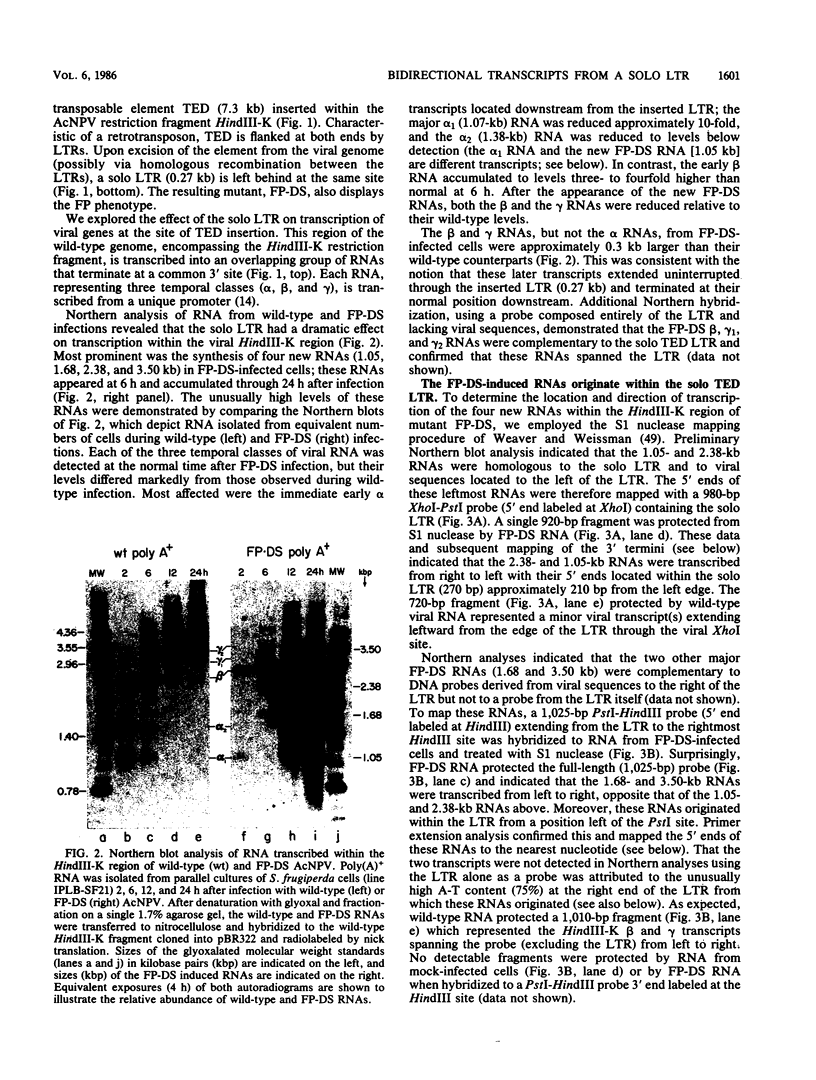
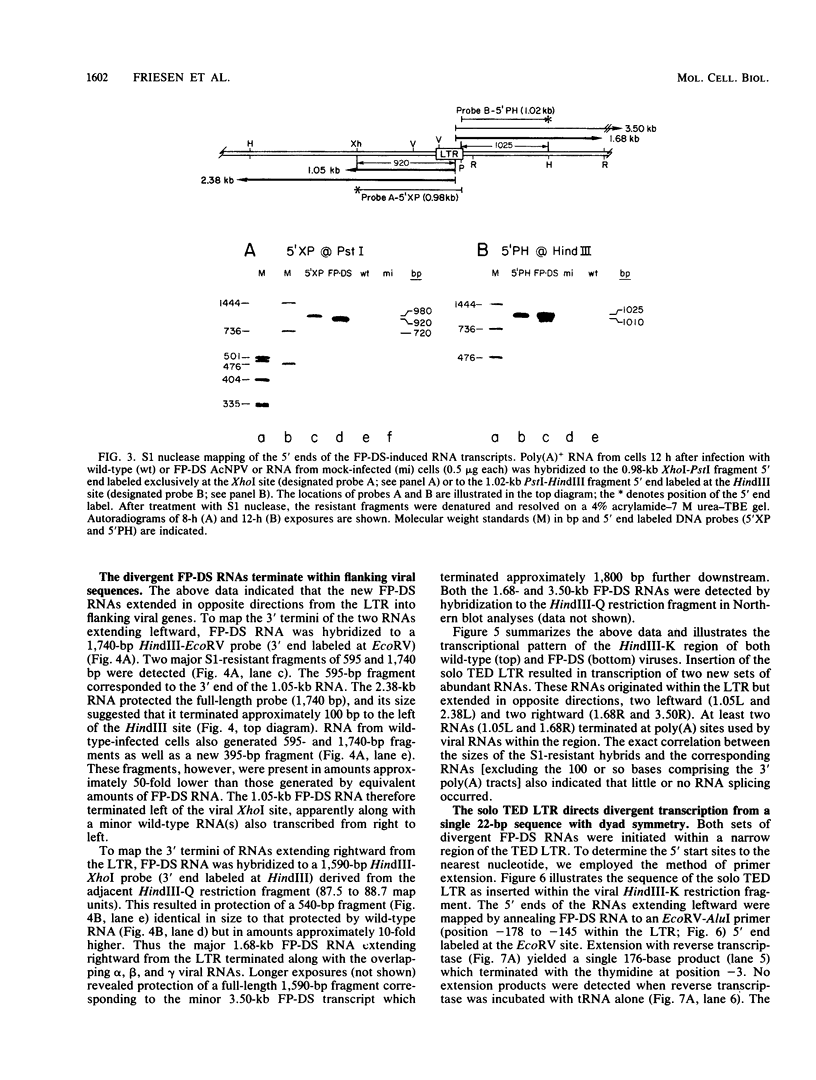
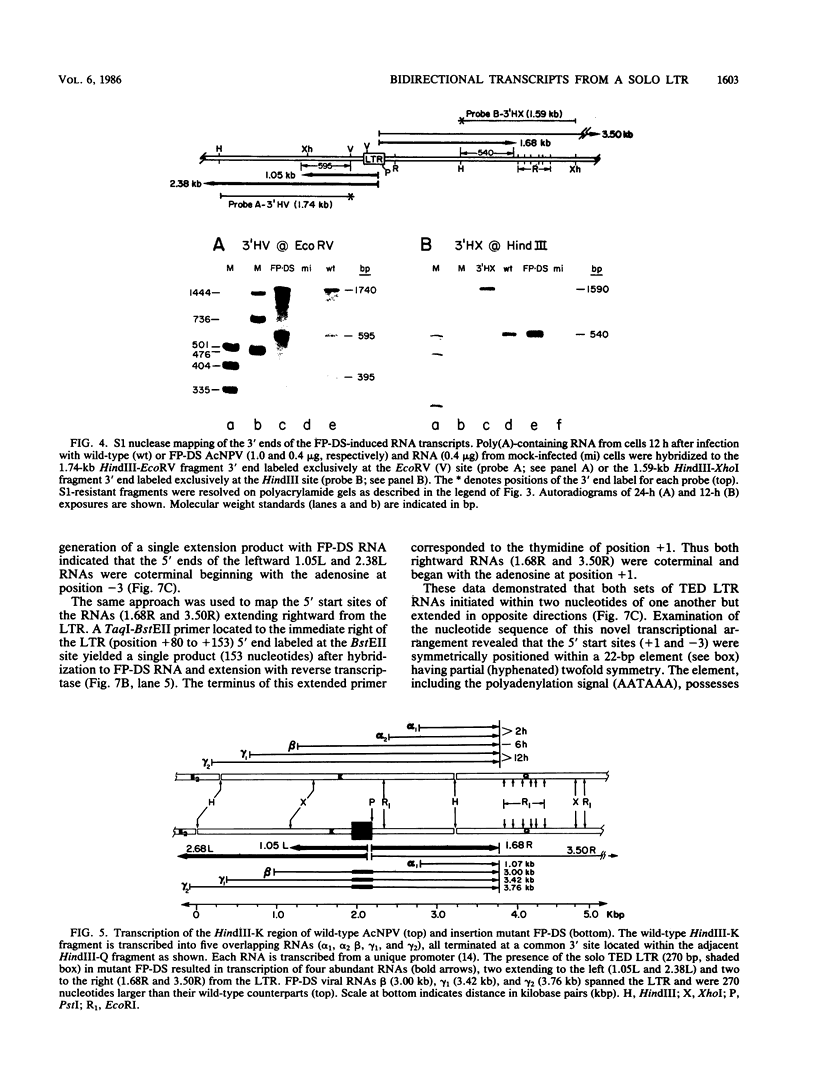
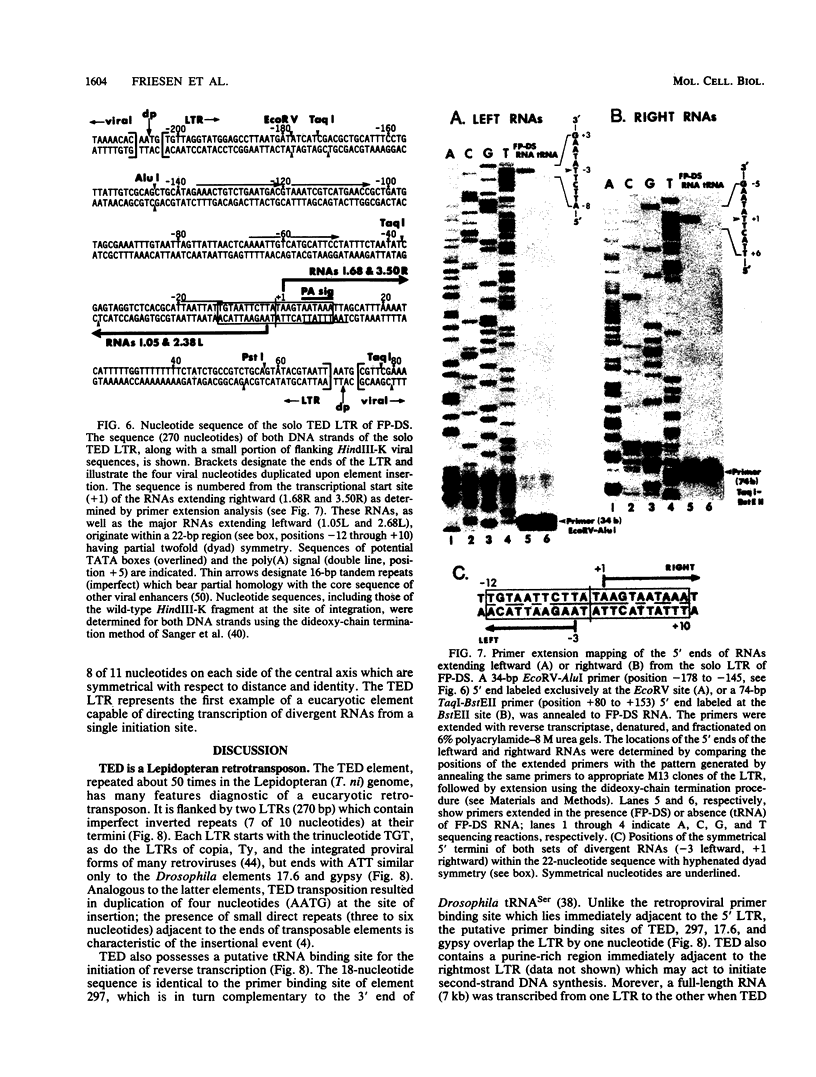
Abstract
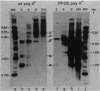
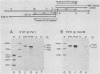
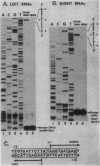
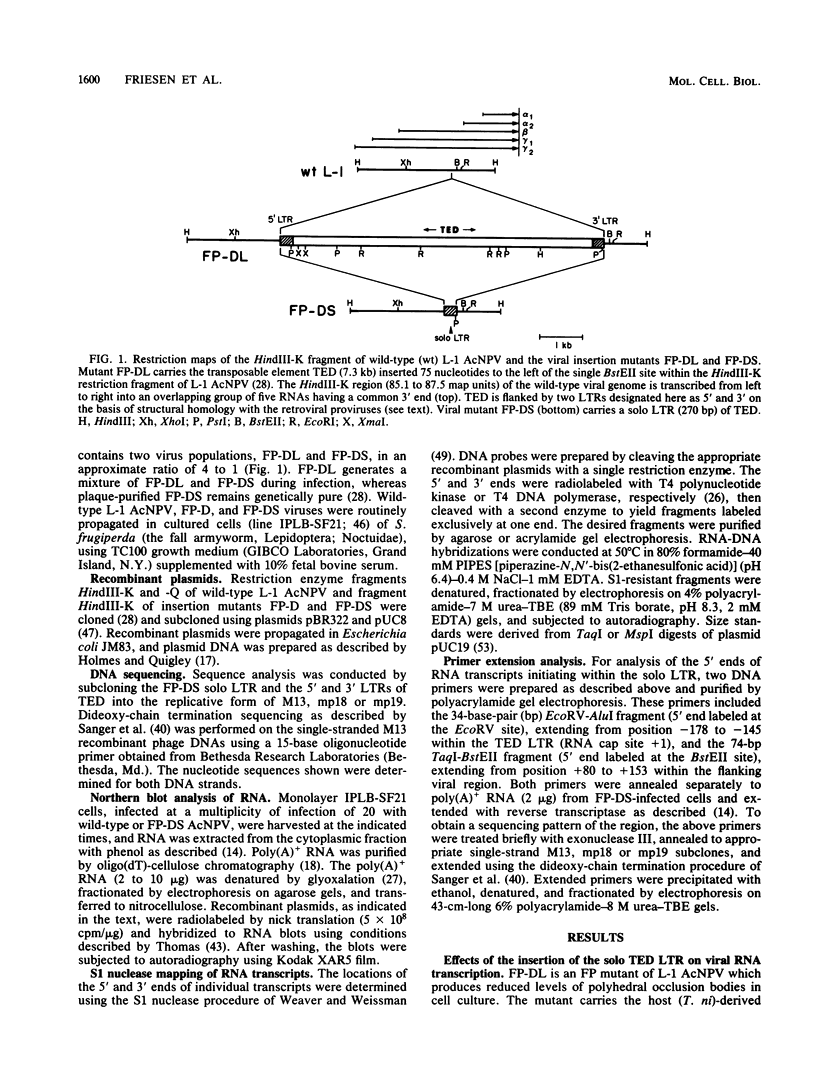
A single copy of the retrotransposon TED was found integrated within the DNA genome of the insect baculovirus, Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. After excision of the element from the viral genome, a single long terminal repeat (LTR) remained behind. We have examined the effect of this solo TED LTR on the local pattern of viral transcription. Most prominent was the transcription of two sets of abundant RNAs; both originated within the LTR but extended in opposite directions into flanking viral genes. By promoting symmetric transcription of adjacent genes, the solo LTR has the capacity to activate or repress gene expression in two directions. Primer extension analysis demonstrated that the divergent LTR transcripts were initiated near the same point within a 22-base-pair sequence having hyphenated twofold symmetry. Analogous symmetries at the initiation sites of other retrotransposon LTRs, including copia and Ty, suggested that these sequences serve to establish the precise start for transcription.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Retroviruses and retrotransposons: the role of reverse transcription in shaping the eukaryotic genome. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):481–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayev A. A., Jr, Lyubomirskaya N. V., Dzhumagaliev E. B., Ananiev E. V., Amiantova I. G., Ilyin Y. V. Structural organization of transposable element mdg4 from Drosophila melanogaster and a nucleotide sequence of its long terminal repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3707–3723. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Leys E. J., McEwan R. N., Frayne E. G., Kellems R. E. Analysis of the mouse dhfr promoter region: existence of a divergently transcribed gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1847–1858. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Lomedico P. T., Ju G. Transcriptional interference in avian retroviruses--implications for the promoter insertion model of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):241–245. doi: 10.1038/307241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. T., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. RNA from the yeast transposable element Ty1 has both ends in the direct repeats, a structure similar to retrovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2432–2436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Shiba T., Kanaya S., Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. The nucleotide sequences of copia and copia-related RNA in Drosophila virus-like particles. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):773–776. doi: 10.1038/315773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser M. J., Smith G. E., Summers M. D. Acquisition of Host Cell DNA Sequences by Baculoviruses: Relationship Between Host DNA Insertions and FP Mutants of Autographa californica and Galleria mellonella Nuclear Polyhedrosis Viruses. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):287–300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.287-300.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R., Meselson M. Long terminal repeat nucleotide sequence and specific insertion of the gypsy transposon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4462–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Temporal regulation of baculovirus RNA: overlapping early and late transcripts. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):392–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.392-400.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hink W. F. Established insect cell line from the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni. Nature. 1970 May 2;226(5244):466–467. doi: 10.1038/226466b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Roberts W. K. Encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: variations in polyadenylic acid content and biological activity. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.325-330.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Insertion of a movable genetic element, 297, into the T-A-T-A box for the H3 histone gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4143–4147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Weintraub H. Constitutive and conditional suppression of exogenous and endogenous genes by anti-sense RNA. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):345–352. doi: 10.1126/science.2990048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugimiya W., Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Close relationship between the long terminal repeats of avian leukosis-sarcoma virus and copia-like movable genetic elements of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3193–3197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. H., Miller L. K. Isolation of genotypic variants of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):754–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.754-767.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Effects of transposable element insertions on RNA encoded by the white gene of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. W., Miller L. K. A virus mutant with an insertion of a copia-like transposable element. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):562–564. doi: 10.1038/299562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Rubin G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst S. M., Corces V. G. Forked, gypsys, and suppressors in Drosophila. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):429–437. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Daugherty B. L., Jung V., Hotta K., Pestka R. K. Anti-mRNA: specific inhibition of translation of single mRNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7525–7528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K., Kugimiya W., Matsuo Y., Inouye S., Yoshioka K., Yuki S. Identification of the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme in a transposable genetic element in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):659–661. doi: 10.1038/312659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador R., Power M. D., Barr P. J., Steimer K. S., Stempien M. M., Brown-Shimer S. L., Gee W. W., Renard A., Randolph A., Levy J. A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of an AIDS-associated retrovirus (ARV-2). Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):484–492. doi: 10.1126/science.2578227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcich B., Ratner L., Josephs S. F., Okamoto T., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Characterization of long terminal repeat sequences of HTLV-III. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):538–540. doi: 10.1126/science.2981438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Quintrell N., Ortiz S. Retroviruses as mutagens: insertion and excision of a nontransforming provirus alter expression of a resident transforming provirus. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. L., Goodwin R. H., Tompkins G. J., McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro. 1977 Apr;13(4):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02615077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Sonigo P., Danos O., Cole S., Alizon M. Nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, LAV. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Durbin K. J., Fink G. R. The SPT3 gene is required for normal transcription of Ty elements in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90474-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Davison D., Garza D., Bingham P. M. A detailed developmental and structural study of the transcriptional effects of insertion of the Copia transposon into the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1985 Nov;111(3):495–515. doi: 10.1093/genetics/111.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]