Abstract
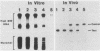
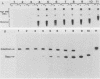
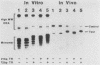
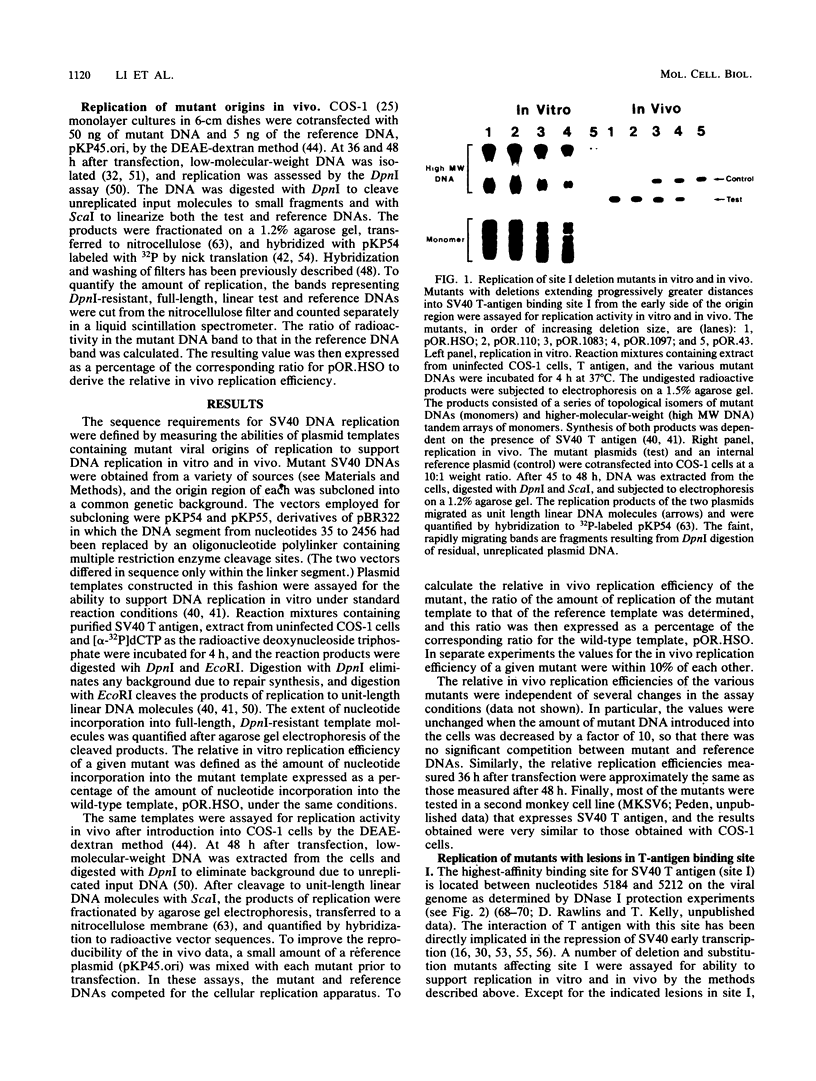
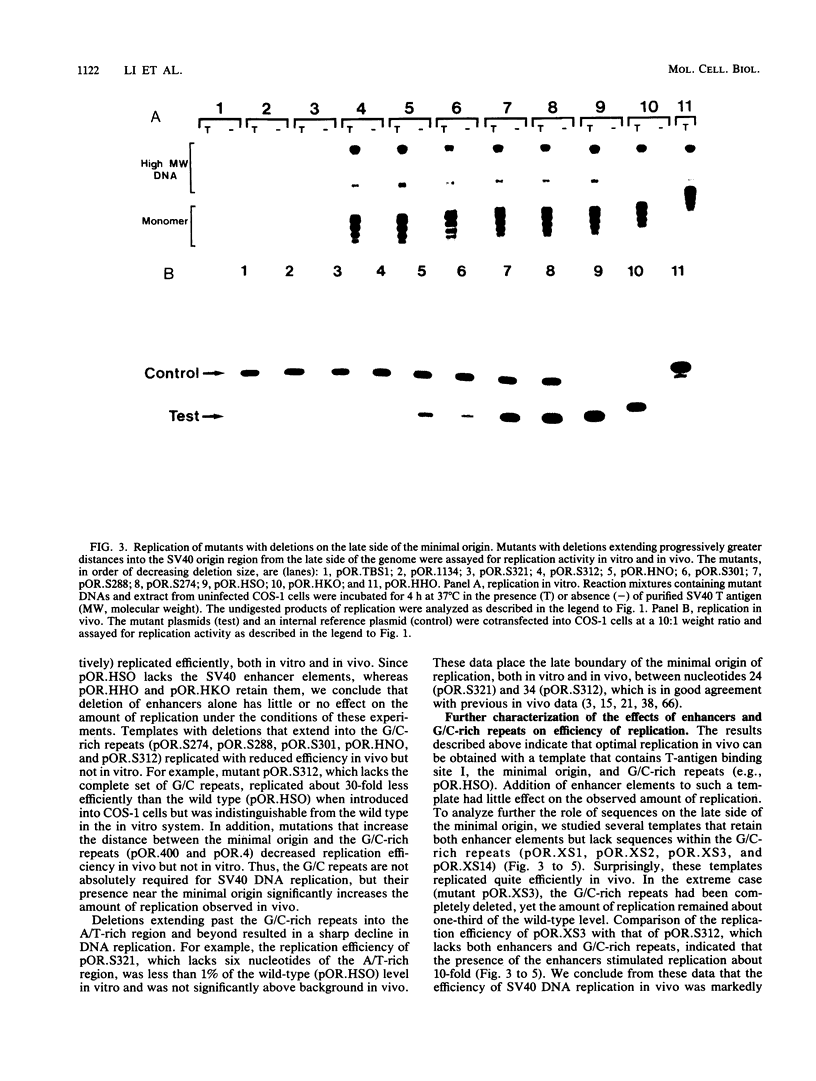
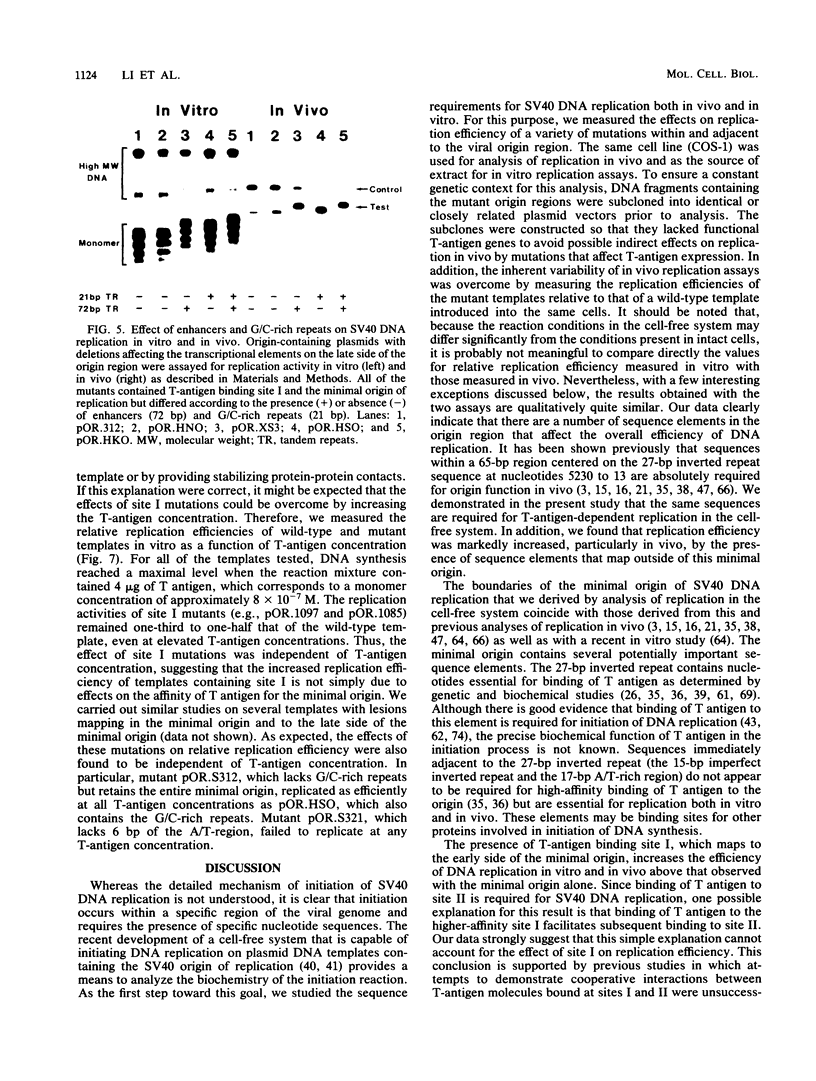
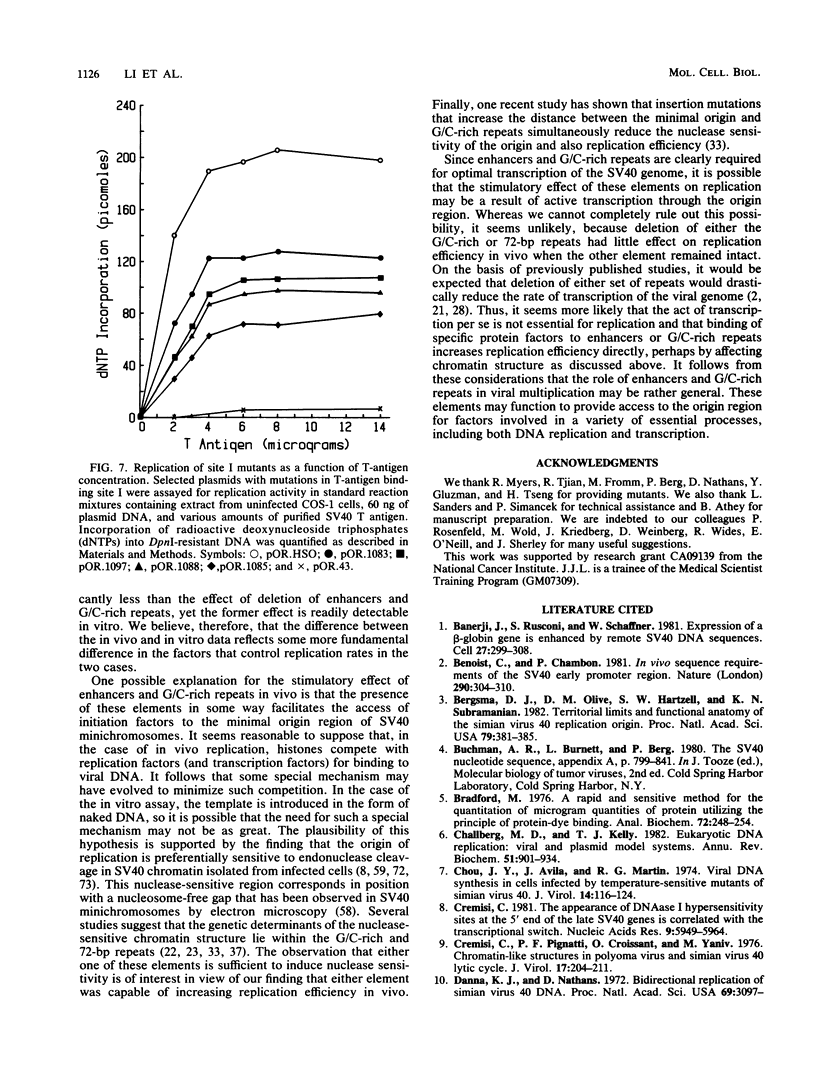
To define the sequence elements involved in initiation of DNA synthesis at the simian virus 40 origin of replication, we determined the relative replication efficiencies in vitro and in vivo of templates containing a variety of mutations within the origin region. Replication of the mutants in vitro was assayed by the cell-free DNA replication system that we recently described (J.J. Li and T.J. Kelly, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:6973-6977, 1984; J.J. Li and T.J. Kelly, Mol. Cell. Biol. 5:1238-1246, 1985), and replication in vivo was assayed after transfection of the mutant templates into COS-1 cells. The minimal origin of replication defined by both assays included a 15-base-pair (bp) imperfect inverted repeat, a 27-bp perfect inverted repeat, and a 17-bp A/T-rich region. T-antigen binding site I was not required for DNA replication, but its presence increased replication efficiency severalfold both in vitro and in vivo. Although SP1 binding sites and enhancers had little or no effect on replication in vitro, the presence of either element markedly increased replication in vivo. Thus, the biological role of these elements is not restricted to stimulating transcription but may be more general.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Olive D. M., Hartzell S. W., Subramanian K. N. Territorial limits and functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Eukaryotic DNA replication: viral and plasmid model systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:901–934. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Avila J., Martin R. G. Viral DNA synthesis in cells infected by temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):116–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.116-124.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C., Pignatti P. F., Croissant O., Yaniv M. Chromatin-like structures in polyoma virus and simian virus 10 lytic cycle. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.204-211.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C. The appearance of DNase I hypersensitive sites at the 5' end of the late SV40 genes is correlated with the transcriptional switch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K. J., Nathans D. Bidirectional replication of Simian Virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3097–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Tjian R., Tegtmeyer P. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of pentanucleotide interaction sites at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.143-150.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Wassarman P. M. Replication of eukaryotic chromosomes: a close-up of the replication fork. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:627–666. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Cold-sensitive regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):129–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. Effect of mutations at a T antigen binding site on DNA replication and expression of viral genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):531–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Nathans D. Purification of simian virus 40 large T antigen by immunoaffinity chromatography. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1001–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1001-1004.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fareed G. C., Garon G. F., Salzman N. P. Origin and direction of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid replication. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):484–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.484-491.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Simian virus 40 early- and late-region promoter functions are enhanced by the 72-base-pair repeat inserted at distant locations and inverted orientations. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):991–999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R. D., Montelone B. A., Walter C. F., Innis J. W., Scott W. A. Role of specific simian virus 40 sequences in the nuclease-sensitive structure in viral chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Frisque R. J., Sambrook J. Origin-defective mutants of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):293–300. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Chromatin structure: deduced from a minichromosome. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1202–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Tenen D. G., Livingston D. M., Sharp P. A. T antigen repression of SV40 early transcription from two promoters. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication in vivo: location and structure of 5' ends of DNA synthesized in the ori region. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis J. W., Scott W. A. DNA replication and chromatin structure of simian virus 40 insertion mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1499–1507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Myers R. M., Tjian R. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 large T antigen DNA binding sites. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3247–3255. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02286.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Essential contact residues within SV40 large T antigen binding sites I and II identified by alkylation-interference. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongstra J., Reudelhuber T. L., Oudet P., Benoist C., Chae C. B., Jeltsch J. M., Mathis D. J., Chambon P. Induction of altered chromatin structures by simian virus 40 enhancer and promoter elements. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):708–714. doi: 10.1038/307708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewton B. A., DeLucia A. L., Tegtmeyer P. Binding of simian virus 40 a protein to DNA with deletions at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):9–13. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.9-13.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6973–6977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: specificity of initiation and evidence for bidirectional replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1238–1246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolskee R. F., Nathans D. Simian virus 40 mutant T antigens with relaxed specificity for the nucleotide sequence at the viral DNA origin of replication. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):386–393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.386-393.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tjian R. Construction and analysis of simian virus 40 origins defective in tumor antigen binding and DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Nathans D. Local mutagenesis within deletion loops of DNA heteroduplexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7214–7217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K., Mounts P., Hayward G. S. Homology between mammalian cell DNA sequences and human herpesvirus genomes detected by a hybridization procedure with high-complexity probe. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90406-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):203–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Tjian R. SV40 T antigen binding site mutations that affect autoregulation. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1227–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D., Robbins A., Myers R., Tjian R. Regulation of simian virus 40 early transcription in vitro by a purified tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5706–5710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Wigmore D. J. Sites in simian virus 40 chromatin which are preferentially cleaved by endonucleases. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Kleinberger T., Livingston D. M. Mapping of SV40 DNA replication origin region binding sites for the SV40 T antigen by protection against exonuclease III digestion. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Nathans D. Regulatory mutants of simian virus 40: constructed mutants with base substitutions at the origin of DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):801–817. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. W., Gluzman Y. Replication and supercoiling of simian virus 40 DNA in cell extracts from human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2051–2060. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B., Gerard R. D., Guggenheimer R. A., Gluzman Y. T antigen and template requirements for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2933–2939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Shenk T. Definition of the boundaries of the origin of DNA replication in simian virus 40. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3635–3642. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Andersen B., Shaw S. B., Wilson V. G. Alternative interactions of the SV40 A protein with DNA. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Taylor T. S., Haines L. L., Bradley M. K., Martin R. G., Livingston D. M. Binding of simian virus 40 large T antigen from virus-infected monkey cells to wild-type and mutant viral replication origins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):791–808. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. Protein-DNA interactions at the origin of simian virus 40 DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):655–661. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O. H., Bohn M. J. SV40 viral minichromosome: preferential exposure of the origin of replication as probed by restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3469–3477. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck W., Föhring B., Chowdhury K., Gruss P., Sauer G. Origin of DNA replication in papovavirus chromatin is recognized by endogenous endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5964–5968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. G., Tevethia M. J., Lewton B. A., Tegtmeyer P. DNA binding properties of simian virus 40 temperature-sensitive A proteins. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):458–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.458-466.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]