Abstract
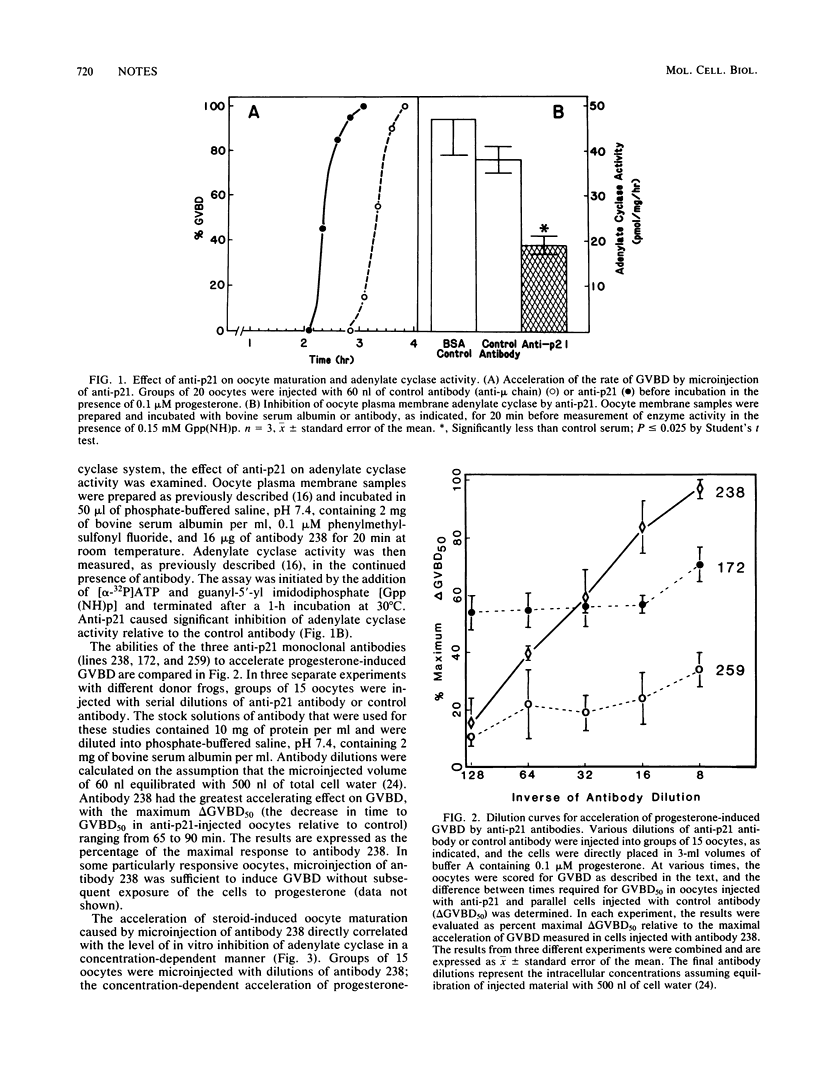
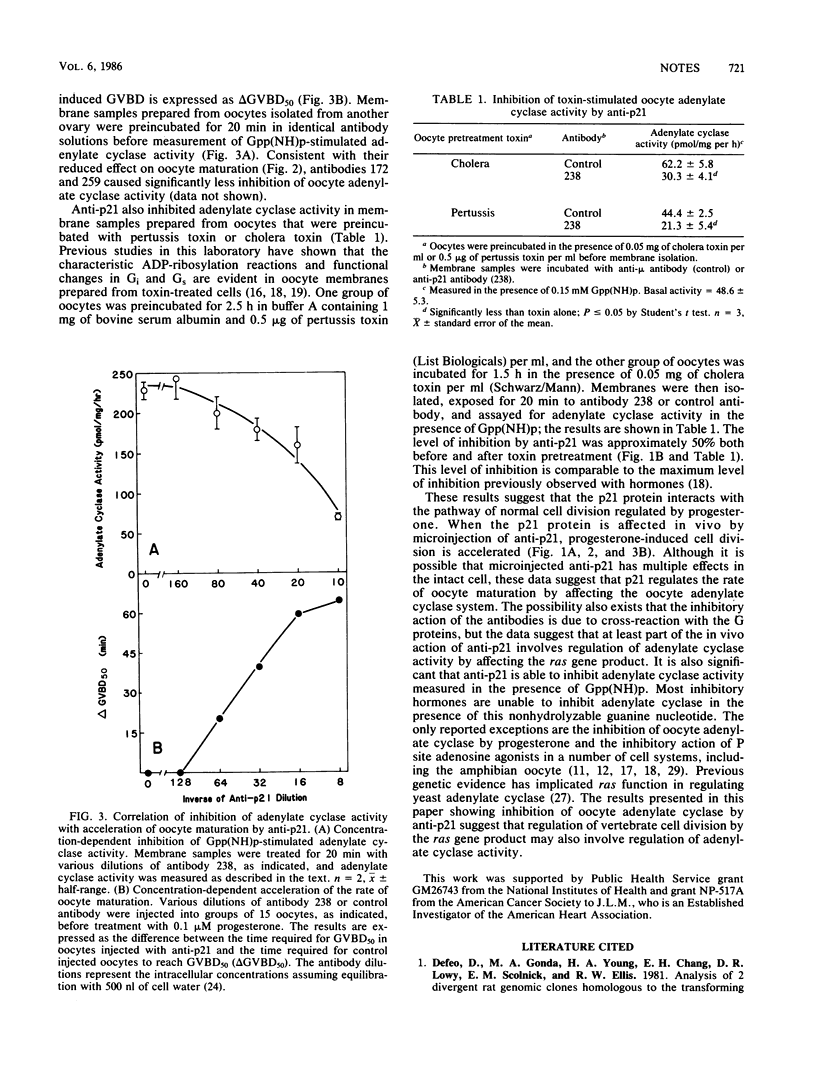
Microinjection of monoclonal antibodies (lines 238, 172, and 259) directed against the ras gene product, p21, into Xenopus laevis oocytes accelerated progesterone-induced germinal vesicle breakdown. Antibody 238 had the greatest effect on the acceleration of progesterone-induced oocyte maturation, and this effect was correlated with in vitro inhibition of adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1) activity in a concentration-dependent manner. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase by antibody 238 was also measured in membranes prepared from oocytes pretreated with either cholera toxin or pertussis toxin. These results suggest a role for the ras gene product in the regulation of vertebrate cell adenylate cyclase activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ellis R. W., Defeo D., Shih T. Y., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Tsuchida N., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. The p21 src genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses originate from divergent members of a family of normal vertebrate genes. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):506–511. doi: 10.1038/292506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finidori-Lepicard J., Schorderet-Slatkine S., Hanoune J., Baulieu E. E. Progesterone inhibits membrane-bound adenylate cyclase in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):255–257. doi: 10.1038/292255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel T., Der C. J., Cooper G. M. Activation of ras genes in human tumors does not affect localization, modification, or nucleotide binding properties of p21. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhardt M., Ferry N., Buscaglia M., Baulieu E. E., Hanoune J. Does the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Ni mediate progesterone inhibition of Xenopus oocyte adenylate cyclase? EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2653–2657. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Simon M. I., Teplow D. B., Robishaw J. D., Gilman A. G. Homologies between signal transducing G proteins and ras gene products. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.6436980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langbeheim H., Shih T. Y., Scolnick E. M. Identification of a normal vertebrate cell protein related to the p21 src of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Virology. 1980 Oct 30;106(2):292–300. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Wolff J. Two distinct adenosine-sensitive sites on adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5482–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):644–649. doi: 10.1038/310644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olate J., Allende C. C., Allende J. E., Sekura R. D., Birnbaumer L. Oocyte adenylyl cyclase contains Ni, yet the guanine nucleotide-dependent inhibition by progesterone is not sensitive to pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80562-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papageorge A., Lowy D., Scolnick E. M. Comparative biochemical properties of p21 ras molecules coded for by viral and cellular ras genes. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):509–519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.509-519.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L., Cooper D. M. Progesterone inhibition of Xenopus oocyte adenylate cyclase is not mediated via the Bordetella pertussis toxin substrate. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):526–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. Inhibition of Xenopus oocyte adenylate cyclase by progesterone and 2',5'-dideoxyadenosine is associated with slowing of guanine nucleotide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7935–7941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. Inhibition of Xenopus oocyte adenylate cyclase by progesterone: a novel mechanism of action. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1985;19:179–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. Progesterone inhibits adenylate cyclase in Xenopus oocytes. Action on the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6368–6373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Papageorge A. G., Shih T. Y. Guanine nucleotide-binding activity as an assay for src protein of rat-derived murine sarcoma viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5355–5359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Weeks M. O., Gruss P., Dhar R., Oroszlan S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of a precursor in the biosynthesis of the p21 transforming protein of harvey murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):253–261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.253-261.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Weeks M. O., Young H. A., Scholnick E. M. Identification of a sarcoma virus-coded phosphoprotein in nonproducer cells transformed by Kirsten or Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):64–79. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Weeks M. O., Young H. A., Scolnick E. M. p21 of Kirsten murine sarcoma virus is thermolabile in a viral mutant temperature sensitive for the maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):546–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.546-546.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stith B. J., Maller J. L. The effect of insulin on intracellular ph and ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. W., Yokoyama S., Kamata T., Feramisco J. R., Rosenberg M., Gross M. The product of ras is a GTPase and the T24 oncogenic mutant is deficient in this activity. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):273–275. doi: 10.1038/311273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Nukada T., Nishikawa Y., Sugimoto K., Suzuki H., Takahashi H., Noda M., Haga T., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of transducin and its relationship to ras proteins. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):242–245. doi: 10.1038/315242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Shih T. Y., Scolnick E. M. Localization of the src gene product of the Harvey strain of MSV to plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1005–1014. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Londos C., Cooper D. M. Adenosine receptors and the regulation of adenylate cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;14:199–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


