Abstract
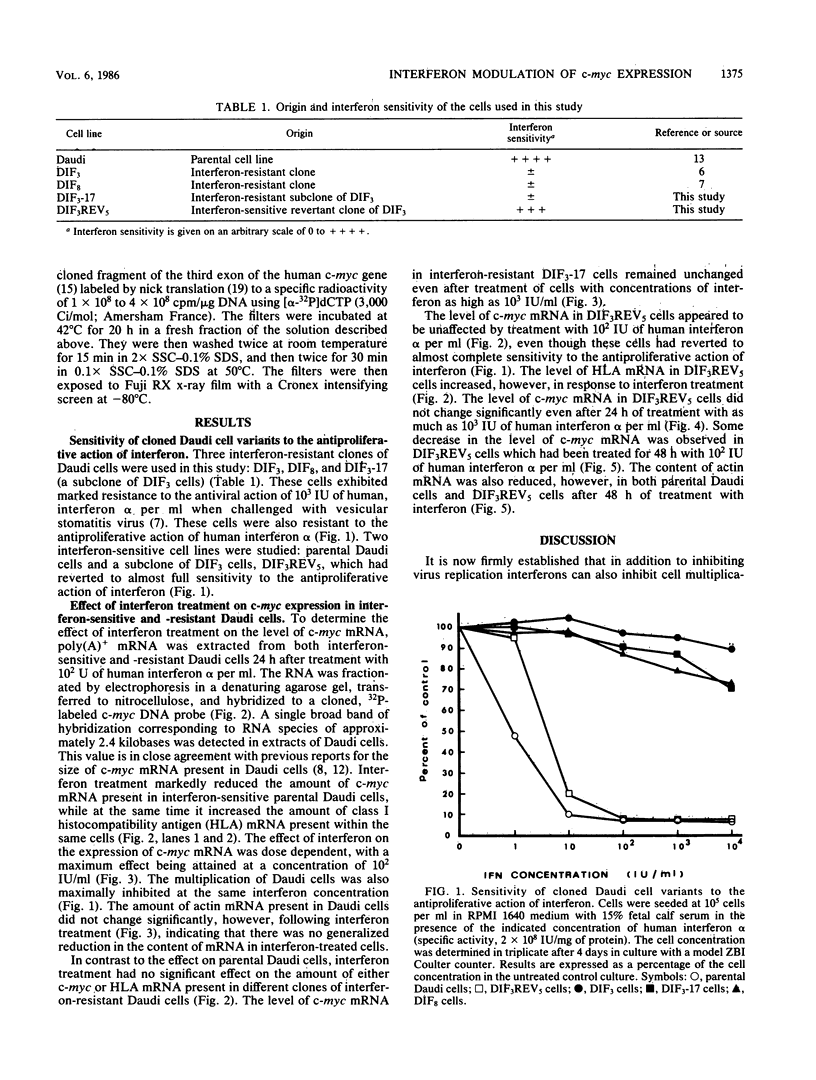
Treatment of interferon-sensitive Daudi cell with electrophoretically pure human interferon alpha markedly reduced the level of c-myc mRNA, increased the level of class I histocompatibility antigen (HLA) mRNA, and did not affect the level of actin mRNA within the same cells. In contrast, the level of c-myc mRNA or HLA mRNA did not change significantly following interferon treatment in different clones of Daudi cells selected for resistance to the antiproliferative action of interferon. These cells possessed interferon receptors, however, and responded to interferon modulation of other genes, including 2',5' oligoisoadenylate synthetase (M. G. Tovey, M. Dron, K. E. Mogensen, B. Lebleu, N. Metchi, and J. Begon-Lours, Guymarho, J. Gen. Virol., 64:2649-2653, 1983; M. Dron, M. G. Tovey, and P. Eid, J. Gen. Virol., 66:787-795, 1985). A clone of interferon-resistant Daudi cells which had reverted to almost complete sensitivity to both the antiproliferative action of interferon and the interferon-enhanced expression of HLA mRNA remained refractory, however, to interferon modulation of c-myc expression, suggesting that a reduced level of c-myc mRNA may not be a prerequisite for inhibition of cell proliferation in interferon-treated cells. Our results do not exclude the possibility, however, that posttranscriptional modification(s) of c-myc expression may precede an inhibition of cell proliferation in interferon-treated cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armelin H. A., Armelin M. C., Kelly K., Stewart T., Leder P., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):655–660. doi: 10.1038/310655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouty-Boyé D. Interferon and reversion of the transformed phenotype. Surv Immunol Res. 1982;1(4):316–322. doi: 10.1007/BF02918542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. Interferons and oncogenes. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):531–532. doi: 10.1038/313531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Mechti N., Piechaczyk M., Lebleu B., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Increased rate of degradation of c-myc mRNA in interferon-treated Daudi cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4896–4899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Tovey M. G., Eid P. Isolation of Daudi cells with reduced sensitivity to interferon. III. Interferon-induced proteins in relation to the phenotype of interferon resistance. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):787–795. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Tovey M. G. Isolation of Daudi cells with reduced sensitivity to interferon. I. Characterization. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2641–2647. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Tovey M. G., Uzé G. Isolation of Daudi cells with reduced sensitivity to interferon. IV. Characterization of clones with altered binding of human interferon alpha subspecies. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):663–669. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I. How does interferon inhibit tumor growth? Interferon. 1985;6:93–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonak G. J., Knight E., Jr Selective reduction of c-myc mRNA in Daudi cells by human beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1747–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Anton E. D., Fahey D., Friedland B. K., Jonak G. J. Interferon regulates c-myc gene expression in Daudi cells at the post-transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1151–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen K. E., Cantell K. Non-specific adsorption of interferon to immobilized serum immunoglobulin. J Gen Virol. 1979 Oct;45(1):171–175. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-1-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldham R. K. Interferon: a model for future biologicals. Interferon. 1985;6:127–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pereira D., Weissman S. M. Isolation and partial nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B by use of an oligodeoxynucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Pattengale P. K., Leder P. Spontaneous mammary adenocarcinomas in transgenic mice that carry and express MTV/myc fusion genes. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga S., Lengyel P. beta-Interferon alters the pattern of proteins secreted from quiescent and platelet-derived growth factor-treated BALB/c-3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):1975–1978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Dron M., Mogensen K. E., Lebleu B., Mechti N., Begonlours-Guymarho J. Isolation of Daudi cells with reduced sensitivity to interferon. II. On the mechanisms of resistance. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2649–2653. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G. Use of chemostat culture for the study of the effect of interferon on tumor cell multiplication. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):391–404. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]