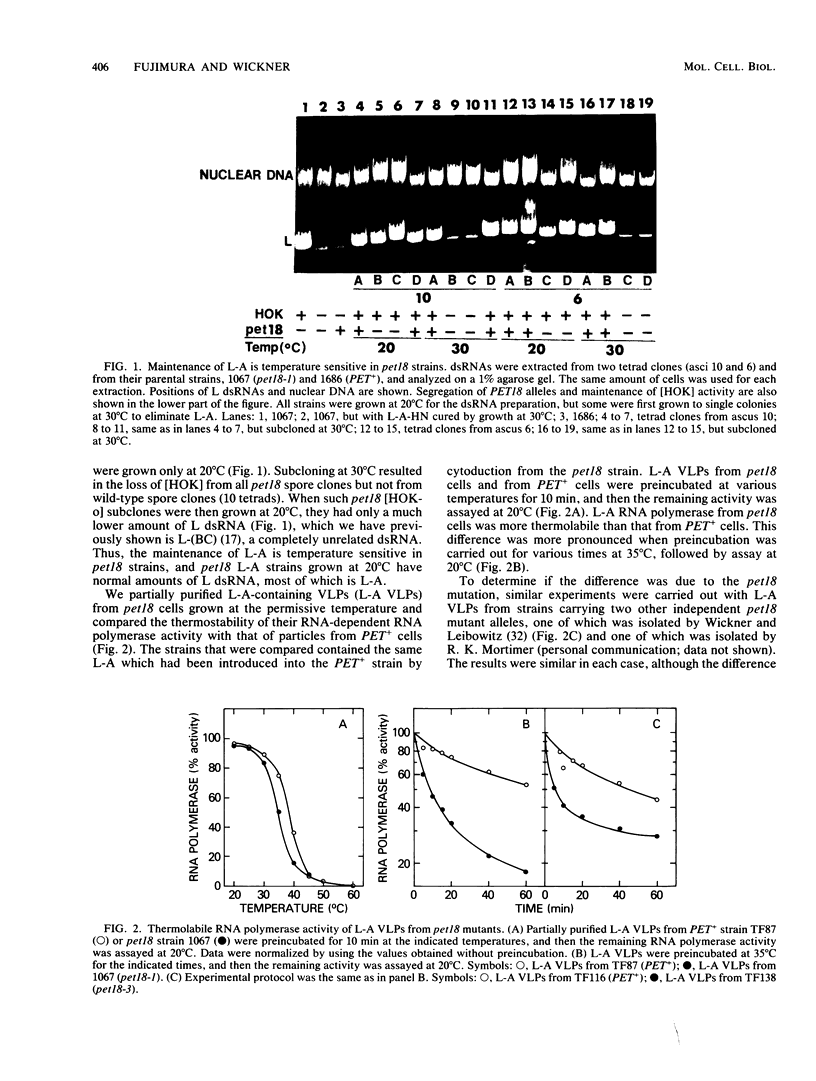
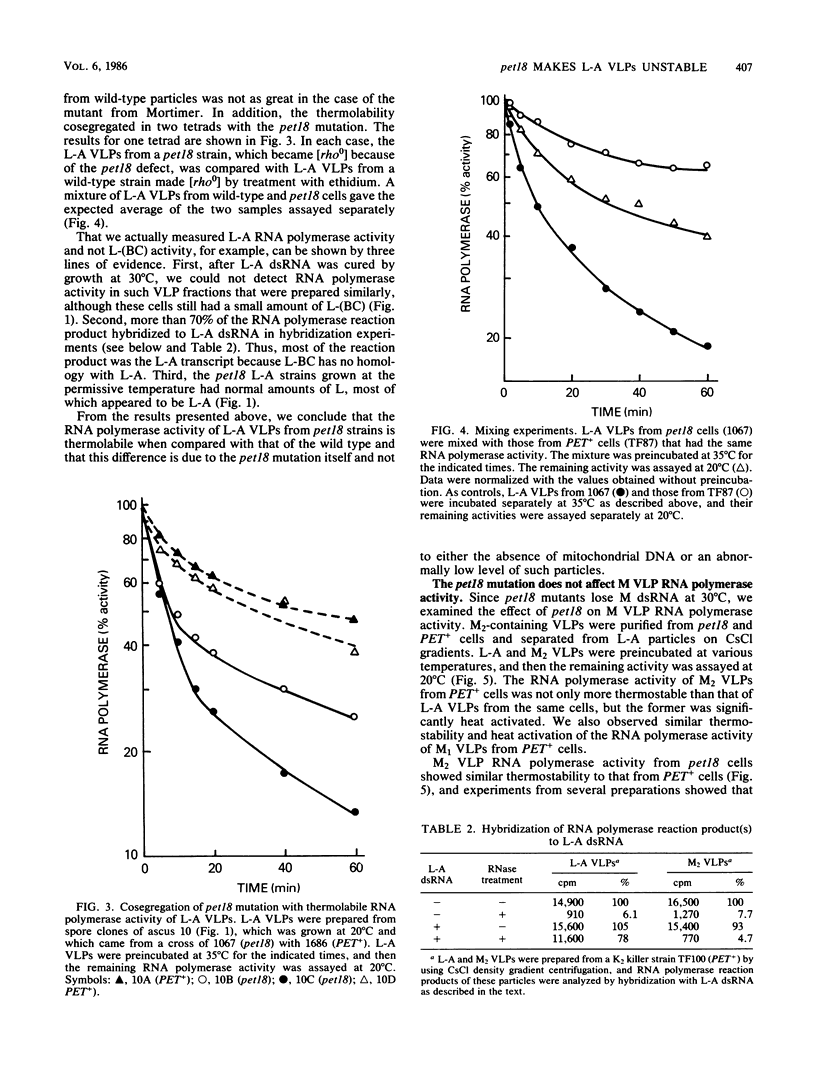
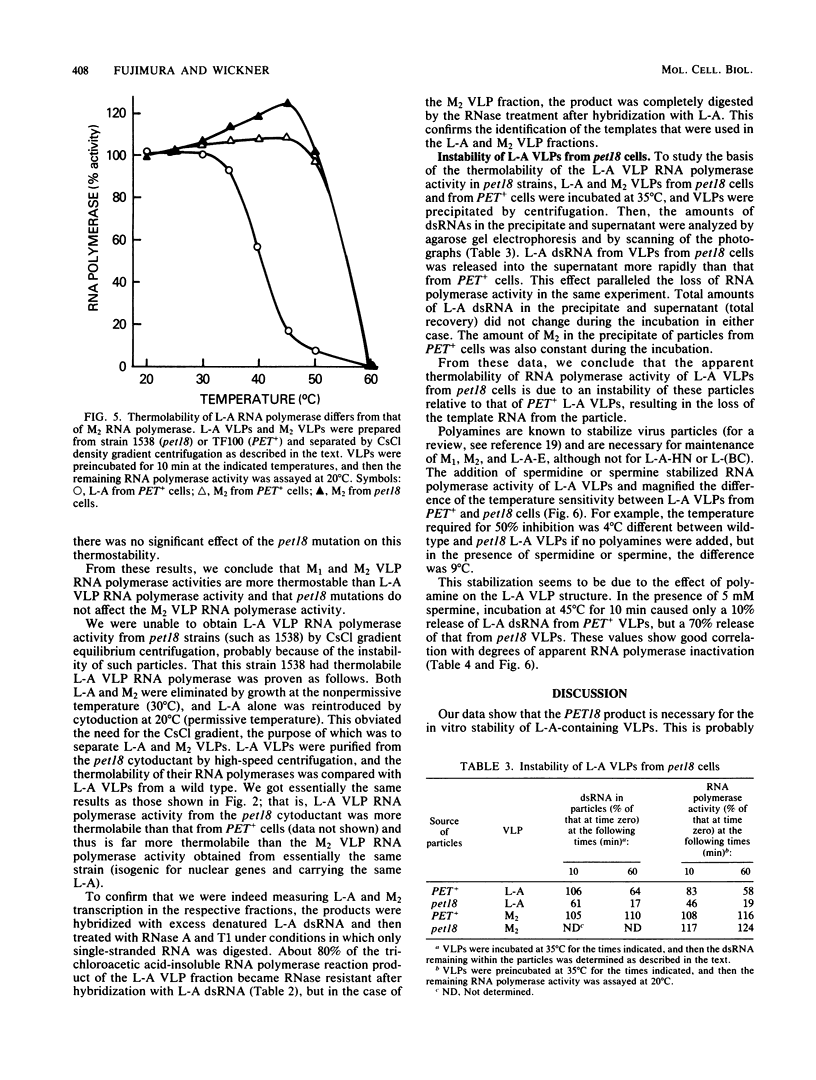
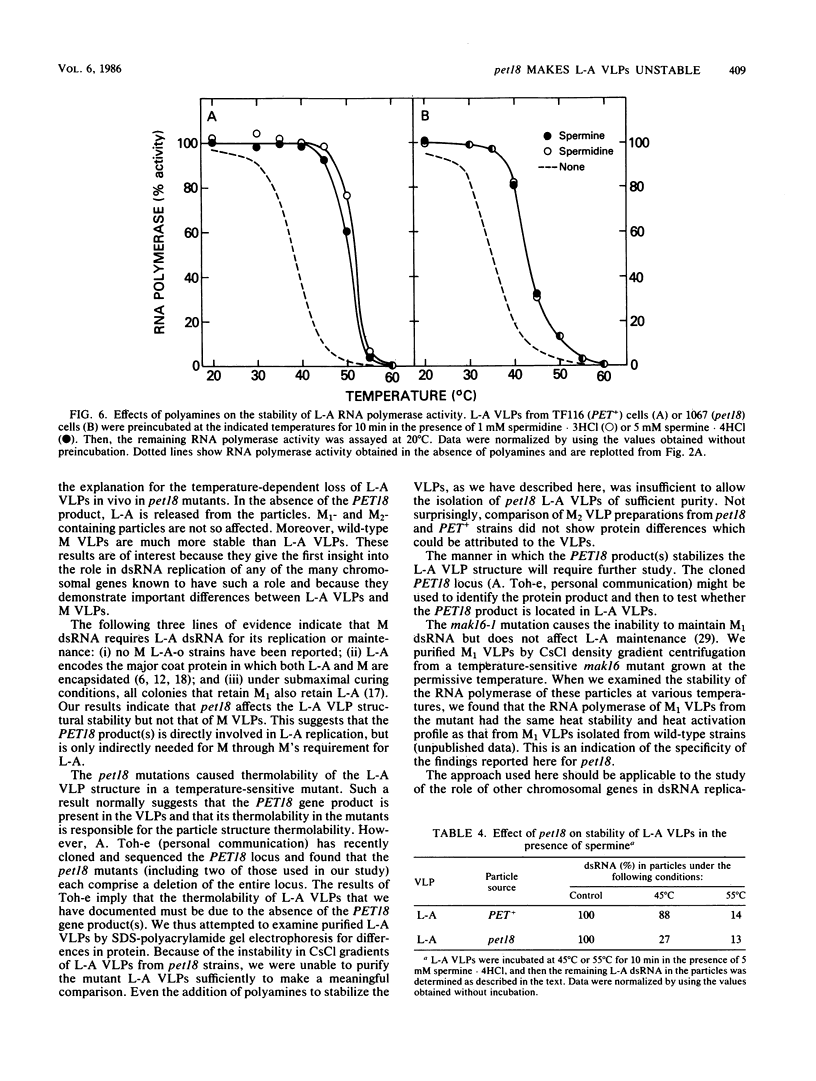
pet18 mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae confer on the cell the inability to maintain either L-A or M double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) at the nonpermissive temperature. In in vitro experiments, we examined the effects of pet18 mutations on the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity associated with virus-like particles (VLPs). pet18 mutations caused thermolabile RNA polymerase activity of L-A VLPs, and this thermolability was found to be due to the instability of the L-A VLP structure. The pet18 mutations did not affect RNA polymerase activity of M VLPs. Furthermore, the temperature sensitivity of wild-type L-A RNA polymerase differed substantially from that of M RNA polymerase. From these results, and from other genetic and biochemical lines of evidence which suggest that replication of M dsRNA requires the presence of L-A dsRNA, we propose that the primary effect of the pet18 mutation is on the L-A VLP structure and that the inability of pet18 mutants to maintain M dsRNA comes from the loss of L-A dsRNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J., Wood H. A., Bozarth R. F. Virus-like particles from killer, neutral, and sensitive strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):472–476. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.472-476.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan E. A., Herring A. J., Mitchell D. J. Preliminary characterization of two species of dsRNA in yeast and their relationship to the "killer" character. Nature. 1973 Sep 14;245(5420):81–86. doi: 10.1038/245081b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Hopper J. E., Rogers D. T., Tipper D. J. Translational analysis of the killer-associated virus-like particle dsRNA genome of S. cerevisiae: M dsRNA encodes toxin. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90514-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn M. S., Tabor C. W., Tabor H., Wickner R. B. Spermidine or spermine requirement for killer double-stranded RNA plasmid replication in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5225–5227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde J., Fink G. R. A mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective for nuclear fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3651–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Sherbeini M., Tipper D. J., Mitchell D. J., Bostian K. A. Virus-like particle capsid proteins encoded by different L double-stranded RNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: their roles in maintenance of M double-stranded killer plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2818–2827. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., SINGER B., TSUGITA A. Purification of viral RNA by means of bentonite. Virology. 1961 May;14:54–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink G. R., Styles C. A. Curing of a killer factor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2846–2849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Fink G. R. Electron microscopic heteroduplex analysis of "killer" double-stranded RNA species from yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4224–4228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. S. Virus-like particles and double stranded RNA from killer and non-killer strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbios. 1978;21(85-86):161–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring A. J., Bevan E. A. Virus-like particles associated with the double-stranded RNA species found in killer and sensitive strains of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Virol. 1974 Mar;22(3):387–394. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper J. E., Bostian K. A., Rowe L. B., Tipper D. J. Translation of the L-species dsRNA genome of the killer-associated virus-like particles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):9010–9017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz M. J., Wickner R. B. Pet18: a chromosomal gene required for cell growth and for the maintenance of mitochondrial DNA and the killer plasmid of yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 4;165(2):115–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00269899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Hawthorne D. C. Genetic Mapping in Saccharomyces IV. Mapping of Temperature-Sensitive Genes and Use of Disomic Strains in Localizing Genes. Genetics. 1973 May;74(1):33–54. doi: 10.1093/genetics/74.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Hawthorne D. C. Genetic mapping in yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;11:221–233. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley S. P., Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Superkiller mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae suppress exclusion of M2 double-stranded RNA by L-A-HN and confer cold sensitivity in the presence of M and L-A-HN. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):761–770. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Co-curing of plasmids affecting killer double-stranded RNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: [HOK], [NEX], and the abundance of L are related and further evidence that M1 requires L. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.545-551.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Yeast L dsRNA consists of at least three distinct RNAs; evidence that the non-Mendelian genes [HOK], [NEX] and [EXL] are on one of these dsRNAs. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):429–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor H., Tabor C. W. Biosynthesis and metabolism of 1,4-diaminobutane, spermidine, spermine, and related amines. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1972;36:203–268. doi: 10.1002/9780470122815.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrash C., Voelkel K., DiNardo S., Sternglanz R. Identification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants deficient in DNA topoisomerase I activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1375–1377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-E A., Guerry P., Wickner R. B. Chromosomal superkiller mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1002–1007. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1002-1007.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-E A., Wickner R. B. "Superkiller" mutations suppress chromosomal mutations affecting double-stranded RNA killer plasmid replication in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):527–530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-E A., Wickner R. B. A mutant killer plasmid whose replication depends on a chromosomal "superkiller" mutation. Genetics. 1979 Apr;91(4):673–682. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.4.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi A. K., Wickner R. B., Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Specificity of polyamine requirements for the replication and maintenance of different double-stranded RNA plasmids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1149–1153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M., Katterman F., Fink G. R. Yeast killer mutants with altered double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.681-686.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh D., Leibowitz M. J. Transcription of killer virion double-stranded RNA in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 11;8(11):2365–2375. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.11.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J. D., Leibowitz M. J., Wickner R. B. Virion DNA-independent RNA polymerase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 11;8(11):2349–2363. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.11.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesolowski M., Wickner R. B. Two new double-stranded RNA molecules showing non-mendelian inheritance and heat inducibility in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):181–187. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. Genetic control of replication of the double-stranded RNA segments of the killer systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 1;222(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. Killer systems in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: three distinct modes of exclusion of M2 double-stranded RNA by three species of double-stranded RNA, M1, L-A-E, and L-A-HN. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):654–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Leibowitz M. J. Chromosomal genes essential for replication of a double-stranded RNA plasmid of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the killer character of yeast. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 15;105(3):427–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90102-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Ridley S. P., Fried H. M., Ball S. G. Ribosomal protein L3 is involved in replication or maintenance of the killer double-stranded RNA genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4706–4708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Toh-e A. [HOK], a new yeast non-Mendelian trait, enables a replication-defective killer plasmid to be maintained. Genetics. 1982 Feb;100(2):159–174. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. Twenty-six chromosomal genes needed to maintain the killer double-stranded RNA plasmid of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1978 Mar;88(3):419–425. doi: 10.1093/genetics/88.3.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



